Low Back Muscle Chart Lower Back Muscle Anatomy Chart Vrog
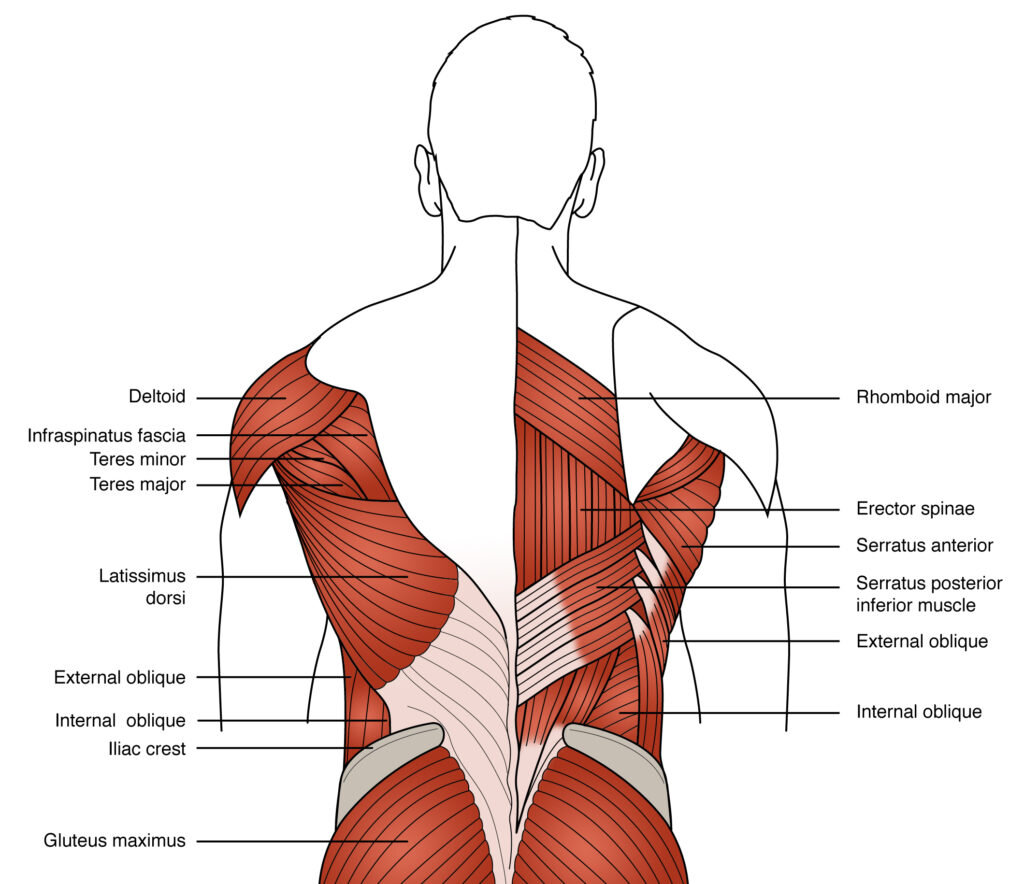
Easy Low Back Anatomy вђ For The Wellness Right lateral views of the musculature of the low back (lumbar spine) and pelvis region. (a) superficial view. deeper view. courtesy joseph e. muscolino. manual therapy for the low back and pelvis – a clinical orthopedic approach (2015). figure 18. anterior views of the musculature of the low back (lumbar spine) and pelvis region. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.

Low Back Muscle Chart Lower Back Muscle Anatomy C Back anatomy. the back is the body region between the neck and the gluteal regions. it comprises the vertebral column (spine) and two compartments of back muscles; extrinsic and intrinsic. the back functions are many, such as to house and protect the spinal cord, hold the body and head upright, and adjust the movements of the upper and lower limbs. Back muscles. your back muscles extend from the bones of your neck (cervical vertebrae) to your lower back (lumbar spine) and then to the base of your lumbar spine (sacrum) and tailbone (coccyx). some of these muscles are quite large and cover broad areas, e.g. large areas of the trunk. other muscles are small and cover much less space. The deep muscles of the back fit into or affix parts of themselves to the grooves in the spinous processes, or the protrusion of the bone than can be felt through the skin. important muscles of. The muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. they provide movements of the spine, stability to the trunk, as well as the coordination between the movements of the limbs and trunk. the extrinsic (superficial) back muscles, which lie most superficially on the back.

Lower Back Muscle Anatomy And Low Back Pain The deep muscles of the back fit into or affix parts of themselves to the grooves in the spinous processes, or the protrusion of the bone than can be felt through the skin. important muscles of. The muscles of the back are a group of strong, paired muscles that lie on the posterior aspect of the trunk. they provide movements of the spine, stability to the trunk, as well as the coordination between the movements of the limbs and trunk. the extrinsic (superficial) back muscles, which lie most superficially on the back. Bones, discs, and joints in your lower back. your lower back contains 5 vertebral bones stacked above each other with intervertebral discs in between. these bones are connected at the back with specialized joints. the lumbar spine connects to the thoracic spine above and the hips below. individual anatomical structures include 2 cramer gd. The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles.
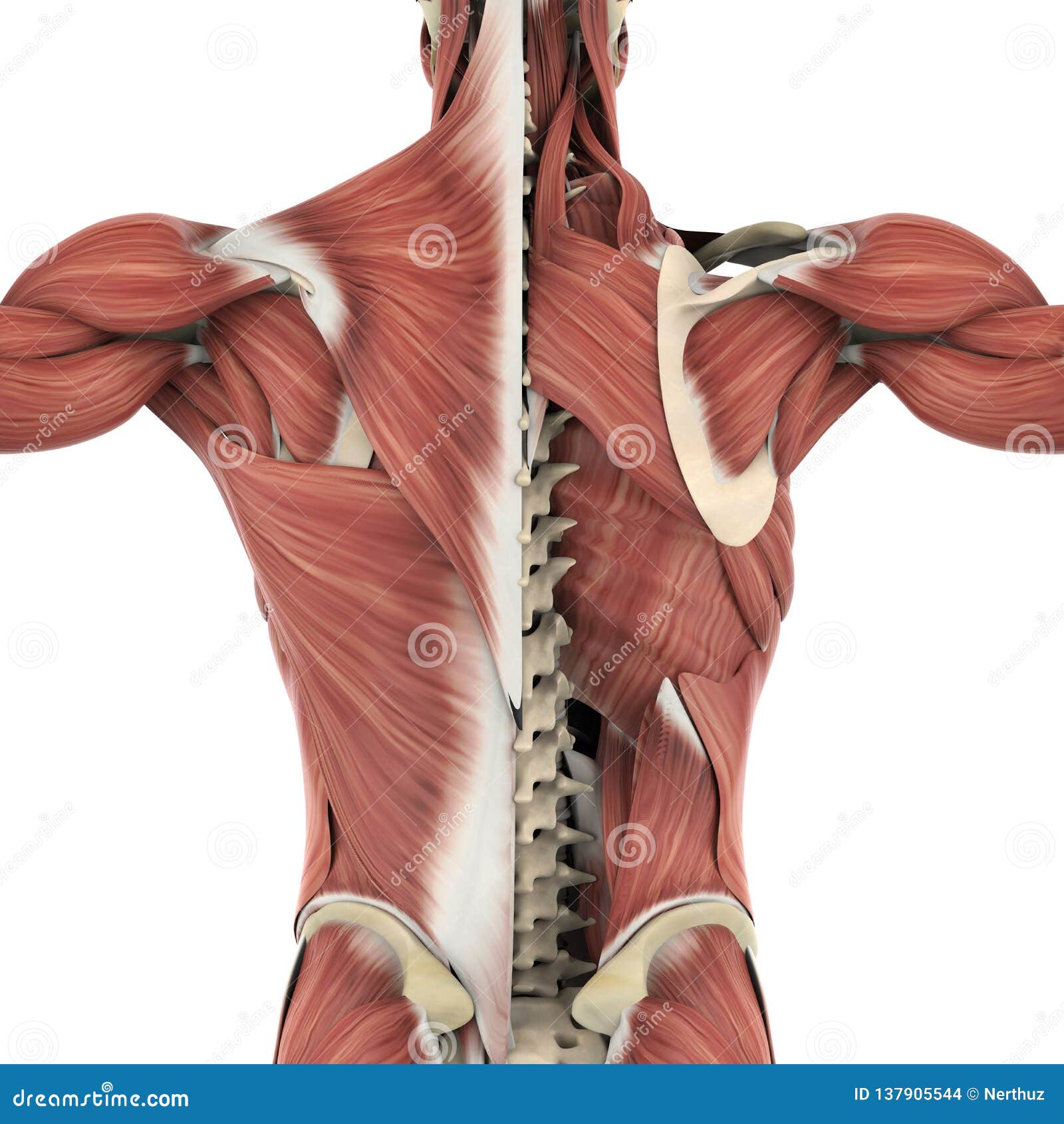
Muscle Chart Back Understanding Low Back Pain Anatomical Char Bones, discs, and joints in your lower back. your lower back contains 5 vertebral bones stacked above each other with intervertebral discs in between. these bones are connected at the back with specialized joints. the lumbar spine connects to the thoracic spine above and the hips below. individual anatomical structures include 2 cramer gd. The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles.

Comments are closed.