Pid Control Introduction Pdf
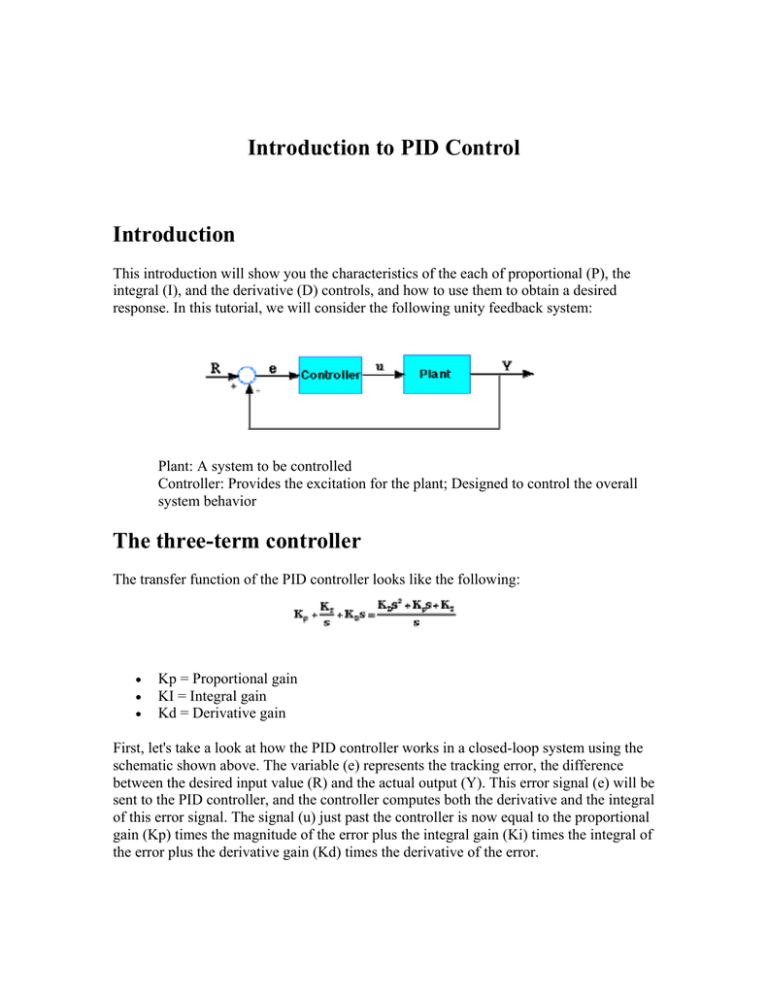
Pdf Introduction To Pid Control Pid control most widely used control strategy today. over 90% of control loops employ pid control, often the derivative gain set to zero (pi control) the three terms are intuitive a non specialist can grasp the essentials of the pid controller’s action. it does not require the operator to be familiar with advanced math to use pid controllers. 1 introduction. the proportional integral derivative (pid) controllers are without a doubt the most widely used controllers in industry today. ̊astr ̈om and h ̈agglund [1, p. 198] regard the pid con troller as the “bread and butter” of control engineering. knospe [3] estimates that over 90% of control loops employ pid control.

Pid Control Pdf Control Theory Applied Mathematics 1. ontrol1.1 introductiona proportional–integral–derivative (pid) controller is a three term controller that has a long history in the automatic control field, starting from the be ginning of the last. entury (bennett, 2000). owing to its intuitiveness and its relative simplicity, in addition to satisfactory performance which it is able to. 6.1 introduction. the pid controller is the most common form of feedback. it was an es sential element of early governors and it became the standard tool when process control emerged in the 1940s. in process control today, more than 95% of the control loops are of pid type, most loops are actually pi con trol. Pid control is used to control and maintain processes. it can be used to control physical variables such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and tank level. the technique is widely used in today’s manufacturing industry to achieve accurate process control under different process conditions. Of instrument and control engineers worldwide are using such controllers in their daily work. the pid algorithm can be approached from many difierent directions. it can be viewed as a device that can be operated with a few empirical rules, but it can also be approached analytically. this chapter gives an introduction to pid control. the basic.
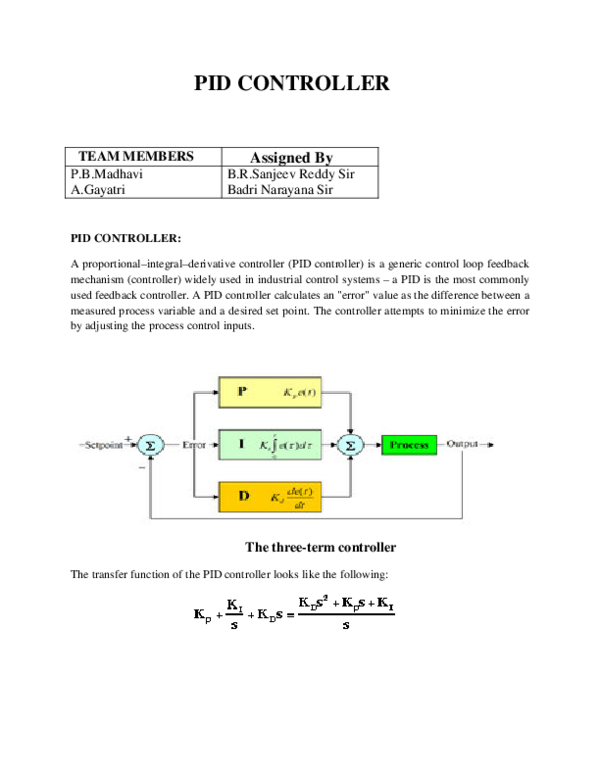
Pdf Pid Controller Without Noise Gayathri Addanki Academia Edu Pid control is used to control and maintain processes. it can be used to control physical variables such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and tank level. the technique is widely used in today’s manufacturing industry to achieve accurate process control under different process conditions. Of instrument and control engineers worldwide are using such controllers in their daily work. the pid algorithm can be approached from many difierent directions. it can be viewed as a device that can be operated with a few empirical rules, but it can also be approached analytically. this chapter gives an introduction to pid control. the basic. Pid controllers: an overview (continue) nitnyquist it tti fznfrminterpretation of znfrm using pid control, it is possible to move a given point on the nyquist curve to an arbitrary position in the complex plane. • the point where the nyquist curve of the plant intersects the negative real axis μ ¡ 1 k u;0 ¶ 2 t 25o c(j! u)=0:6k u ¡j μ 1. Pid control theory 217 fig. 4. a) step response of pid ideal formb) step response of pid real form 2.1 the transfer function of the pid controller the transfer function of the pid controller is () us gs es (7) () i p d k gs k k s s = 2 ks ks kd p i s (8) 2.2 pid pole zero cancellation the pid equation can be written in this form: ()2 p i d.
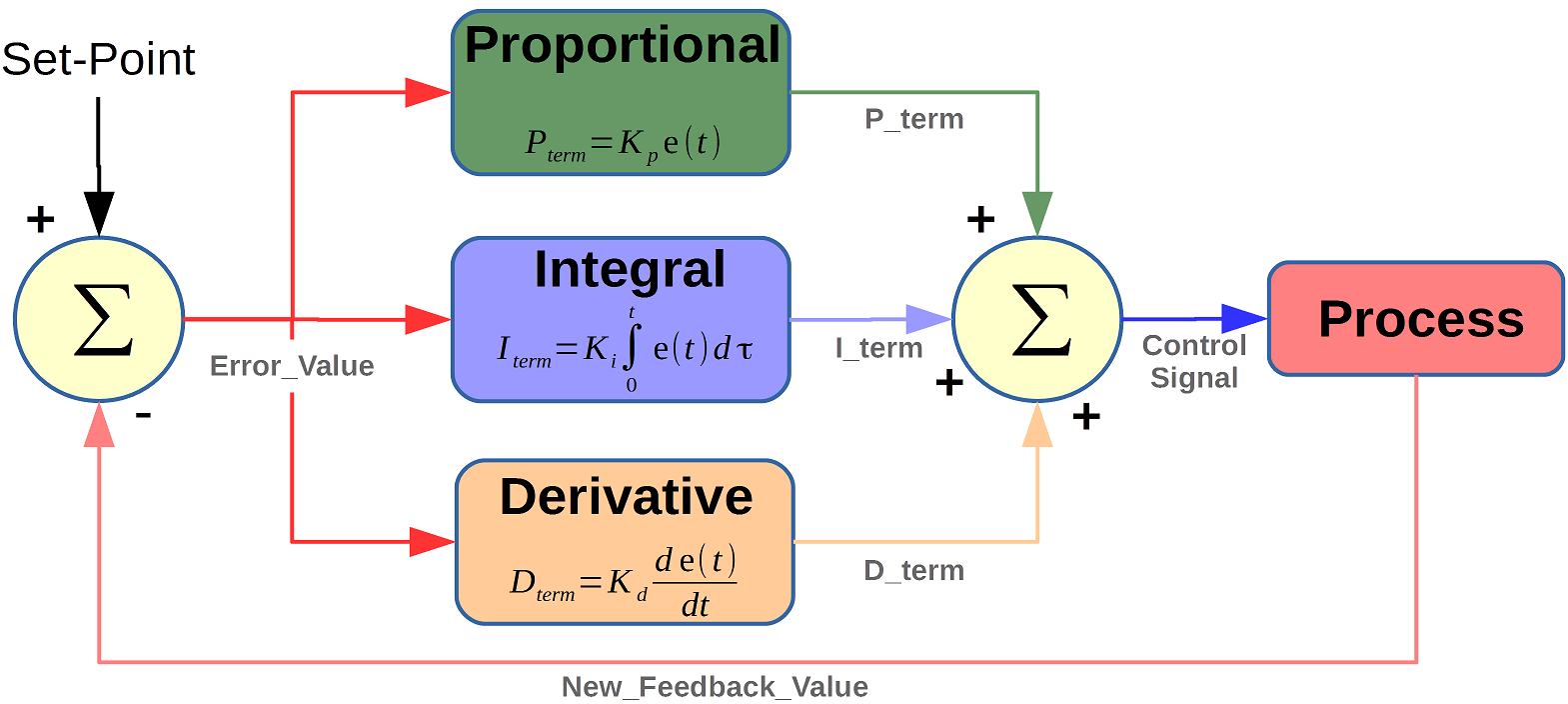
Pid Controller What Is Pid Controller How It Works Pid controllers: an overview (continue) nitnyquist it tti fznfrminterpretation of znfrm using pid control, it is possible to move a given point on the nyquist curve to an arbitrary position in the complex plane. • the point where the nyquist curve of the plant intersects the negative real axis μ ¡ 1 k u;0 ¶ 2 t 25o c(j! u)=0:6k u ¡j μ 1. Pid control theory 217 fig. 4. a) step response of pid ideal formb) step response of pid real form 2.1 the transfer function of the pid controller the transfer function of the pid controller is () us gs es (7) () i p d k gs k k s s = 2 ks ks kd p i s (8) 2.2 pid pole zero cancellation the pid equation can be written in this form: ()2 p i d.

Pid Control Introduction Pdf

Comments are closed.