Importance Of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Let S
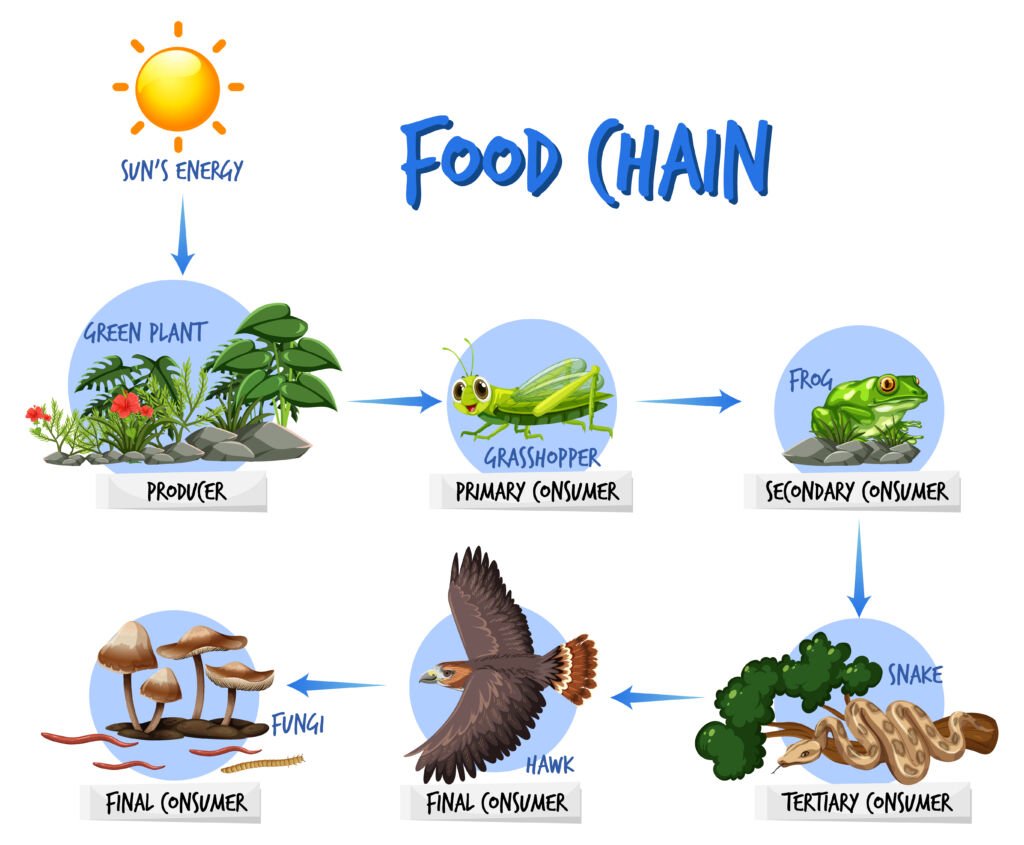
Importance Of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Let S A food chain demonstrates how every living organism relies on other organisms for survival. the food chain is a diagram that depicts the flow of energy inside an ecosystem. the food web is made up of various types of life forms. the web’s producers are green plants that can produce their food through photosynthesis. The energy flow takes place via the food chain and food web. during the process of energy flow in the ecosystem, plants being the producers absorb sunlight with the help of the chloroplasts and a part of it is transformed into chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis. this energy is stored in various organic products in the plants and.
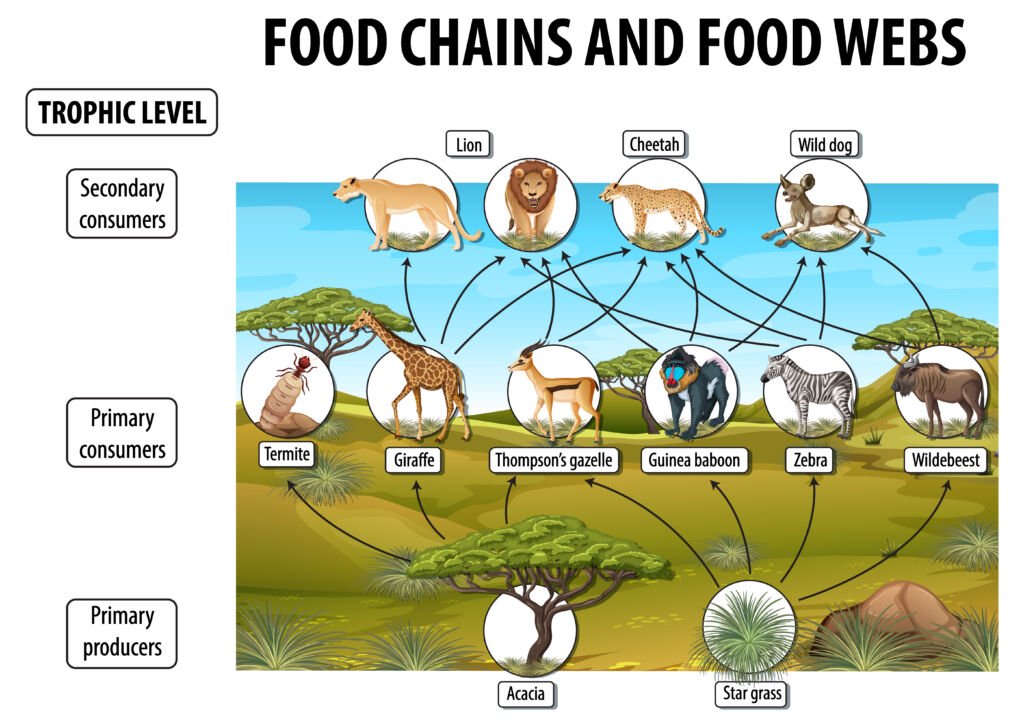
Importance Of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Let S Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. This process can lead to the complete destruction or irreversible altering of the ecosystem. food chains and food webs. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally. As illustrated in figure 26.2.2 26.2. 2, large amounts of energy are lost from the ecosystem from one trophic level to the next level as energy flows from the primary producers through the various trophic levels of consumers and decomposers. figure 26.2.2 26.2. 2: this conceptual model shows the flow of energy through a spring ecosystem in. Food webs describe the relationships — links or connections — among species in an ecosystem, but the relationships vary in their importance to energy flow and dynamics of species populations.
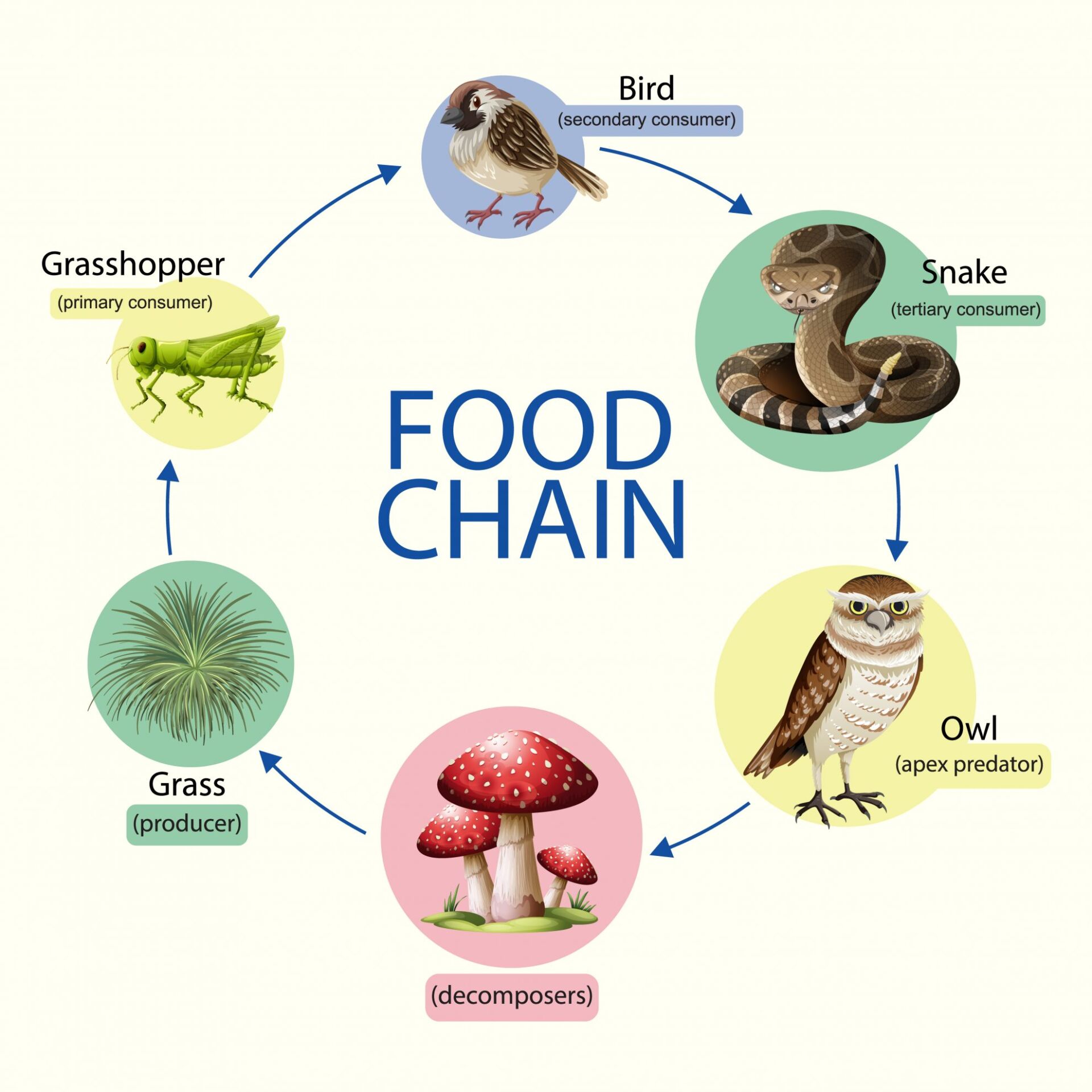
Importance Of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Let S As illustrated in figure 26.2.2 26.2. 2, large amounts of energy are lost from the ecosystem from one trophic level to the next level as energy flows from the primary producers through the various trophic levels of consumers and decomposers. figure 26.2.2 26.2. 2: this conceptual model shows the flow of energy through a spring ecosystem in. Food webs describe the relationships — links or connections — among species in an ecosystem, but the relationships vary in their importance to energy flow and dynamics of species populations. Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.
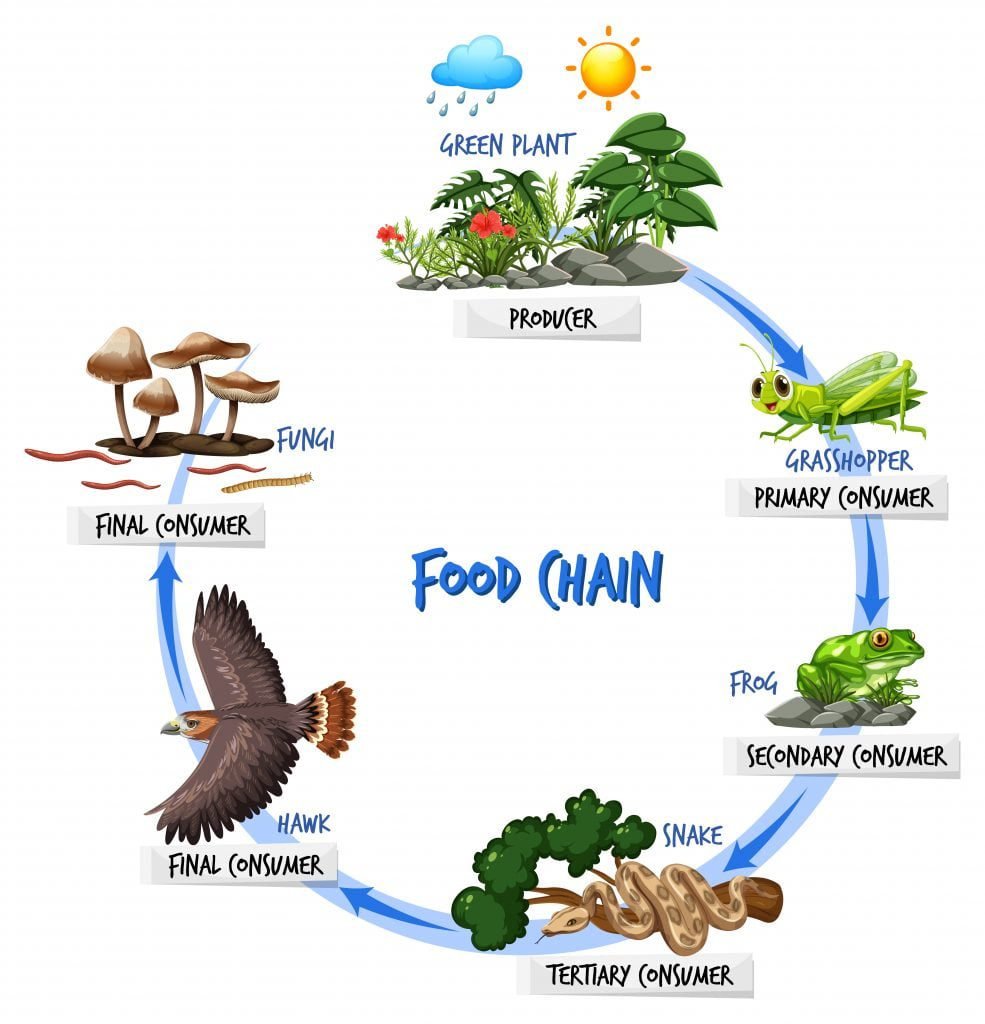
Importance Of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Let S Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Importance Of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Let S

Comments are closed.