Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages
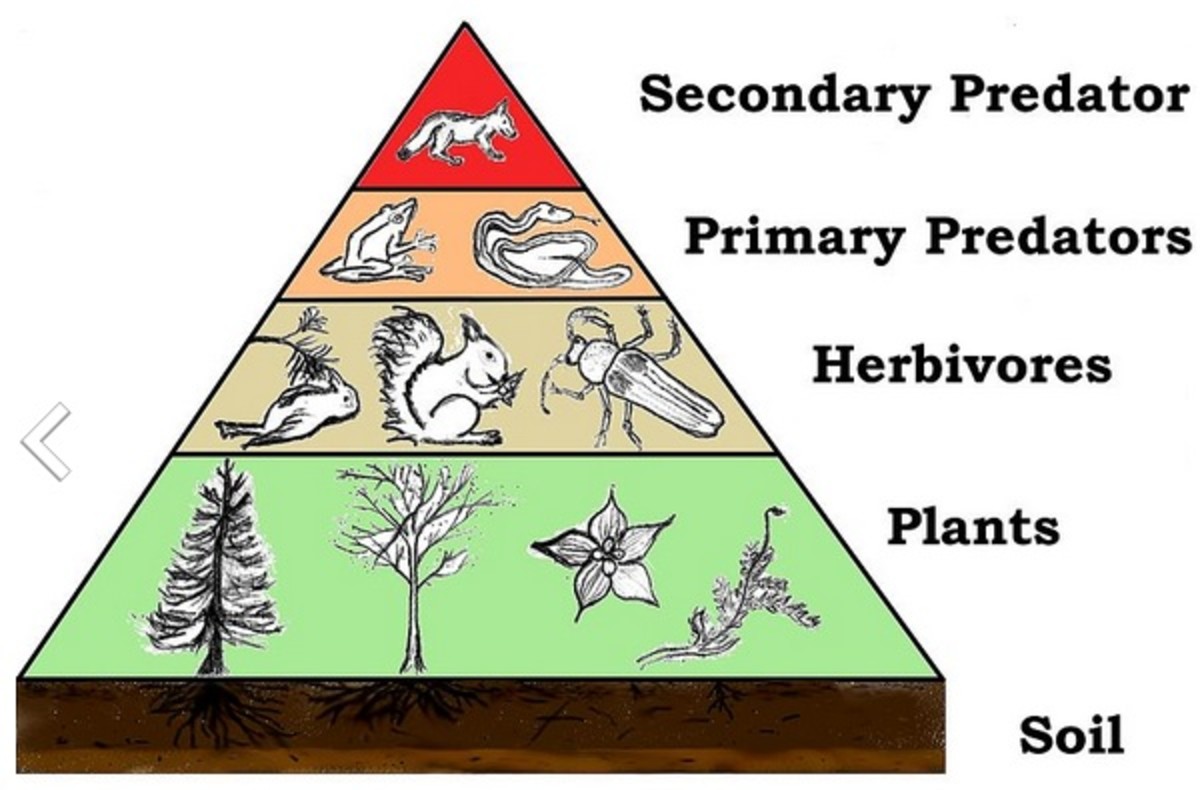
Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages In the ecosystems of the world, there is more there is more than one food chain for most organisms, since most organisms are eaten and prey for more than one organism. humans are both apex predators and omnivores. plants are situated at the bottom in a food chain. herbivores occupy the second trophic level. carnivores are situated above these two. One major factor that limits the number of steps in a food chain is energy. energy is lost at each trophic level and between trophic levels as heat and in the transfer to decomposers (figure \(\pageindex{3}\)). only a fraction of the energy captured by one trophic level is assimilated into biomass, which makes it available to the next trophic.

Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages Draw a terrestrial food chain that includes four trophic levels. identify the trophic level of each organism in the food chain. this page titled 6.5: trophic levels is shared under a ck 12 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by ck 12 foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. The trophic levels refer to the position of a group of organisms in the food chain, food web, or ecological pyramid based on their feeding pattern. they are shown in a series or a succession to represent energy flow from one tropic level to another. the position of the trophic level depends upon the number of steps the organism takes from the. A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differ in their nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea. Trophic level is the position within a food chain that is occupied by a group of organisms in an ecosystem. the classification of organisms into the different food chains is based on their feeding behavior. trophic level is a step in the nutritive series of food chains which in some cases might form a complicated path called a food web.

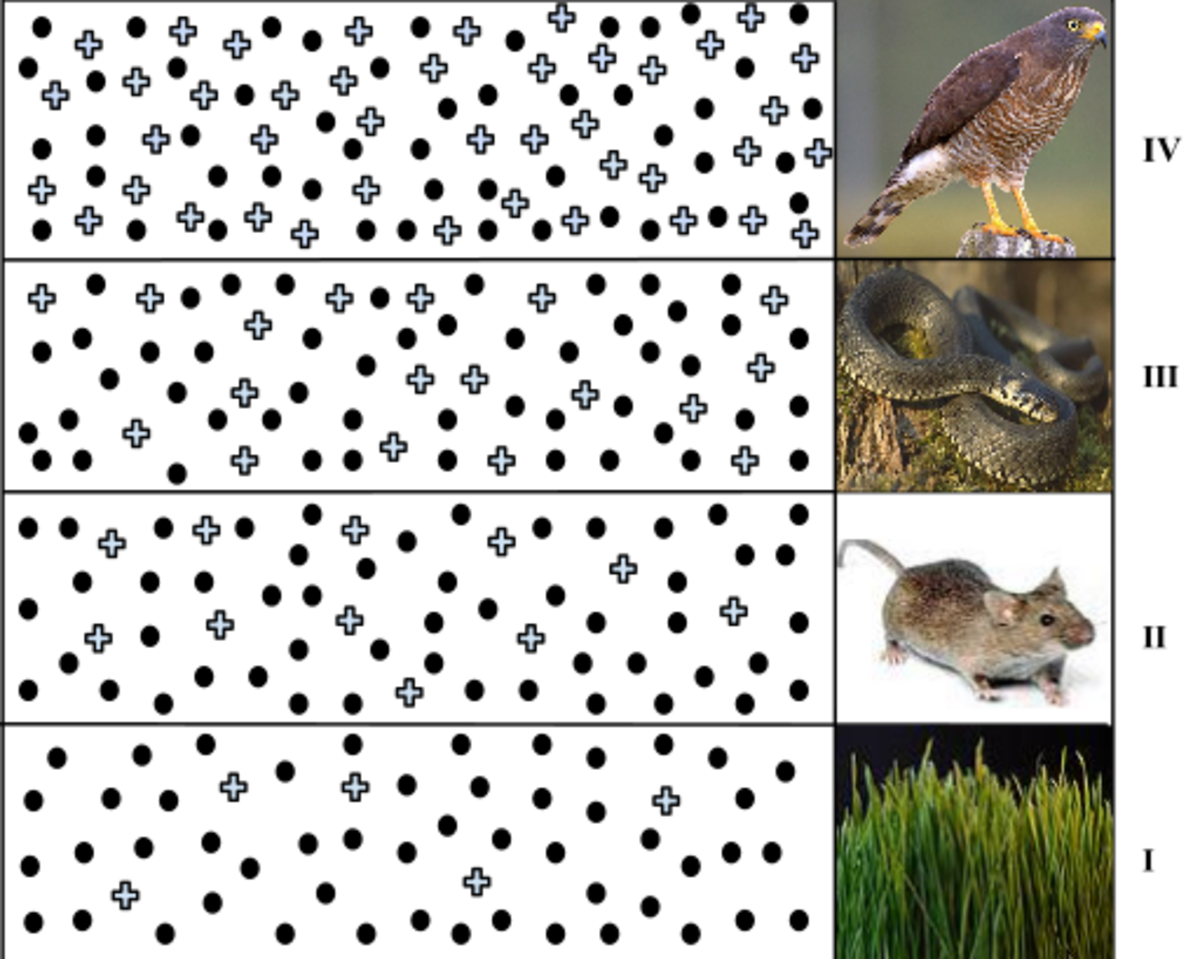
Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differ in their nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea. Trophic level is the position within a food chain that is occupied by a group of organisms in an ecosystem. the classification of organisms into the different food chains is based on their feeding behavior. trophic level is a step in the nutritive series of food chains which in some cases might form a complicated path called a food web. There is a single path through a food chain. figure 56.3.4.g 56.3.4. g: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the united states–canada border. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae (producers) at the base to the primary consumers, which are mollusks, or snails. Food chains food webs connect many different food chains, and many different trophic levels. food webs can support food chains that are long and complicated, or very short. for example, grass in a forest clearing produces its own food through photosynthesis. a rabbit eats the grass. a fox eats the rabbit.
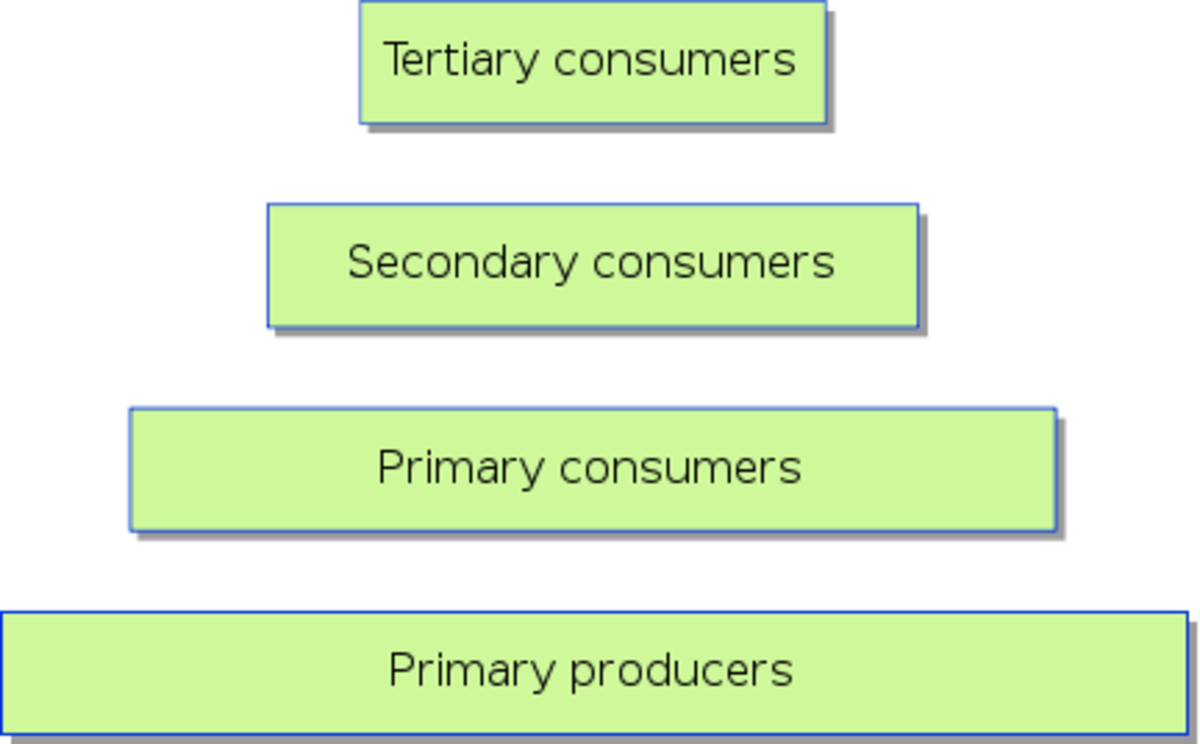
Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages There is a single path through a food chain. figure 56.3.4.g 56.3.4. g: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the united states–canada border. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae (producers) at the base to the primary consumers, which are mollusks, or snails. Food chains food webs connect many different food chains, and many different trophic levels. food webs can support food chains that are long and complicated, or very short. for example, grass in a forest clearing produces its own food through photosynthesis. a rabbit eats the grass. a fox eats the rabbit.
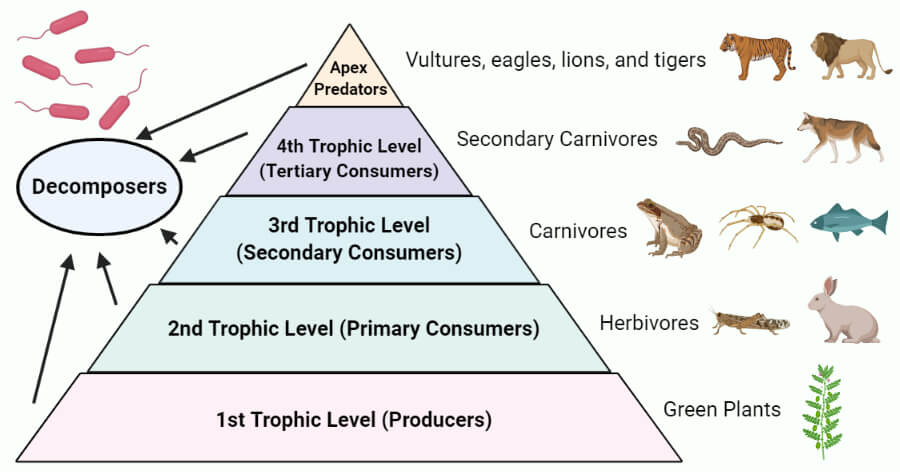
Trophic Level Food Chain Food Web Pyramid Examples

Comments are closed.