What Is Venous Disease Exactly
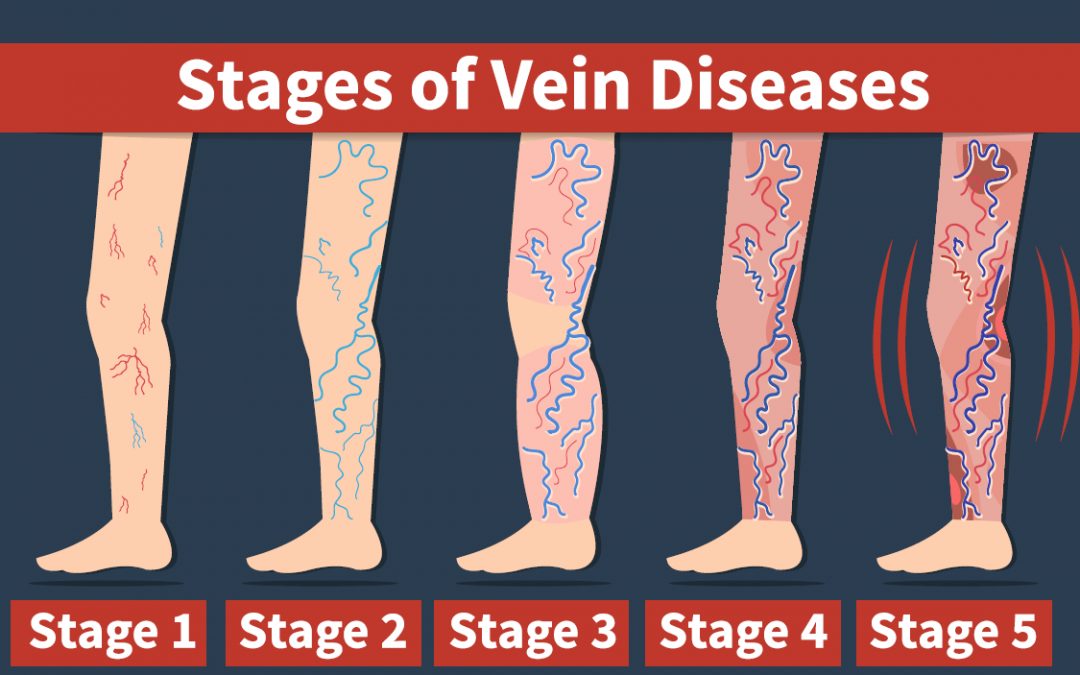
Venous Disease Millions Suffer But Treatments Can Be Life Changing Types of venous disease. venous diseases include: blood clots: these can happen in your legs, arms, veins of your internal organs (kidney, spleen, intestines, liver and pelvic organs), in your brain (cerebral vein thrombosis), in your kidneys (renal vein thrombosis), or in your lungs (pulmonary embolism). deep vein thrombosis (dvt): this is a. Symptoms of venous disease include: varicose veins: enlarged, swollen, knotted clusters of purple veins; edema (swelling in the legs); aching or a sensation of heaviness in the legs; itching skin above the affected veins; skin discoloration and ulcers on the inner aspect of the ankles (in advanced cases). superficial thrombophlebitis: a red.
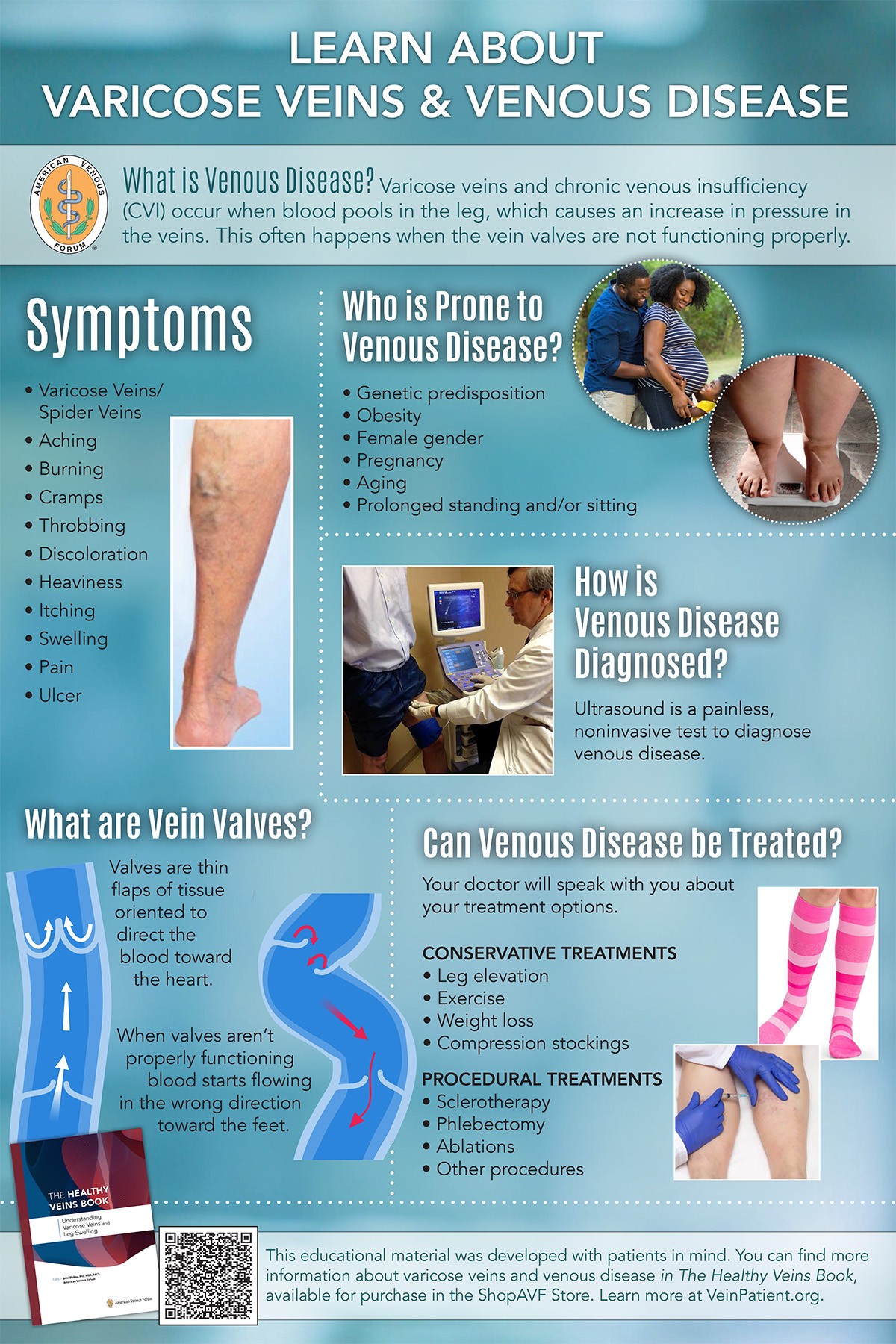
Venous Disease Poster Avf Store Venous disease treatments restore proper blood flow and lower your risk of complications. these treatments include medications, catheter based procedures and surgery. your provider creates your treatment plan based on the type of venous disease you have. common types of venous disease include: blood clots. chronic venous insufficiency (cvi). Chronic venous disease (cvd) is a prevalent and multifaceted medical condition affecting the venous system, particularly the veins of the lower extremities. it encompasses a spectrum of venous disorders, ranging from mild cosmetic concerns to severe and debilitating conditions. cvd arises due to impaired blood flow within the venous system. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood to your heart. this talk will provide a broad overview of venous disease with a review of its history, diagnosis, tr. What is vein disease? the circulatory system is composed of the heart (the central pump), arteries (vessels that carry oxygenated blood to the entire body), and veins (vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart). blood flow in veins in the legs and lower parts of the body travels upstream against gravity on its way back to the heart.

Comments are closed.