How To Write Learning Objectives With Blooms Taxonomy

юааbloomтащsюаб юааtaxonomyюаб тау Um3d Instructional Impact Blog However, these advanced students should be able to master higher order learning objectives. too many lower level outcomes might cause boredom or apathy. how bloom’s works with learning outcomes. fortunately, there are “verb tables” to help identify which action verbs align with each level in bloom’s taxonomy. Bloom’s taxonomy: the gist bloom’s taxonomy classifies learning objectives based on a hierarchy of 6 cognitive levels. these levels capture what constitutes subject matter knowledge at different stages of familiarity. to meet goals at a higher level, a learner must first exhibit mastery of the earlier levels.
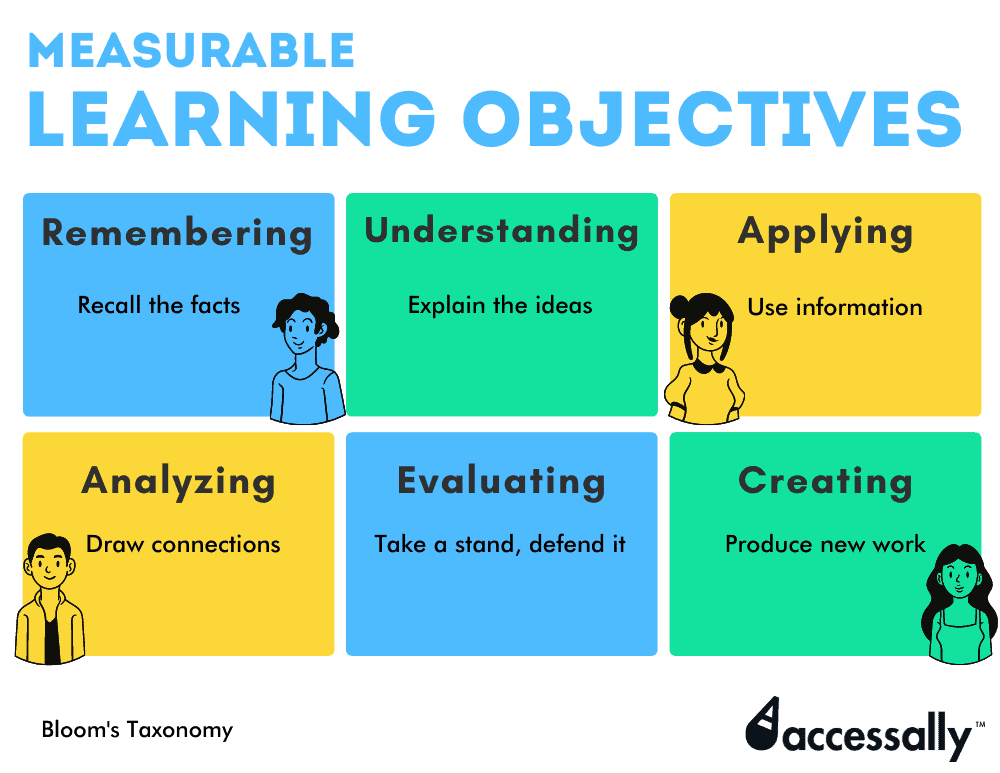
How To Write Learning Objectives Accessally Read our article: 8 tips to write effective learning objectives using bloom’s taxonomy. 4. analyze. at this stage, students are finally able to break down the concepts into individual parts, think critically to draw a connection between the broken parts, analyze, draw inferences and make attributions. examples of bloom’s taxonomy learning. An observable objective objective is measurable check & list. is objective. observable. the learning objective the learning an action. targets the objective is supported of performance. by the session. the learning level action objective objective is learner only when activity. centered. a complex appropriate. or. Here is a list of the classifications by the bloom’s taxonomy to measure proficiency and competence from a learner: domains of bloom’s taxonomy benjamin samuel bloom (1913 – 1999) was an american educational psychologist who made contributions to the classification of educational objectives and to the theory of mastery learning. The following are some of the most significant benefits bloom’s taxonomy offers when it comes to developing and revising learning objectives for both in person and elearning content: clear and measurable objectives: the taxonomy helps in defining clear and measurable learning objectives. it provides precise verbs for each cognitive level.
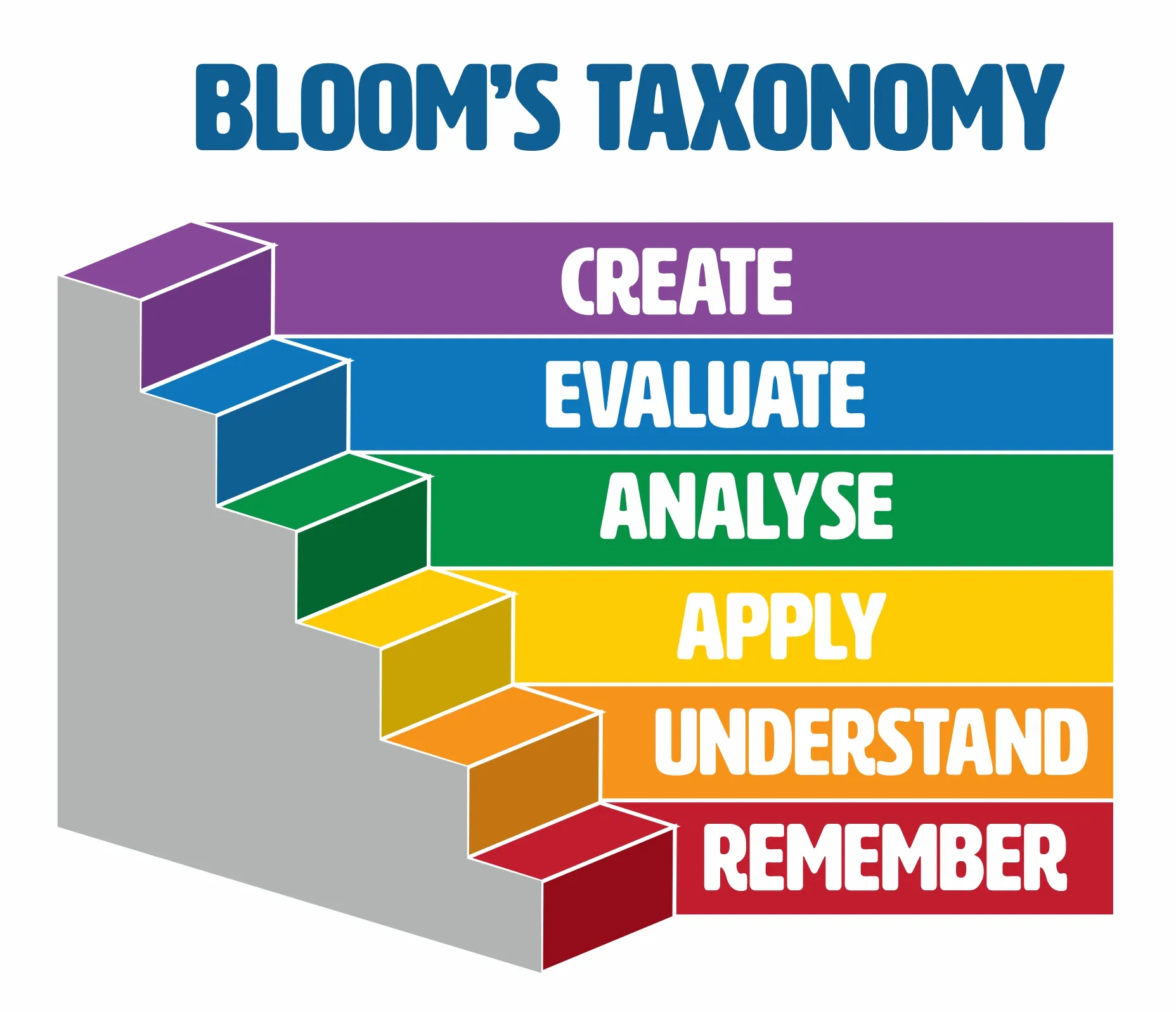
Using Bloom S Taxonomy For Setting Learning Objectives Here is a list of the classifications by the bloom’s taxonomy to measure proficiency and competence from a learner: domains of bloom’s taxonomy benjamin samuel bloom (1913 – 1999) was an american educational psychologist who made contributions to the classification of educational objectives and to the theory of mastery learning. The following are some of the most significant benefits bloom’s taxonomy offers when it comes to developing and revising learning objectives for both in person and elearning content: clear and measurable objectives: the taxonomy helps in defining clear and measurable learning objectives. it provides precise verbs for each cognitive level. Bloom’s taxonomy is a hierarchical model of cognitive skills in education, developed by benjamin bloom in 1956. it categorizes learning objectives into six levels, from simpler to more complex: remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. this framework aids educators in creating comprehensive learning goals and. Section iii of a taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: a revision of bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, entitled “the taxonomy in use,” provides over 150 pages of examples of applications of the taxonomy. although these examples are from the k 12 setting, they are easily adaptable to the university setting.
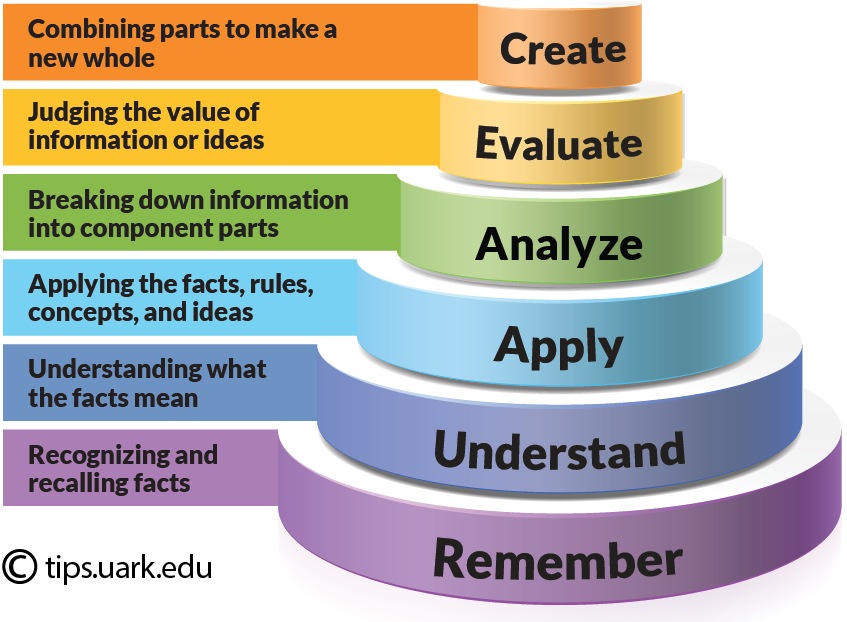
Using юааbloomтащsюаб юааtaxonomyюаб To юааwriteюаб Effective юааlearningюаб юааobjectivesюаб Bloom’s taxonomy is a hierarchical model of cognitive skills in education, developed by benjamin bloom in 1956. it categorizes learning objectives into six levels, from simpler to more complex: remembering, understanding, applying, analyzing, evaluating, and creating. this framework aids educators in creating comprehensive learning goals and. Section iii of a taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: a revision of bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, entitled “the taxonomy in use,” provides over 150 pages of examples of applications of the taxonomy. although these examples are from the k 12 setting, they are easily adaptable to the university setting.

Comments are closed.