Trigonometry Evaluating Angles Solutions Examples Videos
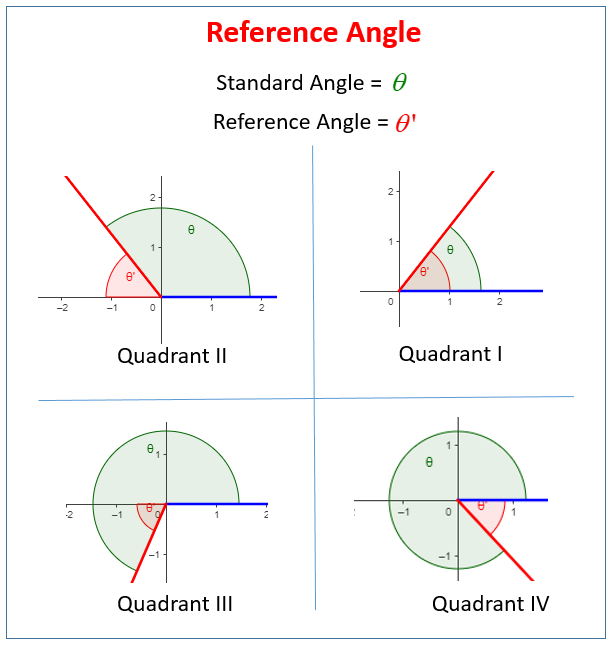
Evaluating Trigonometric Functions Using The Reference Angle Solutions Trigonometry: evaluate using special angles and calculators. how to find the trigonometric functions of special angles 30, 45 and 60, how to use the calculator to evaluate the trigonometric functions of any angle, with video lessons, examples and step by step solutions. This trigonometry video tutorial explains how to use reference angles to evaluate trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant, an.
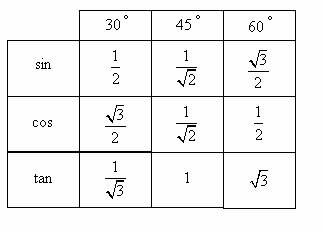
Trigonometry Evaluating Angles Solutions Examples Videos Trigonometry is an important tool for evaluating measurements of height and distance. it plays an important role in surveying, navigation, engineering, astronomy and many other branches of physical science. basic trigonometry involves the ratios of the sides of right triangles. the three ratios are called tangent, sine and cosine. We should commit all of the trigonometric functions evaluated at angles of 30 degrees, 45 degrees, and 60 degrees to memory. one way of doing this is to use a table of values as shown. in the columns, we have the angles of 30 degrees, 45 degrees, and 60 degrees. and in our rows, we have the trigonometric functions. Examples: evaluate: (a) cos (45°) (b) sin (150°) (c) tan (225°) (d) csc (150°) show step by step solutions. evaluating trigonometric functions using the reference angle, example 1. this video reviews the unit circle in quadrant 1 and discusses how to use the reference angle to evaluate some trig functions. 1 hr 19 min 20 examples. examples #1 2: find the distance between points p and q. examples #3 4: find the domain and range, and determine if a function. examples #5 6: for each rotation, find the measure in degrees and sketch the angle. examples #7 10: convert to decimal degree or degrees minutes seconds.
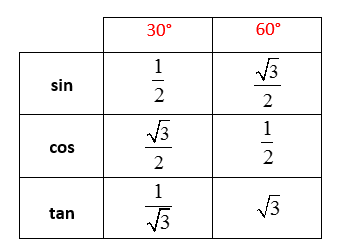
Trigonometry Evaluating Angles Solutions Examples Videos Examples: evaluate: (a) cos (45°) (b) sin (150°) (c) tan (225°) (d) csc (150°) show step by step solutions. evaluating trigonometric functions using the reference angle, example 1. this video reviews the unit circle in quadrant 1 and discusses how to use the reference angle to evaluate some trig functions. 1 hr 19 min 20 examples. examples #1 2: find the distance between points p and q. examples #3 4: find the domain and range, and determine if a function. examples #5 6: for each rotation, find the measure in degrees and sketch the angle. examples #7 10: convert to decimal degree or degrees minutes seconds. Example 2: evaluating trigonometric expressions involving special angles. evaluate 2 𝜋 6 − 8 4 𝜋 3 t a n s i n. answer . we begin by recalling that 𝜋 = 1 8 0 r a d i a n s ∘. so, 𝜋 6 = 3 0. r a d i a n s ∘. also, 𝜋 3 = 6 0 4 𝜋 3 = 2 4 0. r a d i a n s r a d i a n s ∘ ∘. we therefore need to calculate 2 3 0 − 8 2 4. Now we can evaluate the trigonometric functions by using right triangles. however, to extend these functions even further, we need to use the unit circle. and that’s the circle of radius one centered at the origin. we can then use this to evaluate trigonometric functions. for example, let’s sketch the angle 150 degrees in standard position.
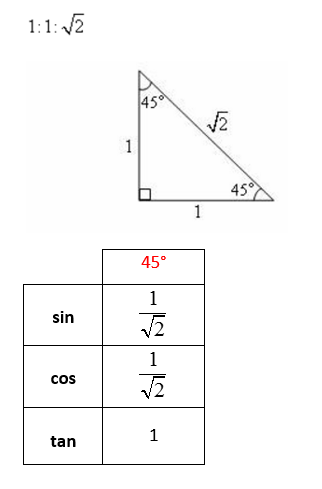
Trigonometry Evaluating Angles Solutions Examples Videos Example 2: evaluating trigonometric expressions involving special angles. evaluate 2 𝜋 6 − 8 4 𝜋 3 t a n s i n. answer . we begin by recalling that 𝜋 = 1 8 0 r a d i a n s ∘. so, 𝜋 6 = 3 0. r a d i a n s ∘. also, 𝜋 3 = 6 0 4 𝜋 3 = 2 4 0. r a d i a n s r a d i a n s ∘ ∘. we therefore need to calculate 2 3 0 − 8 2 4. Now we can evaluate the trigonometric functions by using right triangles. however, to extend these functions even further, we need to use the unit circle. and that’s the circle of radius one centered at the origin. we can then use this to evaluate trigonometric functions. for example, let’s sketch the angle 150 degrees in standard position.

Comments are closed.