Pollination Explained
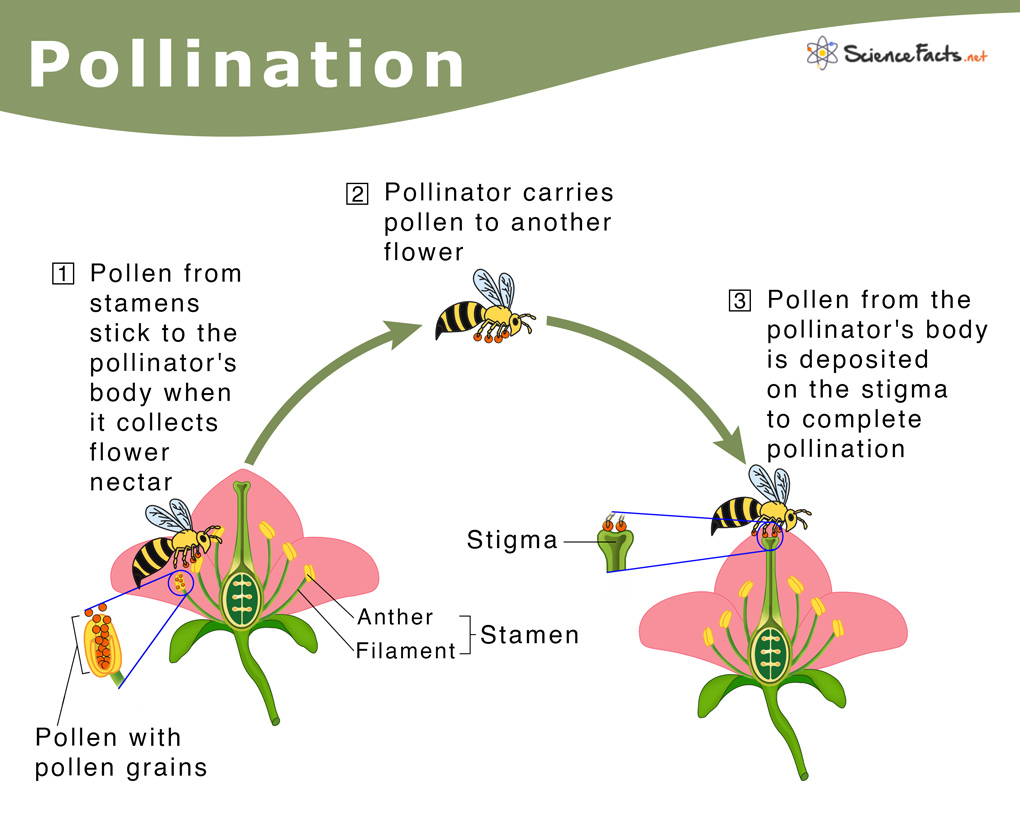
Pollination Explained For Kids Learn how pollination is essential for plant reproduction and ecosystem health, and how different pollinators and plants interact. discover how to create a pollinator friendly habitat with native plants and diverse blooms. Pollination is the act of transferring pollen grains from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma. the goal of every living organism, including plants, is to create offspring for the next generation. one of the ways that plants can produce offspring is by making seeds. seeds contain the genetic information to produce a new plant.
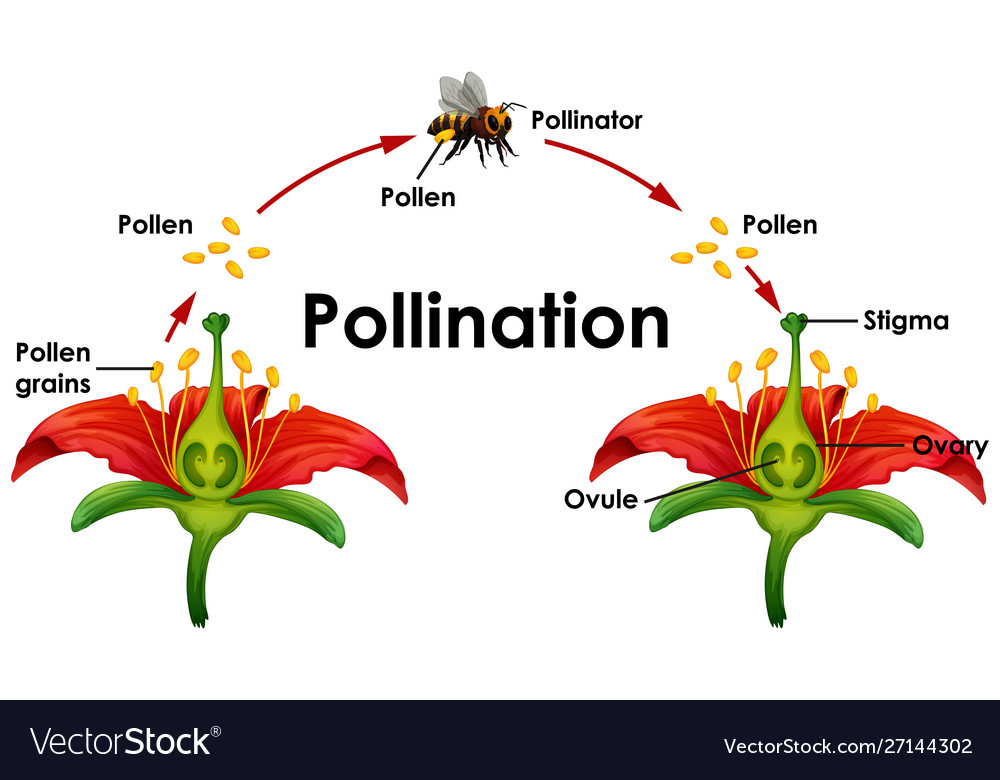
Diagram Showing Pollination With Flower And Bee Vector Image Pollination, transfer of pollen grains from the stamens (the flower parts that produce them) to the ovule bearing organs or to the ovules (seed precursors) themselves. in gymnosperm plants such as conifers and cycads, in which the ovules are exposed, the pollen is simply caught in a drop of fluid secreted by the ovule. Pollination. pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. [1] pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example beetles or butterflies; birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves. Pollination diagram. here are the steps through which pollination occurs. step 1: the first step is to transfer pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same or different flower. step 2: after the pollen’s successful transfer, a pollen tube starts forming along the length of the style. the style is a long stalk that connects the stigma to. What is pollination. – pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or of another flower borne by the same plant (i.e., genetically similar flower) or of another flower borne on a different plant (i.e., genetically different plant of the same species). – it occurs only in gymnosperms and.

Diagram Showing Pollination Cycle Royalty Free Vector Image Pollination diagram. here are the steps through which pollination occurs. step 1: the first step is to transfer pollen from the anther to the stigma of the same or different flower. step 2: after the pollen’s successful transfer, a pollen tube starts forming along the length of the style. the style is a long stalk that connects the stigma to. What is pollination. – pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or of another flower borne by the same plant (i.e., genetically similar flower) or of another flower borne on a different plant (i.e., genetically different plant of the same species). – it occurs only in gymnosperms and. At the most basic level, pollination is the way plants achieve fertilization and genetic diversity. pollination process occurs when pollen grains from the male part of one flower (anther) are transferred to the female part (stigma) of another flower. once pollination occurs, the fertilized flowers produce seeds, which enable the associated. Flowers have male and female structures, and it is the process of pollination that transfers pollen from the male part to the female part. after pollination, pollen releases a male gamete that fertilises a female gamete in the ovule and mixes their genetic material. after this fertilisation, the ovule grows to form a seed.

Comments are closed.