Probability Distribution Functions Pmf Pdf Cdf
Ppt Summarizing Measured Data Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Here’s how we can use the poisson distribution: probability mass function (pmf): the pmf of the poisson distribution gives the probability of observing a specific number of events (in this case. A probability distribution is a function or a list of all possible outcomes of a random variable and their corresponding probabilities. it describes the likelihood of each event in a random.

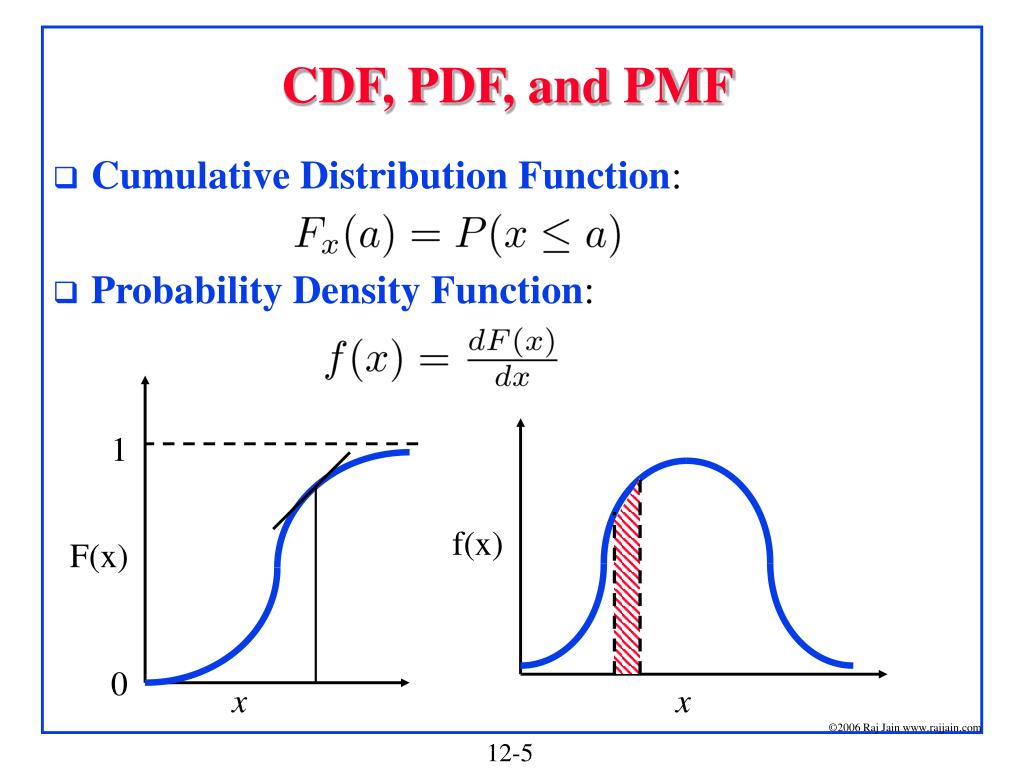
Probability Distributions Clearly Explained Visually Pmf Pdf And Cdf See all my videos at zstatistics videos0:00 intro0:43 terminology defineddiscrete variable:2:24 probability mass function (pmf)3:31 cumulative. The probability mass function (pmf) (or frequency function) of a discrete random variable \(x\) assigns probabilities to the possible values of the random variable. more specifically, if \(x 1, x 2, \ldots\) denote the possible values of a random variable \(x\), then the probability mass function is denoted as \(p\) and we write. Fig: formula for pmf. pmf is a statistical term that describes the probability distribution of the discrete random variable. people often get confused between pdf and pmf. the pdf is applicable. It is a cumulative function because it sums the total likelihood up to that point. its output always ranges between 0 and 1. cdfs have the following definition: cdf (x) = p (x ≤ x) where x is the random variable, and x is a specific value. the cdf gives us the probability that the random variable x is less than or equal to x.

Probability Distribution Functions Pdf Cdf Pmf Fig: formula for pmf. pmf is a statistical term that describes the probability distribution of the discrete random variable. people often get confused between pdf and pmf. the pdf is applicable. It is a cumulative function because it sums the total likelihood up to that point. its output always ranges between 0 and 1. cdfs have the following definition: cdf (x) = p (x ≤ x) where x is the random variable, and x is a specific value. the cdf gives us the probability that the random variable x is less than or equal to x. The relationship between a cdf and a pdf. in technical terms, a probability density function (pdf) is the derivative of a cumulative distribution function (cdf). furthermore, the area under the curve of a pdf between negative infinity and x is equal to the value of x on the cdf. for an in depth explanation of the relationship between a pdf and. As another reminder, a probability distribution has an associated function f() that is referred to as a probability mass function (pmf) or probability distribution function (pdf). for discrete random variables, the pmf is a function from sto the interval [0;1] that associates a probability with each x2s, i.e., f(x) = p(x= x). for continuous random.

Comments are closed.