Nutrients Free Full Text Evolution Of The Human Diet And Its Impact
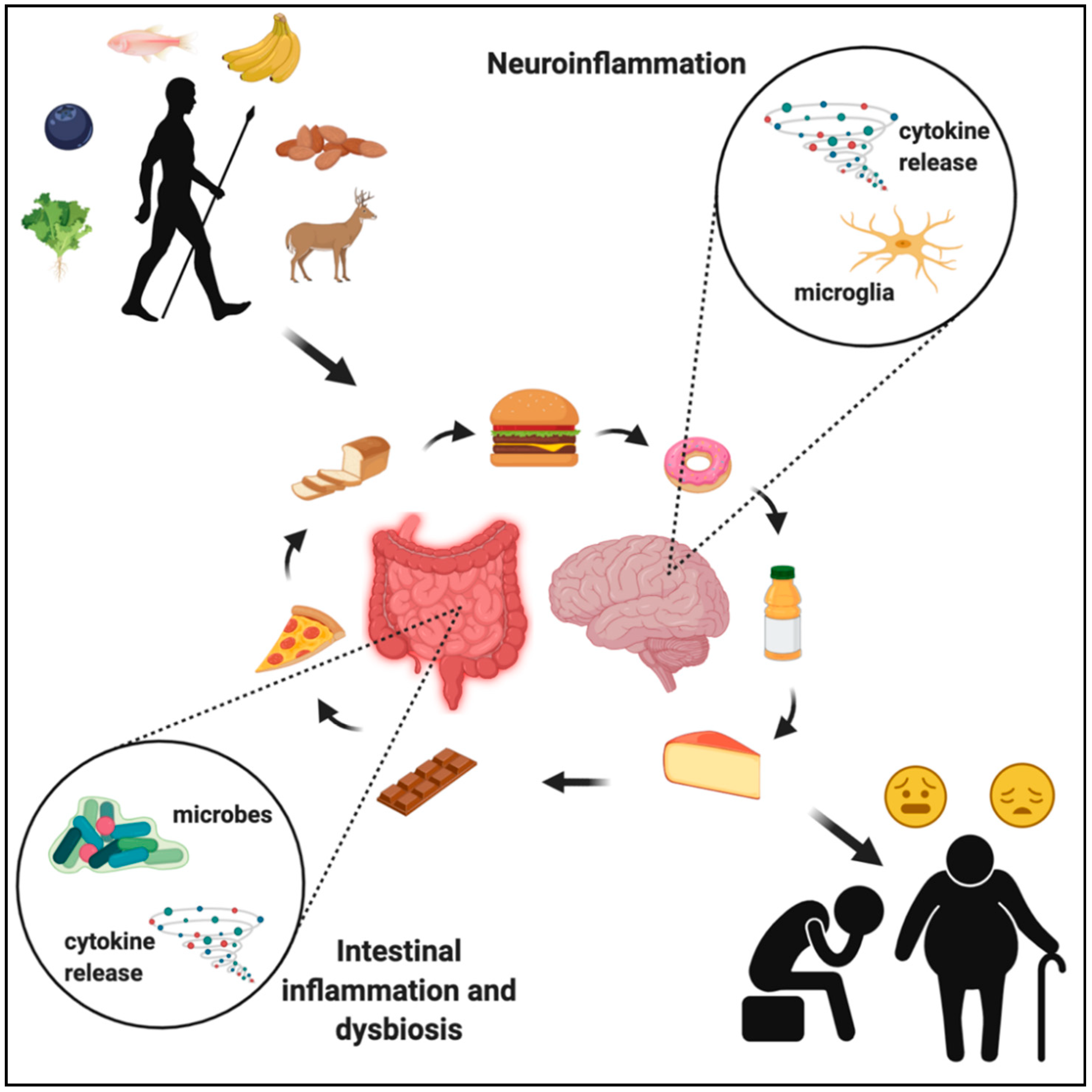
Nutrients Free Full Text Evolution Of The Human Diet And Its Impact The relatively rapid shift from consuming preagricultural wild foods for thousands of years, to consuming postindustrial semi processed and ultra processed foods endemic of the western world less than 200 years ago did not allow for evolutionary adaptation of the commensal microbial species that inhabit the human gastrointestinal (gi) tract, and this has significantly impacted gut health. the. Search text. search type 2021. "evolution of the human diet and its impact on gut microbiota, immune responses, and brain health" nutrients 13, no. 1: 196. https.

Changes In The Nutrient Content Of Evolutionary Diet And Emergence Of There is growing recognition of the role of diet and other environmental factors in modulating the composition and metabolic activity of the human gut microbiota, which in turn can impact health. this narrative review explores the relevant contemporary scientific literature to provide a general perspective of this broad area. molecular technologies have greatly advanced our understanding of. In fact, seafood consumption was a staple of the early modern human diet and constituted up to 50% of the energy consumption [7,8]. this inclusion of n 3 fas, particularly docosahexaenoic acid (dha), in the hominid diet likely contributed to the evolution of modern human immune and nervous systems . as such, the recent depletion of n 3 fas due. The human gut microbiota, the diverse and dynamic population of microbes, has been demonstrated to have extensive and important interactions with the digestive, immune, and nervous systems. western diet induced dysbiosis of the gut microbiota has been shown to negatively impact human digestive physiology, to have pathogenic effects on the. We use only a fraction of the plants consumed by our ancestors and have almost reversed the original ratio between plant based food (75%) and meat fish (25%). the result is overnutrition, malnutrition and undernourishment [166], which is why nutrition is one of the most important risk factors in terms of health.
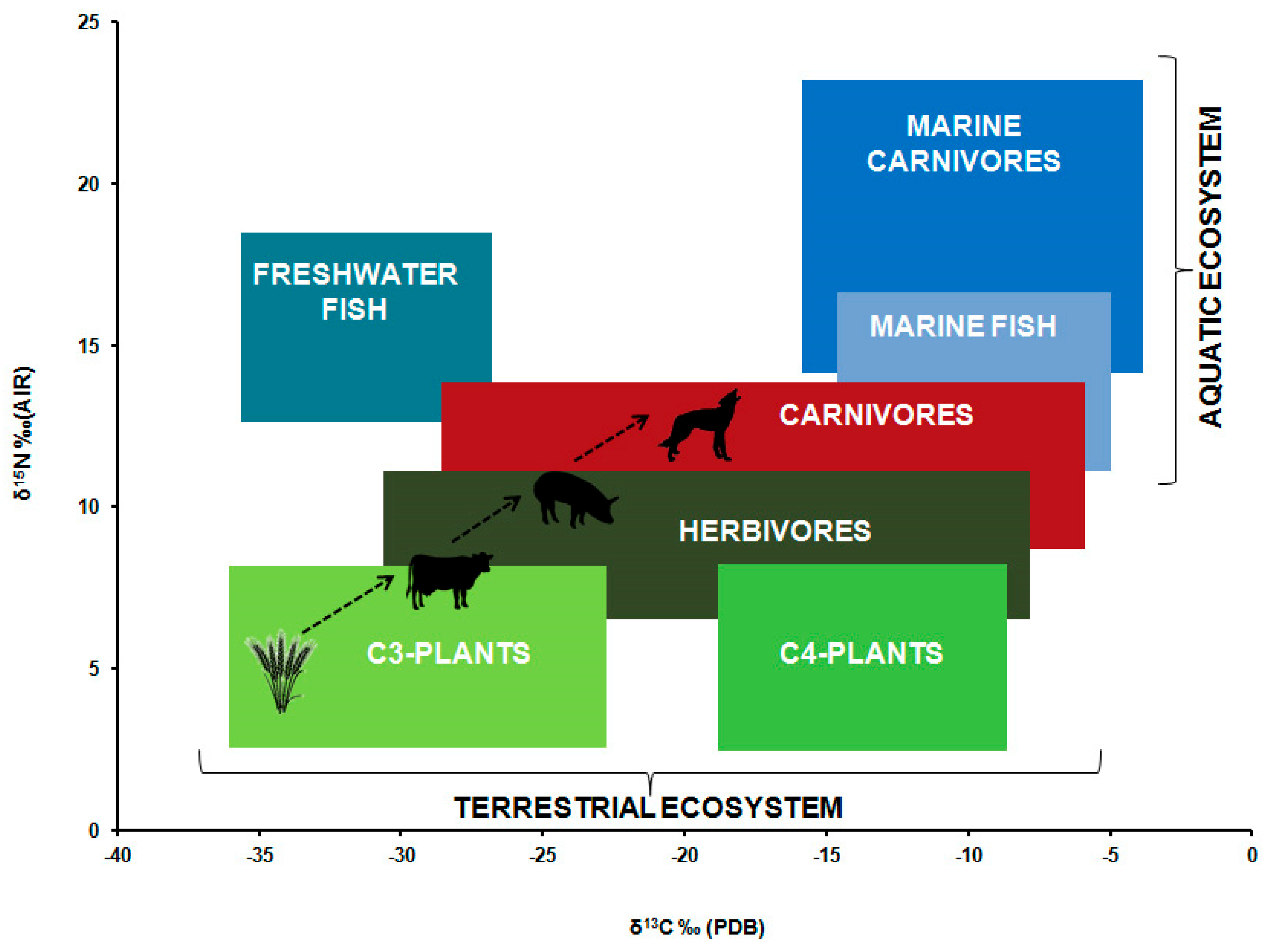
Nutrients Free Full Text Nutrition And Health In Human Evolut The human gut microbiota, the diverse and dynamic population of microbes, has been demonstrated to have extensive and important interactions with the digestive, immune, and nervous systems. western diet induced dysbiosis of the gut microbiota has been shown to negatively impact human digestive physiology, to have pathogenic effects on the. We use only a fraction of the plants consumed by our ancestors and have almost reversed the original ratio between plant based food (75%) and meat fish (25%). the result is overnutrition, malnutrition and undernourishment [166], which is why nutrition is one of the most important risk factors in terms of health. The impact that the evolution of the human diet has had on the connection from the gut to the brain, with a focus on the role of gut microbes and immune signaling as potential mechanisms. Saladino, a medical doctor, is a popular proponent of an animal based diet that exalts meat and organs and demonizes vegetables. through videos like this one on tiktok, as well as the podcast he.

Comments are closed.