Lumbar Spine Muscles Anatomy
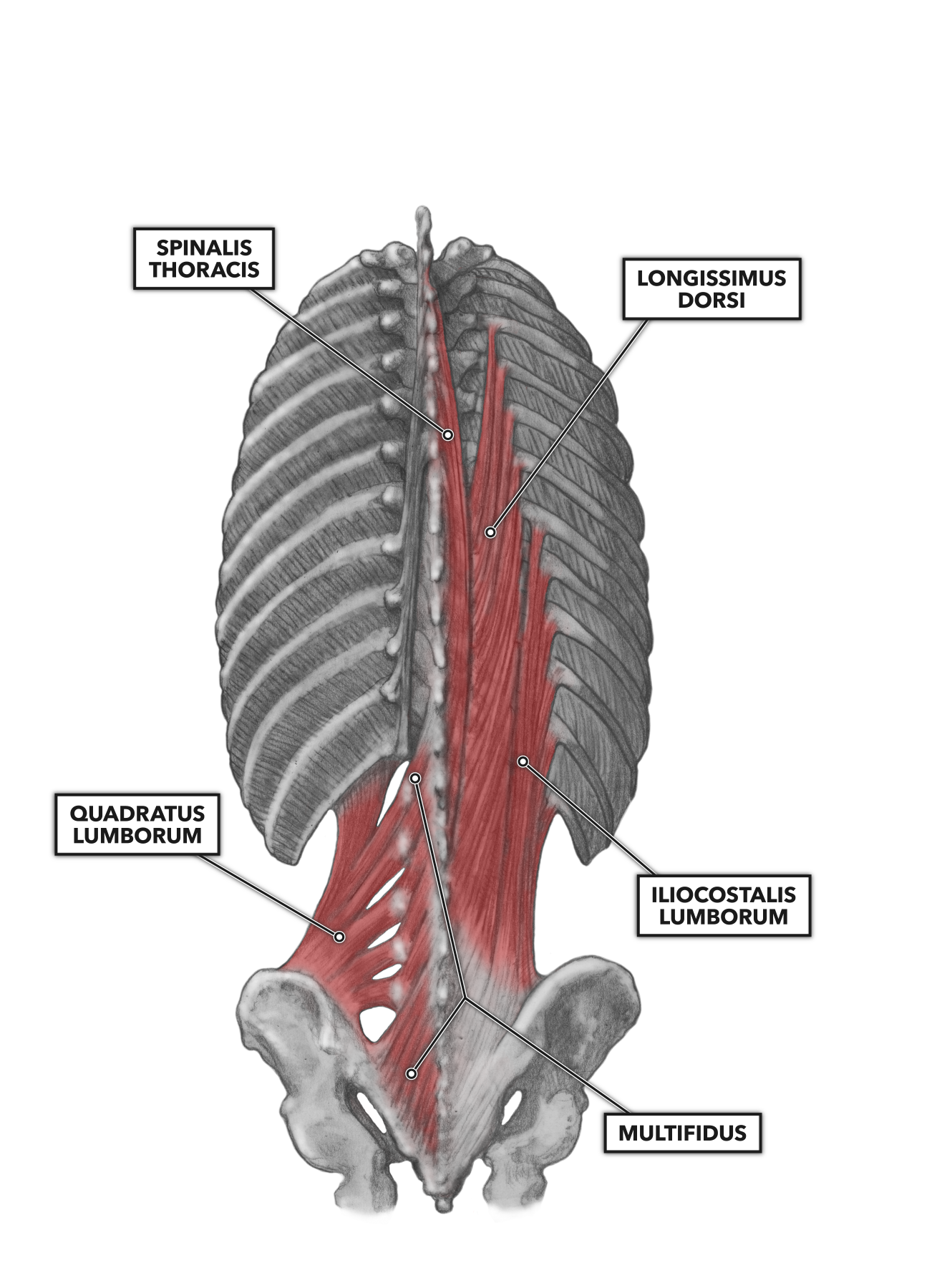
Lumbar Spine Muscles Anatomy Learn the anatomy and function of the muscles of the lumbar spine and trunk, including their attachments, actions, and functional groups. see illustrations and explanations of the posterior, anterior, and lateral muscles of the low back and pelvis. The lower back (where most back pain occurs) includes the five vertebrae in the lumbar region and supports much of the weight of the upper body. the spaces between the vertebrae are maintained by intervertebral discs that act like shock absorbers throughout the spinal column to cushion the bones as the body moves. ligaments hold the vertebrae in place, and tendons attach the muscles to the.

Quadratus Lumborum Ql Anatomy Of The Muscle For Yoga Back anatomy. the back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; extrinsic and intrinsic. the back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbs. Your lumbar spine is the lower back region of your spinal column or backbone. it consists of five bones (l1 l5). other structures in or around your lumbar spine are your intervertebral disks, spinal cord and nerves, muscles, tendons and ligaments. your lumbar spine supports the weight of your body and allows a wide range of body movements. The muscles of the lower back help stabilize, rotate, flex, and extend the spinal column, which is a bony tower of 24 vertebrae that gives the body structure and houses the spinal cord. The lumbar spine is comprised of bone, cartilage, ligaments, nerves, and muscle. each of these components plays an integral role in the form and function of the lumbar spine.[1][2] the lumbar spine comprises the lower end of the spinal column between the last thoracic vertebra (t12) and the first sacral vertebra (s1).

Lumbar Muscle Strain вђ Physiou The muscles of the lower back help stabilize, rotate, flex, and extend the spinal column, which is a bony tower of 24 vertebrae that gives the body structure and houses the spinal cord. The lumbar spine is comprised of bone, cartilage, ligaments, nerves, and muscle. each of these components plays an integral role in the form and function of the lumbar spine.[1][2] the lumbar spine comprises the lower end of the spinal column between the last thoracic vertebra (t12) and the first sacral vertebra (s1). The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.

Lumbar Spine Muscles Anatomy The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.

Comments are closed.