Terrestrial Food Chain Examples

Food Chain Definition Types Facts Britannica With this in mind a common terrestrial food chain example is grass grasshopper snake hawk. if you asked us to give another example of a terrestrial food chain, we’d suggest plants grasshopper scorpion fox. similar, but clearly tied to a different habitat, because, as you may have guessed, different terrestrial habitats consist of unique. A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers.
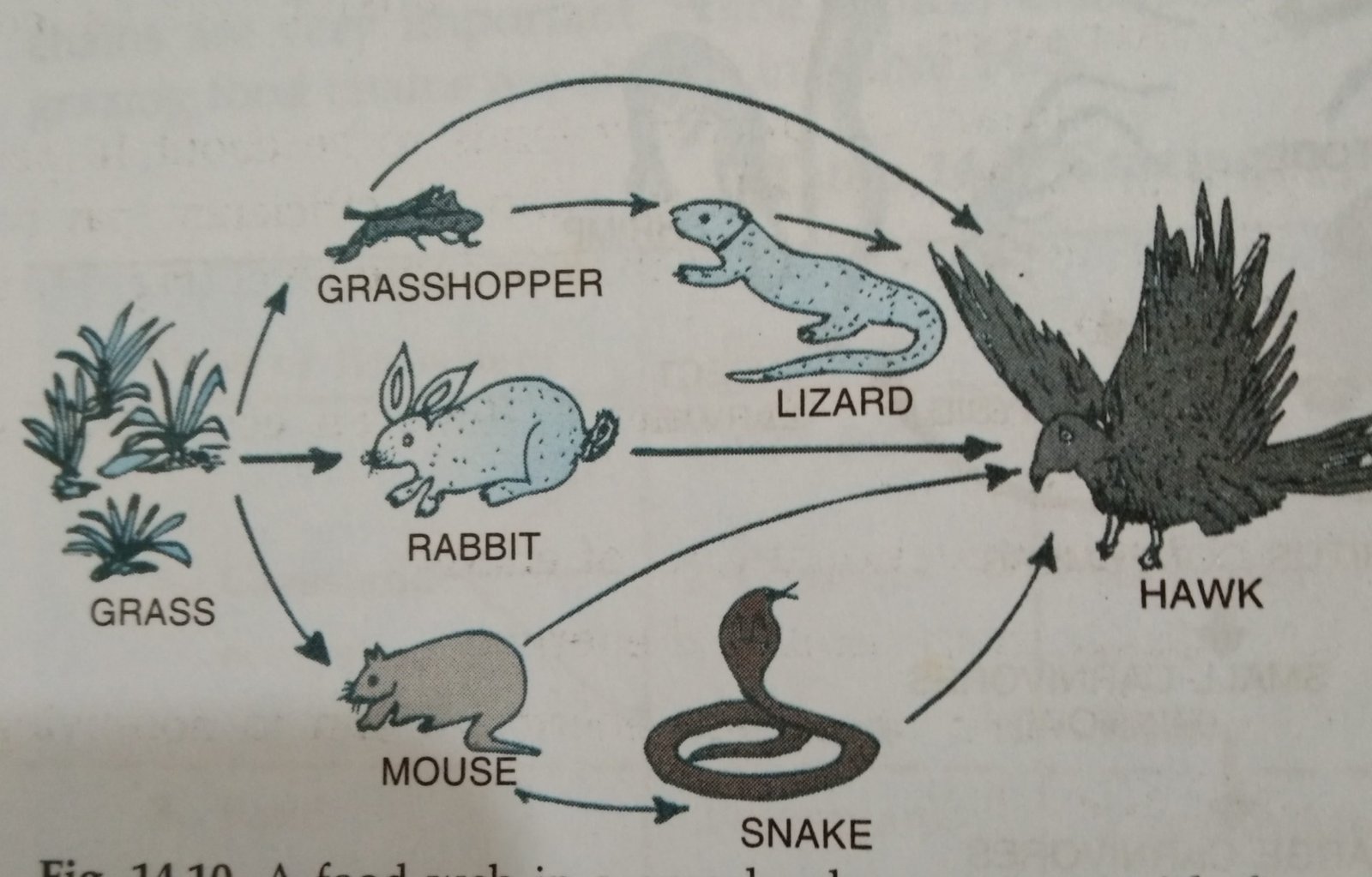
Food Chain And Food Web Definition Diagram And Examples Biologysir Learn how food webs illustrate the feeding relationships and energy flow among species in an ecosystem. explore the types of food webs and examples of indirect interactions among species. Grazing food chain. food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. plants, which convert solar energy to food by photosynthesis, are the primary food source. Terrestrial food webs depict the flow of energy between organisms in land ecosystems like grasslands and forests. they showcase the intricate connections between producers like plants, consumers such as herbivores and carnivores, and decomposers like bacteria and fungi. food webs provide a more accurate model than simple linear food chains. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. every living thing—from one celled algae to giant blue whales (balaenoptera musculus)—needs food to survive. each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrients can follow through the ecosystem. for example, grass produces its own food from sunlight. a rabbit eats the grass.
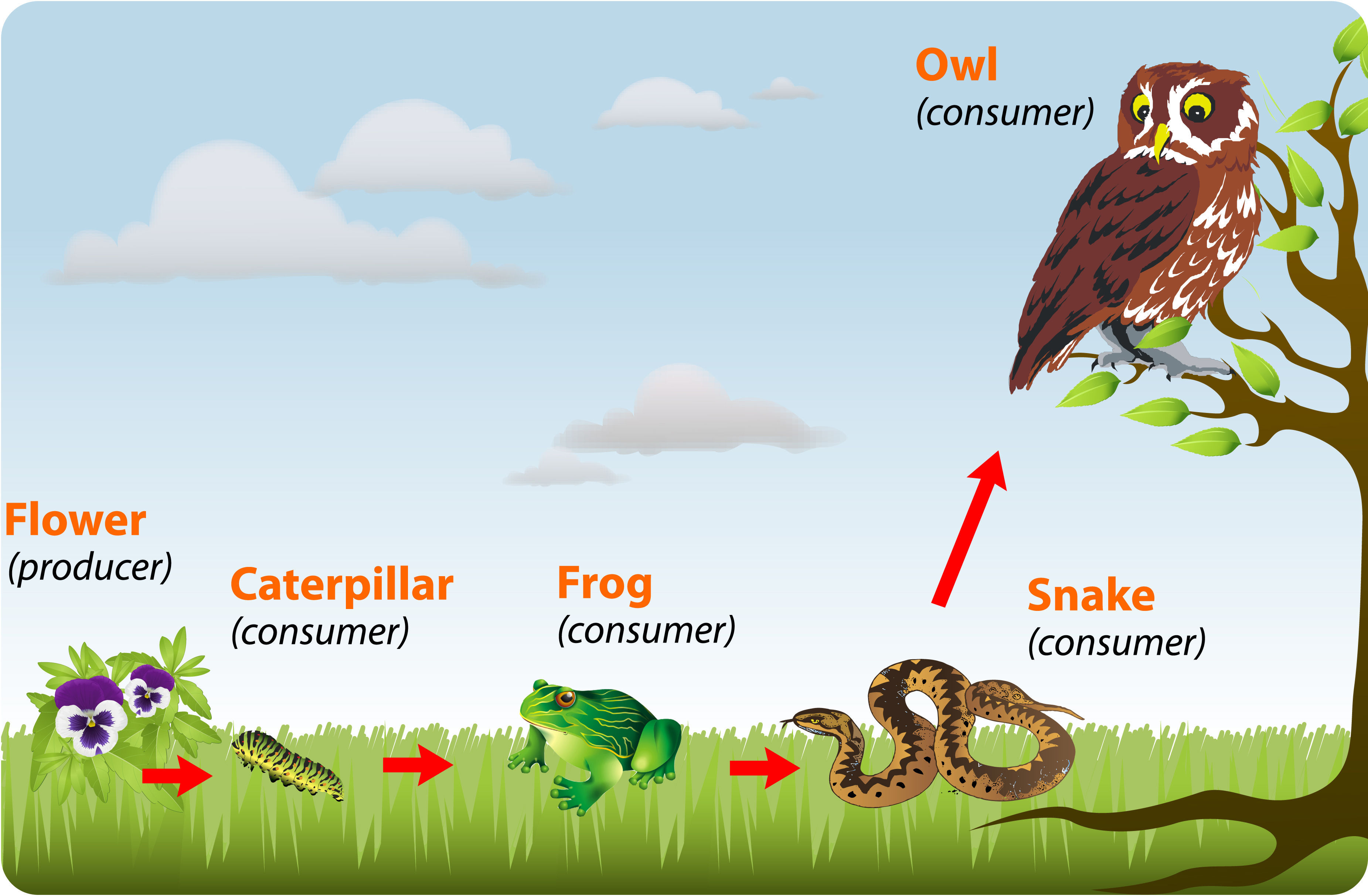
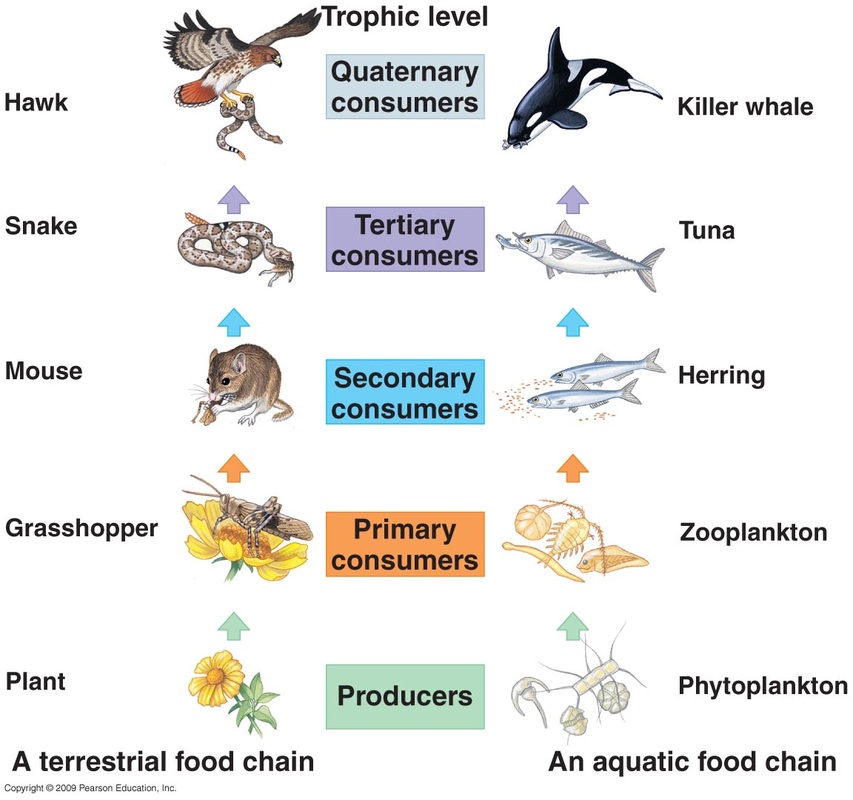
Food Chain In Terrestrial Ecosystem Terrestrial food webs depict the flow of energy between organisms in land ecosystems like grasslands and forests. they showcase the intricate connections between producers like plants, consumers such as herbivores and carnivores, and decomposers like bacteria and fungi. food webs provide a more accurate model than simple linear food chains. The food chain describes who eats whom in the wild. every living thing—from one celled algae to giant blue whales (balaenoptera musculus)—needs food to survive. each food chain is a possible pathway that energy and nutrients can follow through the ecosystem. for example, grass produces its own food from sunlight. a rabbit eats the grass. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those.

Construct A Terrestrial Food Chain Comprising Four Trophic Levels Level Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those.
Terrestrial Food Chain Examples

Comments are closed.