Laws Of Logarithm And Related Simple Examples

Rules Of Logarithms With Examples The laws of logarithms are algebraic rules that allow for the simplification and rearrangement of logarithmic expressions. the 3 main logarithm laws are: the product law: log (mn) = log (m) log (n). the quotient law: log (m n) = log (m) – log (n). the power law: log (m k) = k·log (m). The logarithm of the argument (inside the parenthesis) wherein the argument equals the base is equal to. the logarithm of an exponential number where its base is the same as the base of the log is equal to the exponent. raising the logarithm of a number to its base is equal to the number. then, apply power rule followed by identity rule.

Laws Of Logarithm And Related Simple Examples The quotient rule law. subtraction of two logarithms a and b is equal to dividing the logarithms. log a − log b = log (a b) example: log 10 6 – log 10 3 = log 10 (6 3) = log 10 2. log 2 4x – log 2 x = log 2 (4x x) = log 2 4. the power rule law. log a n = n log a. In this case, 10 2 yields you 100. so, 2 is the exponent value, and the value of log 10 (100)= 2. example 3: use of the property of logarithms, solve for the value of x for log 3 x= log 3 4 log 3 7. solution: by the addition rule, log 3 4 log 3 7= log 3 (4 * 7 ) log 3 ( 28 ). thus, x= 28. example 4:. 1. solved examples for product rule of logarithm. rule: log a xy = log a x log a y. question: solve this: log2 4*16 using log law. the same question can also be written as log2 4 log2 16. answer: log 2 4*16. => log2 4 log2 16. => log2 2 2 log2 2 4. Using laws of logarithms (laws of logs) to solve log problems. the general log rule to convert log functions to exponential functions and vice versa. we know already the general rule that allows us to move back and forth between the logarithm and exponents. and we can continue to use this rule whenever it makes sense in any of these log problems.
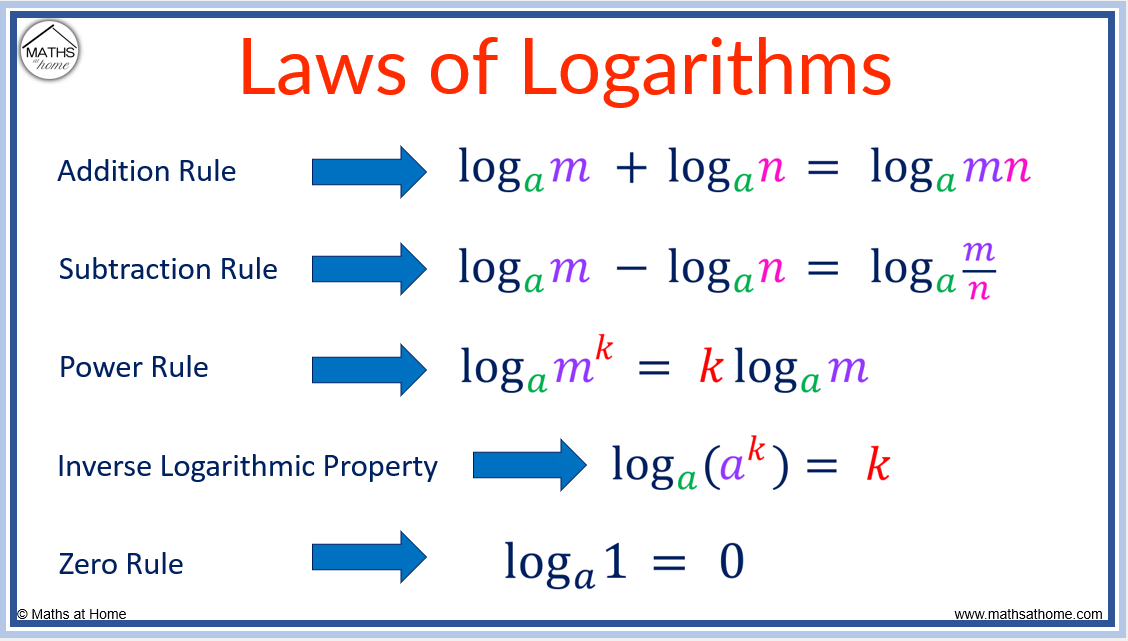
Logarithm Laws Made Easy A Complete Guide With Examples вђ Mathsathome 1. solved examples for product rule of logarithm. rule: log a xy = log a x log a y. question: solve this: log2 4*16 using log law. the same question can also be written as log2 4 log2 16. answer: log 2 4*16. => log2 4 log2 16. => log2 2 2 log2 2 4. Using laws of logarithms (laws of logs) to solve log problems. the general log rule to convert log functions to exponential functions and vice versa. we know already the general rule that allows us to move back and forth between the logarithm and exponents. and we can continue to use this rule whenever it makes sense in any of these log problems. The logarithm of a product is the sum of the logarithms of the factors. log a xy = log a x log a y. 2) quotient rule. the logarithm of a quotient is the logarithm of the numerator minus the logarithm of the denominator. log a = log a x – log a y. 3) power rule. log a x n = nlog a x. 4) change of base rule. where x and y are positive, and a. Sometimes a logarithm is written without a base, like this: log (100) this usually means that the base is really 10. it is called a "common logarithm". engineers love to use it. on a calculator it is the "log" button. it is how many times we need to use 10 in a multiplication, to get our desired number. example: log (1000) = log10(1000) = 3.

Comments are closed.