Polynomials Introduction
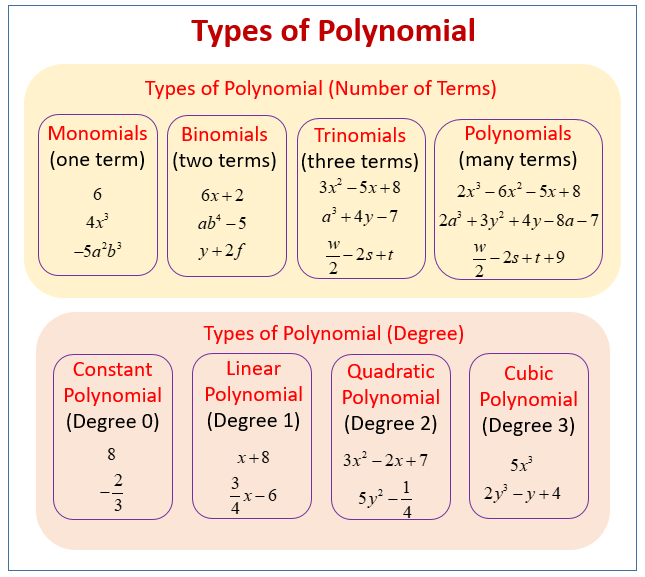
Introduction To Polynomials Examples Solutions Videos Activities Monomial. binomial. trinomial. polynomial containing 4 terms (quadronomial) polynomial containing 5 terms (pentanomial ) and so on …. these polynomials can be combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division but is never divided by a variable. a few examples of non polynomials are: 1 x 2, x 3. A polynomial is a finite expression constructed from variables and constants, using the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and taking non negative integer powers. a polynomial can be written as the sum of a finite number of terms. each term consists of the product of a constant (called the coefficient of the term) and a finite.

Introduction To Polynomials Youtube A polynomial is a special algebraic expression with terms that consist of real number coefficients and variable factors with whole number exponents. examplesofpolynomials: 3x2 7xy 5 3 2x3 3x2 − 1 2x 1 6x2y − 4xy3 − 4xy3 7. polynomials do not have variables in the denominator of any term. examplesthatarenotpolynomials:. The standard form for writing a polynomial is to put the terms with the highest degree first. example: put this in standard form: 3 x2 − 7 4 x3 x6. the highest degree is 6, so that goes first, then 3, 2 and then the constant last: x6 4 x3 3 x2 − 7. you don't have to use standard form, but it helps. The general expressions containing variables of varying degrees, coefficients, positive exponents, and constants are known as polynomial functions. in other words, a polynomial function is a function whose definition is a polynomial. here are some examples of polynomial functions: f (x) = x 2 4. g (x) = 2x 3 x 7. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math algebra x2f8bb11595b61c86:quad.

Introduction Of Polynomials The general expressions containing variables of varying degrees, coefficients, positive exponents, and constants are known as polynomial functions. in other words, a polynomial function is a function whose definition is a polynomial. here are some examples of polynomial functions: f (x) = x 2 4. g (x) = 2x 3 x 7. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math algebra x2f8bb11595b61c86:quad. Is a horizontal line with y intercept a0. the graph of a degree 1 polynomial (or linear function) f(x) = a0 a1x, where a1 ≠ 0, is an oblique line with y intercept a0 and slope a1. the graph of a degree 2 polynomial. f(x) = a0 a1x a2x2, where a2 ≠ 0. is a parabola. the graph of a degree 3 polynomial. A polynomial is an expression that can be written in the form. anxn ⋯ a2x2 a1x a0 a n x n ⋯ a 2 x 2 a 1 x a 0. each real number ai is called a coefficient. the number a0 a 0 that is not multiplied by a variable is called a constant. each product aixi a i x i is a term of a polynomial.

Introduction To Polynomials Youtube Is a horizontal line with y intercept a0. the graph of a degree 1 polynomial (or linear function) f(x) = a0 a1x, where a1 ≠ 0, is an oblique line with y intercept a0 and slope a1. the graph of a degree 2 polynomial. f(x) = a0 a1x a2x2, where a2 ≠ 0. is a parabola. the graph of a degree 3 polynomial. A polynomial is an expression that can be written in the form. anxn ⋯ a2x2 a1x a0 a n x n ⋯ a 2 x 2 a 1 x a 0. each real number ai is called a coefficient. the number a0 a 0 that is not multiplied by a variable is called a constant. each product aixi a i x i is a term of a polynomial.

Comments are closed.