Reversible Reactions Gidemy Class Notes

Reversible Reactions Gidemy Class Notes The concept of equilibrium reversible reactions and equilibrium we have already seen that a reversible reaction is one that occurs in both directions when during the course of reaction, the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, then the overall reaction is said to be in a state of equilibrium characteristics of a read more “equlibrium and le chatelier” ». Analysis of rates of reaction rate graphs 1 what you need to know: how to calculate the reaction rate by finding the gradient of a reaction time graph. there are two main ways to find the rate of a reaction, using the equation above or finding the gradient of a reaction rate graph. the gradient (‘slope’) of the read more “analysis of rates of reaction” ».
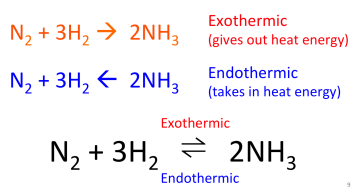
Reversible Reactions Gidemy Class Notes Diagram showing the apparatus needed to investigate the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction. method: measure 50 cm 3 of sodium thiosulfate solution into a flask. measure 5 cm 3 of dilute hydrochloric acid into a measuring cylinder. draw a cross on a piece of paper and put it underneath the flask. Edexcel. spanish. past papers. cie. spanish language & literature. past papers. other subjects. revision notes on reversible reactions for the cie igcse chemistry syllabus, written by the chemistry experts at save my exams. A reversible reaction is one which proceeds in both forward and backward directions under suitable conditions. for example: nh 4 cl (s) nh 3(g) hcl (g) a reversible reaction is said to be in dynamic equilibrium when both the forward and backward reaction is occurring at the same rate, thereby producing no net change in concentrations of the. The symbol for a reversible reaction is a double arrow: ⇋. how does a reversible reaction work. in a reversible reaction, the molecules in a closed system collide with energies to break chemical bonds and form new products. however, the products are highly energetic, and their molecules also collide to break new bonds.

Comments are closed.