Plant Life Cycle Stages And Diagram
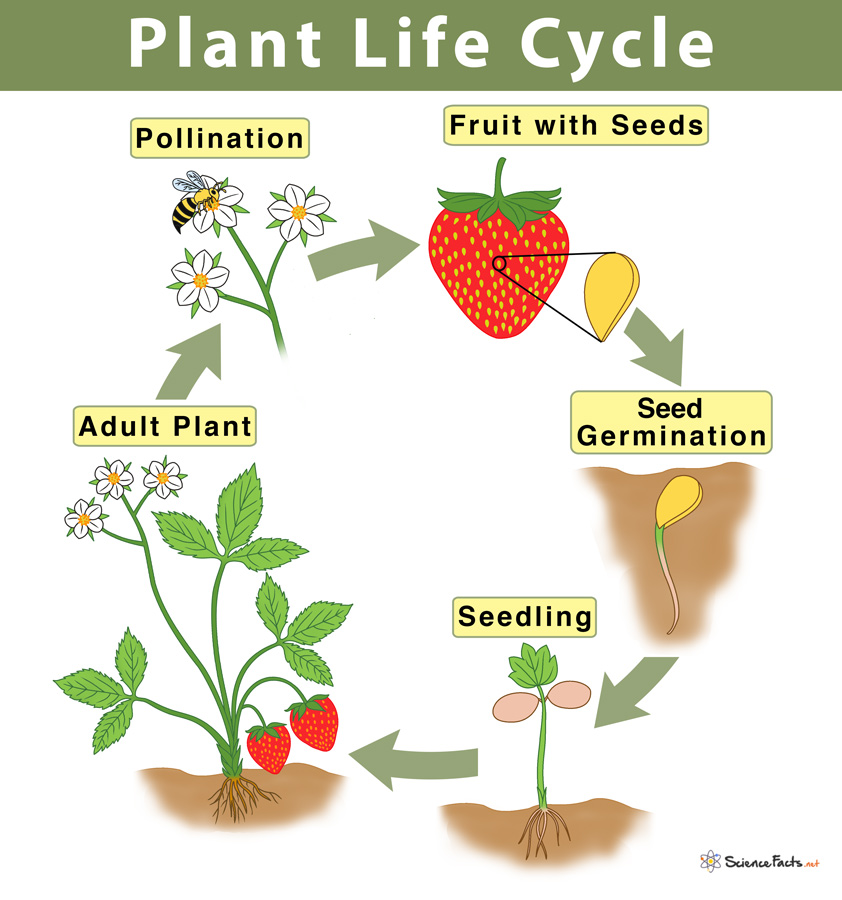
Plant Life Cycle Stages And Diagram Stages of life cycle in flowering plants. a basic plant life cycle goes through five stages: 1) seed, 2) seed germination, 3) seedling, 4) adult plant, and 5) pollination and fertilization. they are discussed below in detail. A general plant life cycle is represented by the diagram in figure below. from the figure, you can see that the diploid sporophyte has a structure called a sporangium (plural, sporangia) that undergoes meiosis to form haploid spores. a spore develops into a haploid gametophyte. the gametophyte has male or female reproductive organs that undergo.
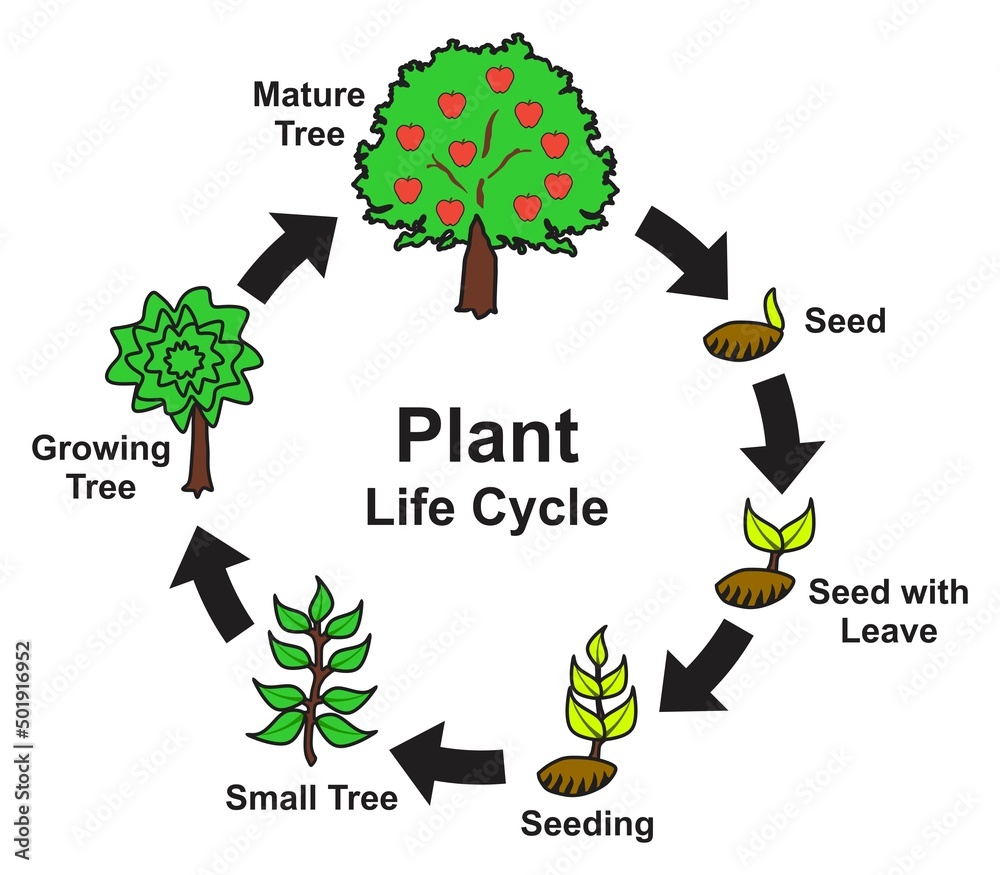
Plant Life Cycle Infographic Diagram Stages Of Growing And Development Key takeaways. – plants go through different stages of growth from seed to seed, which are called the plant life cycle. – the main stages of a plant’s life cycle are seed, germination, seedling, adult plant, pollination, and seed dispersal. – different types of plants have different life cycles, depending on their shape, size, lifespan. Germination. growth. flowering stage. pollination (reproductive stage) fruit stage (seed dispersal stage) maize plant life cycle. generally, the life cycle of the plant is a simple one with fewer complications. there are various plant life cycles, but the more advanced and mainly studied one is – the angiosperms (flowering plant) life cycle. This is the alternation of generations, and is typical of plant reproduction (figure 1). figure 1. the alternation of generations in angiosperms is depicted in this diagram. (credit: modification of work by peter coxhead) the life cycle of higher plants is dominated by the sporophyte stage, with the gametophyte borne on the sporophyte. All flowering plants go through the following life cycle. germination is the process by which a plant begins to grow from a seed. roots form under the soil. the stem, leaves and flower emerge.

Life Cycle Of A Plant Ks1 This is the alternation of generations, and is typical of plant reproduction (figure 1). figure 1. the alternation of generations in angiosperms is depicted in this diagram. (credit: modification of work by peter coxhead) the life cycle of higher plants is dominated by the sporophyte stage, with the gametophyte borne on the sporophyte. All flowering plants go through the following life cycle. germination is the process by which a plant begins to grow from a seed. roots form under the soil. the stem, leaves and flower emerge. Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. this cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte. in this page, explore at how these generations differ with each. L ife cycle of plants. th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need for fertilization. in contrast, most modern plants reproduce.
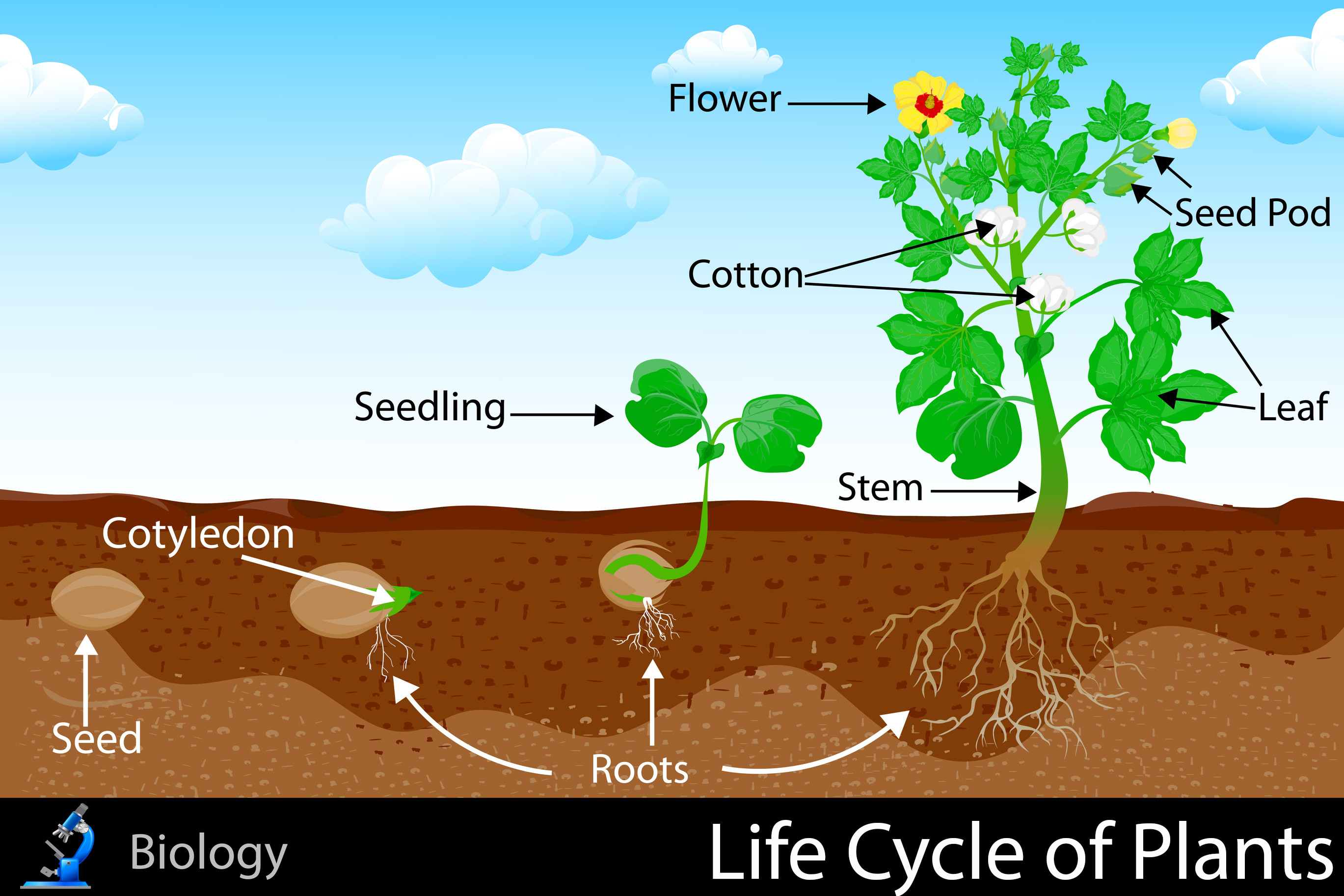
Life Cycle Of Plants Kidspressmagazine Instead, diploid sporophyte cells go through meiosis and produce the haploid spores. throughout the plant life cycle, all plants undergo the alternation of generations. this cycle of generations include both diploid (2n) phase, the sporophyte, and the haploid (n) phase gametophyte. in this page, explore at how these generations differ with each. L ife cycle of plants. th is diagram shows the general life cycle of a plant. early plants reproduced mainly with spores and spent most of their life cycle as haploid gametophytes. spores require little energy and matter to produce, and they grow into new individuals without the need for fertilization. in contrast, most modern plants reproduce.

Comments are closed.