Life Cycle Of A Plant Flower Parts Pollination Photos Vrogue Co

Pollination Learning Station Life Cycle Of Plants Kae Vrogue Co Filament: supports the anther. pistil: the female part of the plant, sometimes called the ‘carpel’. stigma: collects pollen grains. style: allows pollen to pass to the ovary. ovary: produces seeds inside tiny ‘ovules’. sepal: found outside the petals, the sepal protects the flower when it’s unopened. The ovule forms a seed. the ovary forms a fruit containing one or more seeds. the seed is dispersed from the parent plant within the fruit. under the right conditions, the seed will germinate. upon reaching maturity, the plant will produce pollen and ovules of its own, thereby completing the life cycle of the flower.
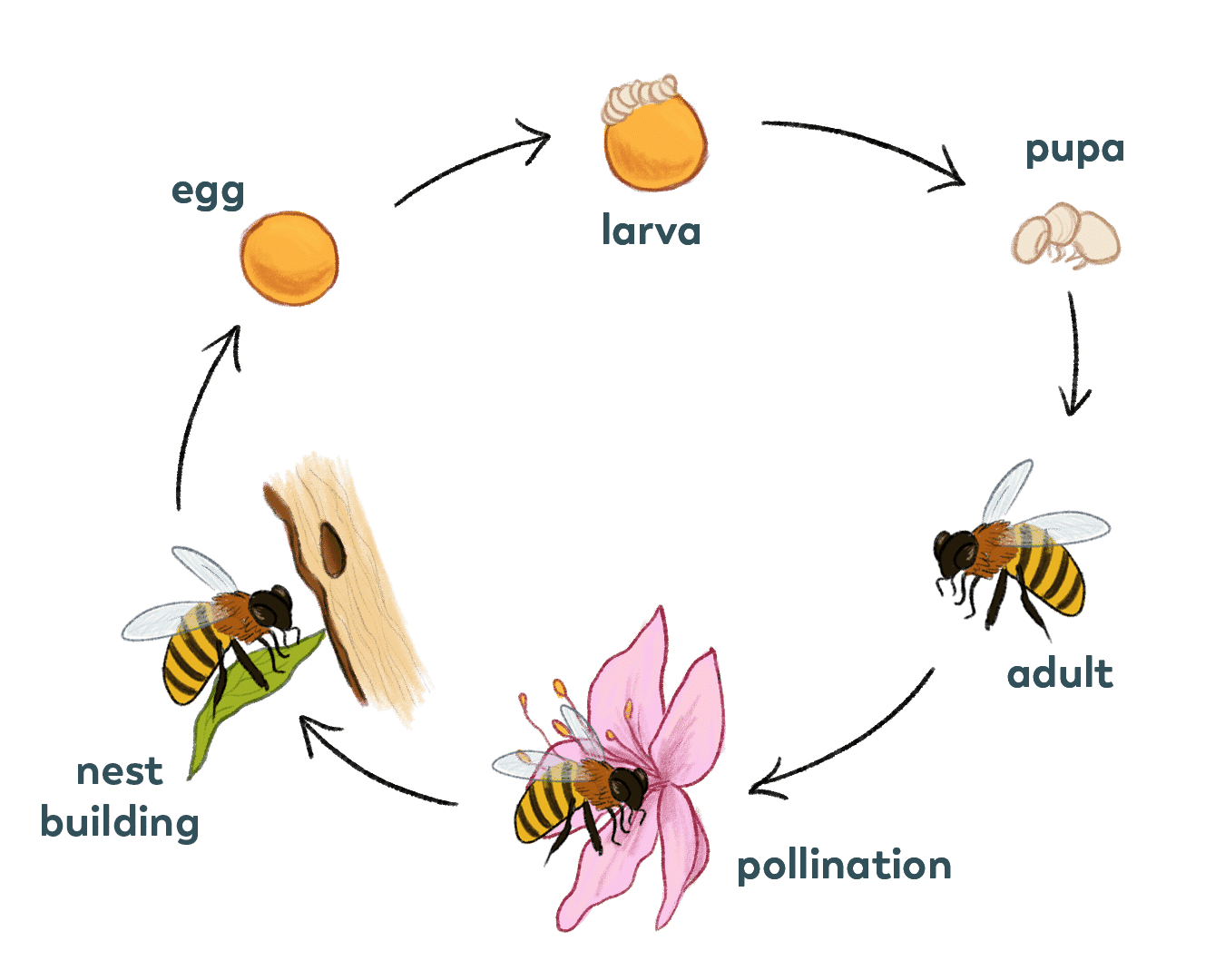
Diagram Showing Pollination Cycle Royalty Free Vector Vrogue Co Step 4: fruit growth. after receiving pollen, a fruit or seed pod begins to grow from the ovary of the flower. many of the flower parts wilt and fall off as the fruit seed pod grows. a fruit starts to form from the flower’s ovary. fun with fruit: a science in the garden botany unit. A basic plant life cycle goes through five stages: 1) seed, 2) seed germination, 3) seedling, 4) adult plant, and 5) pollination and fertilization. they are discussed below in detail. 1) seed. the life cycle of a flowering plant begins with a seed. it has a protective outer covering called the shell. Sub units covered in this lesson plan guide are: parts of a flower: the reproductive powerhouse of the plant kingdom. pollination and fertilization: the fascinating dance of genetic transfer. seed anatomy & germination: from dormant life to sprouting green. parts of a plant & photosynthesis: the structures and processes that sustain plant life. The life cycle of angiosperms begins when a seed is germinated. the germinated seed undergoes vegetative growth, followed by reproductive growth, then pollination, fertilization of the egg, and.
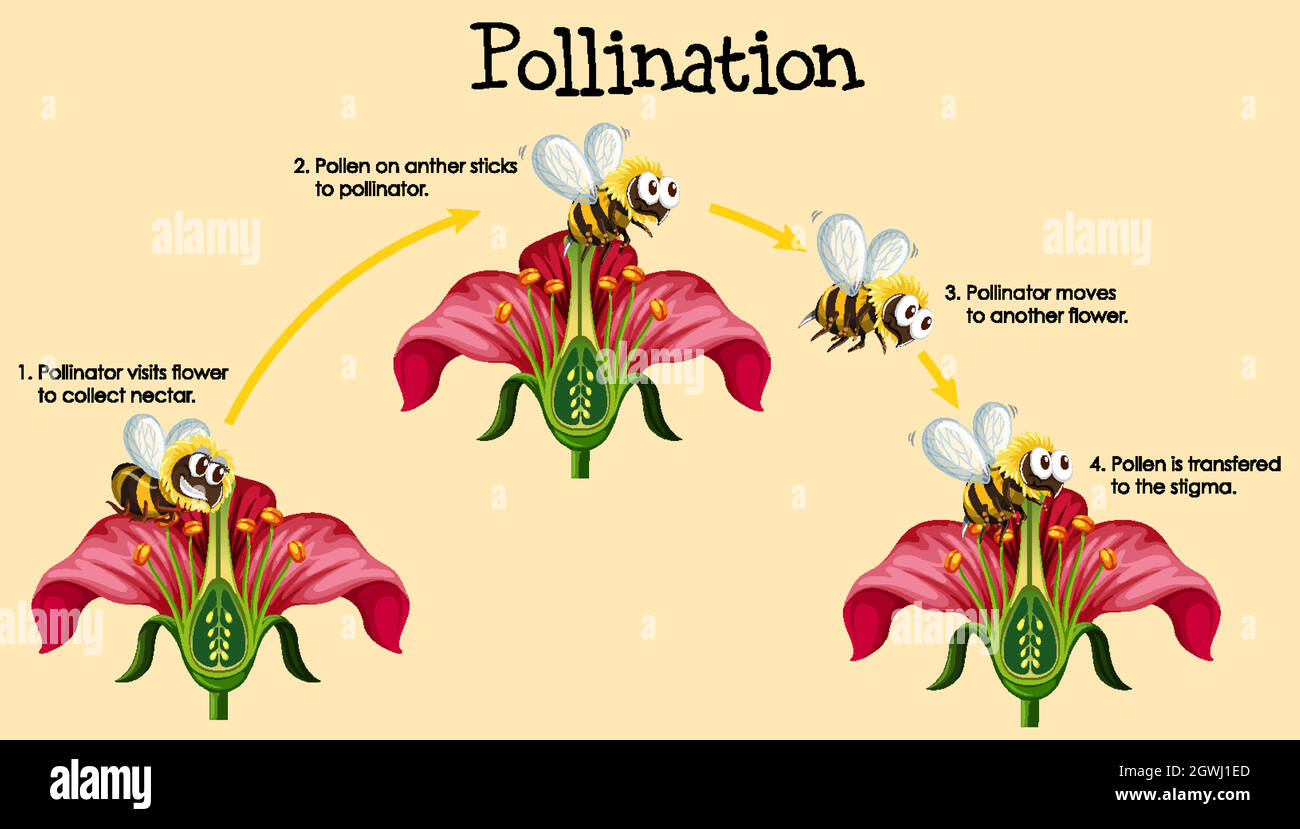
Diagram Showing Pollination Cycle Royalty Free Vector Vrogue Co Sub units covered in this lesson plan guide are: parts of a flower: the reproductive powerhouse of the plant kingdom. pollination and fertilization: the fascinating dance of genetic transfer. seed anatomy & germination: from dormant life to sprouting green. parts of a plant & photosynthesis: the structures and processes that sustain plant life. The life cycle of angiosperms begins when a seed is germinated. the germinated seed undergoes vegetative growth, followed by reproductive growth, then pollination, fertilization of the egg, and. The mature plant – the flowering plant life cycle described here begins with a fully grown wild cherry tree prunus avium. two to four white flowers emerge from each bud in april. mature trees are covered in white flowers for several weeks and are very attractive to bees seeking pollen and nectar. Length of life cycle. flowering plants all go through the same stages of a life cycle, but the length of time they take varies a lot between species. some plants go though their complete cycle in a few weeks – others take many years. annuals are plants that grow from a seed, then flower and make new seeds, then die, all in less than a year.

Comments are closed.