Inflation In India Causes And Consequences

Inflation In India Causes And Consequences Last week, official data showed that in january, india’s retail inflation surged by 6.5%. in other words, the general price level facing the consumers in january 2023 turned out to be 6.5% higher than the price level in january 2022; this is called a year on year (or y o y) growth rate. Inflation is defined as a rise in the cost of most everyday items and services, such as food, clothing, housing, recreation, transportation, consumer staples, and so on. the average change in the price of a basket of goods and services over time is referred to as inflation. deflation is the opposite of inflation, and it refers to a decrease in.

Causes Of Inflation In India Value Economics Inflation Causes for spike in inflation. higher food inflation: consumer food prices increased to 5.94% from 4.2% in december 2022. spices jumped from 20.3% inflation to 21.1% in january. inflation in eggs sped from 6.9% in december to 8.8% in january, while the pace of price rise in meat and fish rose from 5.1% to 6.04%. Inflation in india: causes, effects and curve! meaning of inflation: by inflation we mean a general rise in prices. to be more correct, inflation is a persistent rise in the general price level rather than a once for all rise in it. on the other hand, deflation represents persistently falling prices. inflation or persistently rising prices is a major problem in india today. when price level. As the years have rolled by, overall inflation has been driven by more and more factors. in 2019 20, when overall inflation was 4.8%, the main reason was a 6% spike in food prices. and in 2020 21, when the pandemic hit the economy, food prices rose by an even larger factor (7.3%) and even core inflation rose by 5.5%. Worries grew as the inflation rate (measured as the twelve month change in the consumer price index) rose from 3.7% to 12.1% over 2001 2010. the inflation rate has since fallen to 5.2% in early 2015, leading to a debate about whether this moderation is likely to endure or inflation will rise again.
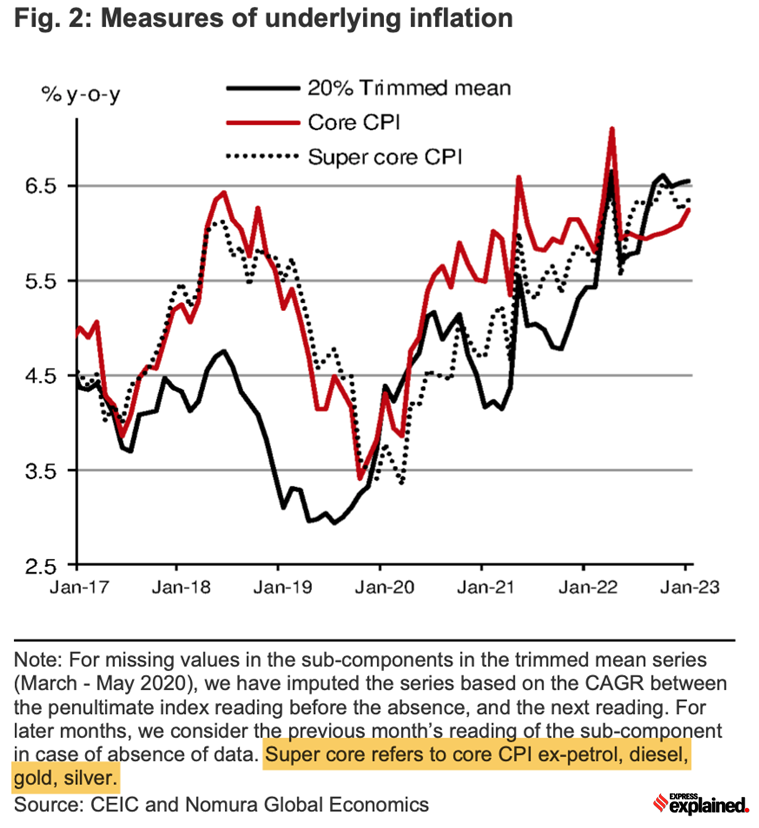
Explainspeaking юааindiaюабтащs Sticky юааinflationюаб юааcausesюаб юааand Consequencesюаб As the years have rolled by, overall inflation has been driven by more and more factors. in 2019 20, when overall inflation was 4.8%, the main reason was a 6% spike in food prices. and in 2020 21, when the pandemic hit the economy, food prices rose by an even larger factor (7.3%) and even core inflation rose by 5.5%. Worries grew as the inflation rate (measured as the twelve month change in the consumer price index) rose from 3.7% to 12.1% over 2001 2010. the inflation rate has since fallen to 5.2% in early 2015, leading to a debate about whether this moderation is likely to endure or inflation will rise again. The sharp rise in commodity prices across the world is a major reason behind the inflation spike in india. this is increasing the import cost for some of the crucial consumables, pushing inflation higher. brent crude prices crossed $65 per barrel in may 2021, more than double of what it was a year ago. price of vegetable oils, a major import item, shot up 57% to reach a decadal high in april. Food inflation for july 2024 is the lowest since june 2023. the y o y inflation rate based on the all india consumer food price index (cfpi) is 5.42 percent (provisional) for july. the.

Comments are closed.