Medical Encyclopedia Structure Components Of The Ear Aviva

Medical Encyclopedia Structure Components Of The Ear Aviva The ear is the organ of hearing and balance. the parts of the ear include: pinna or auricle. this is the outside part of the ear. external auditory canal or tube. this is the tube that connects the outer ear to the inside or middle ear. tympanic membrane (eardrum). the tympanic membrane divides the external ear from the middle ear. The ear is a complex part of an even more complex sensory system. it is situated bilaterally on the human skull, at the same level as the nose. the main functions of the ear are, of course, hearing, as well as constantly maintaining balance. the ear is anatomically divided into three portions: external ear. middle ear.

Human Ear Structure Function Parts Britannica Organs of human hearing are located on either side of the head. essential for hearing and balance, each ear has an intricate structure of bones, nerves, and muscles. the ears can be affected by bacterial infections, viral infections, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), meniere’s disease, and more. The human ear, like that of other mammals, contains sense organs that serve two quite different functions: that of hearing and that of postural equilibrium and coordination of head and eye movements. anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable parts: the outer, middle, and inner ear. the outer ear consists of the visible portion called the. The external ear is the visible part of the hearing apparatus. it is comprised of the auricle (pinna) and external auditory canal, including the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. together with the tympanic membrane and the middle ear, the pinna serves to amplify sound. the pinna acts as a funnel to deliver sound to the external acoustic meatus, and the external auditory canal. Introduction. the ear can be divided into three parts: the external, middle and inner ear. the ears are an organ of hearing and balance, converting information from our external environment into electrical signals that can be processed by the brain. this article will explore the three anatomical sections of the ear, highlighting their.
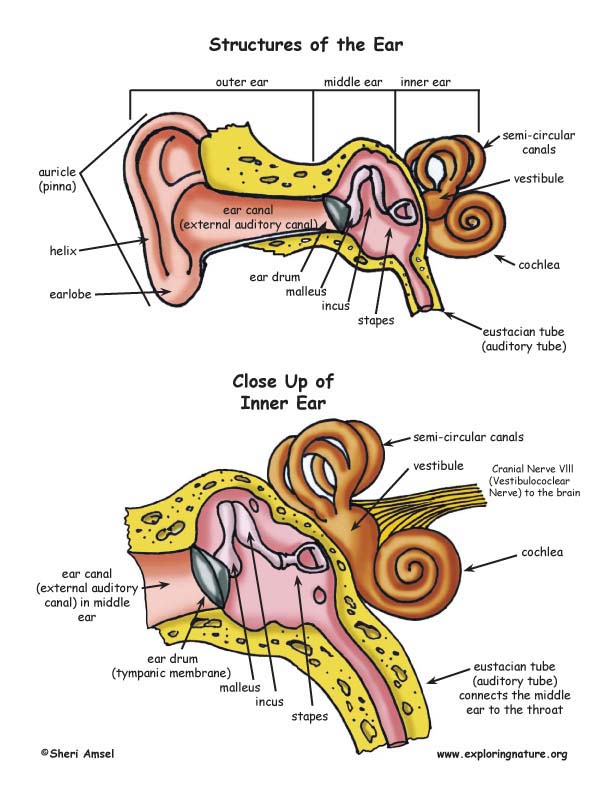
Structures Of The Ear The external ear is the visible part of the hearing apparatus. it is comprised of the auricle (pinna) and external auditory canal, including the lateral surface of the tympanic membrane. together with the tympanic membrane and the middle ear, the pinna serves to amplify sound. the pinna acts as a funnel to deliver sound to the external acoustic meatus, and the external auditory canal. Introduction. the ear can be divided into three parts: the external, middle and inner ear. the ears are an organ of hearing and balance, converting information from our external environment into electrical signals that can be processed by the brain. this article will explore the three anatomical sections of the ear, highlighting their. Inner ear: the inner ear, also called the labyrinth, operates the body’s sense of balance and contains the hearing organ. a bony casing houses a complex system of membranous cells. the inner ear. The auricle is a paired structure found on either side of the head. it functions to capture and direct sound waves towards the external acoustic meatus. it is a mostly cartilaginous structure, with the lobule being the only part not supported by cartilage. the cartilaginous part of the auricle forms an outer curvature, known as the helix.

Comments are closed.