Ray Diagrams Mirrors

Ray Diagram Of Concave And Convex Mirror The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (c) of a concave mirror. yet the same method works for drawing a ray diagram for any object location. 1. pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. A plane mirror is a flat, smooth reflective surface with a clear, undistorted reflection. when an object is reflected in a plane mirror, it always forms a virtual image that is upright, of the same shape and size as the object. on the other hand, a spherical mirror exhibits a consistent curvature. it possesses a constant radius of curvature (in.

Drawing Ray Diagrams For Plane Mirrors Mini Physics Free Physics Notes Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. the virtual image that is formed will appear smaller and closer to the mirror than the object. change to concave mirror. ray diagrams for mirrors. 121 ray diagram mirrorsin this video paul andersen explains how ray diagrams can be used to determine the size and location of a reflected image. ray di. A ray diagram is a tool that is used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. ray diagrams for concave mirrors were drawn in lesson 3. in this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for convex mirrors. Ray diagrams. the way that we can predict how a reflection will look is by drawing a ray diagram. these diagrams can be used to find the position and size of the image and whether that image is real or virtual. these are the steps you follow to draw a ray diagram: draw the plane mirror as a straight line on a principal axis.
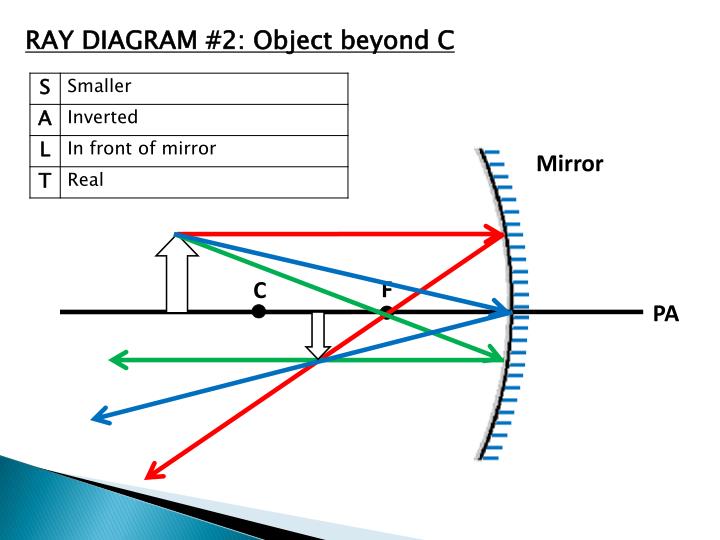
Ppt Ray Diagrams For Concave Mirrors Powerpoint Presentation Id 2680017 A ray diagram is a tool that is used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. ray diagrams for concave mirrors were drawn in lesson 3. in this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for convex mirrors. Ray diagrams. the way that we can predict how a reflection will look is by drawing a ray diagram. these diagrams can be used to find the position and size of the image and whether that image is real or virtual. these are the steps you follow to draw a ray diagram: draw the plane mirror as a straight line on a principal axis. Consider yourself to be 1.55 m tall. learn ray diagrams for mirrors with free step by step video explanations and practice problems by experienced tutors. The four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. 1. draw the image of the object. use the principle that the object distance is equal to the image distance to determine the exact location of the object. pick one extreme on the object and carefully measure the distance from this extreme point.

Comments are closed.