What Is Fiat Currency And Its Pros And Cons
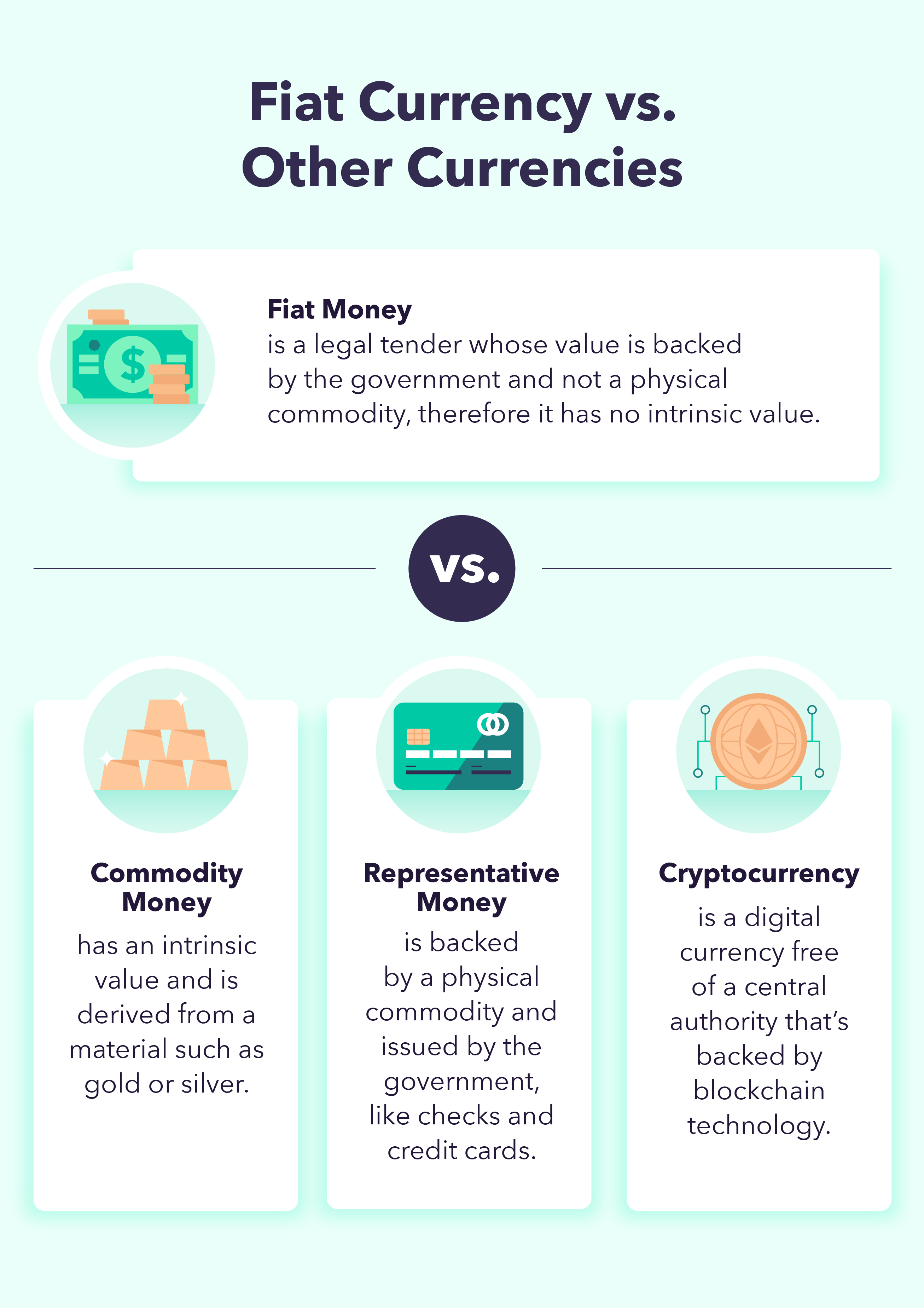
Fiat Money Explained Definition How It Works Examples Pros Cons Examples of fiat money. the u.s. dollar, the euro, the british pound, the japanese yen, the albanian lek, and the indian rupee are all examples of fiat money. it's a currency that's backed by an. Pros and cons of fiat money. pros. cons. it gives issuers greater control over the money supply, helping them manage the economy. it's cost effective and easy to produce for cheap. it is.
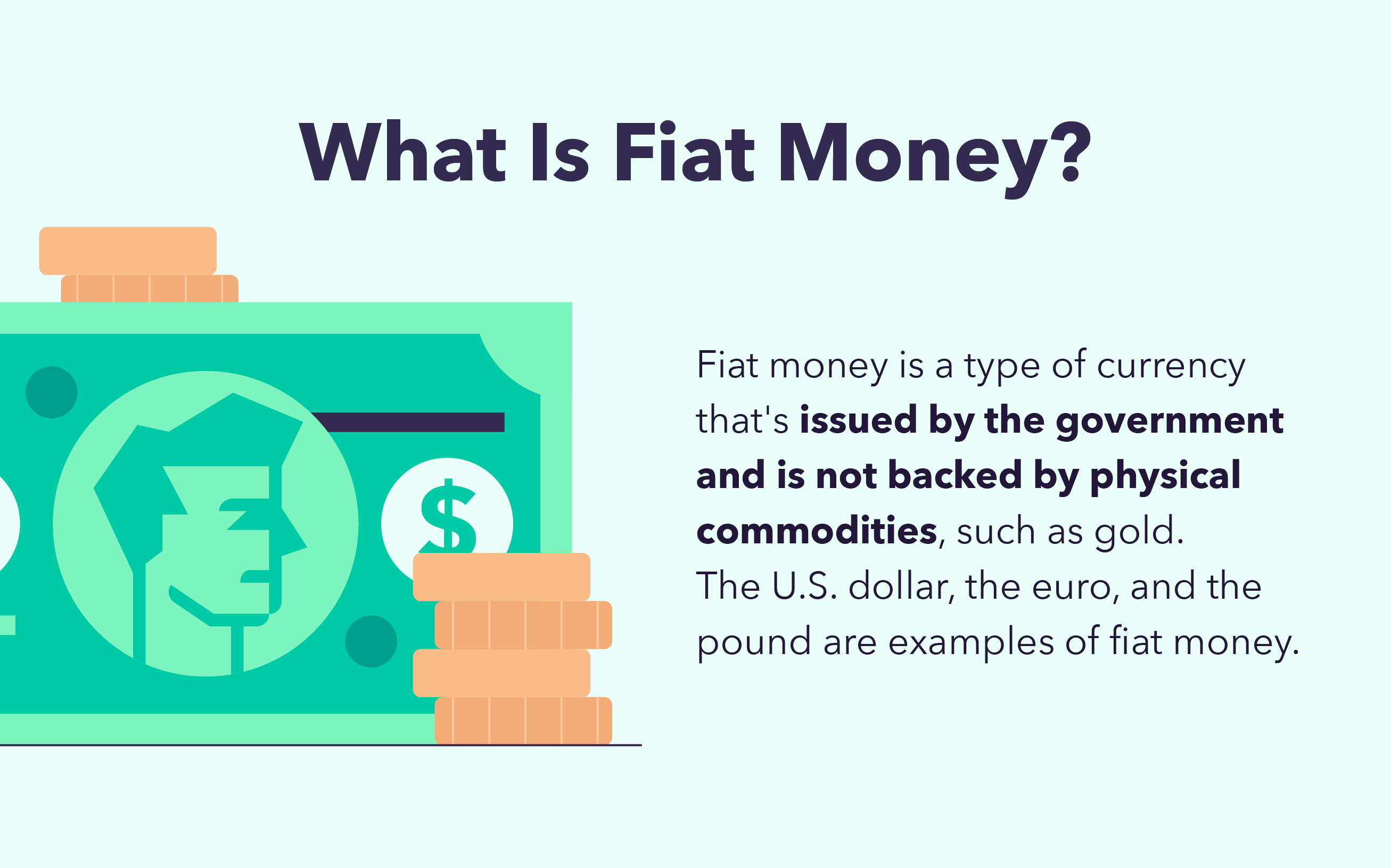
How Is Fiat Currency Defined And Different From Cryptocurrency Write Fiat money is a currency issued by a government with value derived from trust and authority, not tied to any physical commodity. its purpose is to enhance currency stability and facilitate central banks' control over money supply. while lacking intrinsic value, fiat money offers flexibility, convenience, and stability when effectively managed. Definition: fiat currency is a form of money or tender not backed by a tangible asset or commodity like gold or silver. it’s usually mandated by governments, but this isn’t always the case. A "fiat" is an official order or decree. so if a currency is created by a government order, you could say it was created by fiat — making it a fiat currency. an expression of such a fiat is. Fiat money is currency without intrinsic value, deriving its worth from government backing. the value of fiat money lies in the trust people place in it, regulated by governments. the shift away from commodity backed currencies allows governments greater flexibility in managing currency, stabilizing markets, and implementing monetary policy.

Comments are closed.