Gcse Trigonometry Sine Cosine Tangent Angles And Triangles
Trigonometry Formula Gcse Maths Steps Examples Revise trigonometric ratios of sine, cosine and tangent and calculate angles in right angled triangles with this bitesize gcse maths edexcel guide. Learn and revise trigonometric ratios of sine, cosine and tangent and calculate angles and lengths in right angled triangles with gcse bitesize aqa maths.
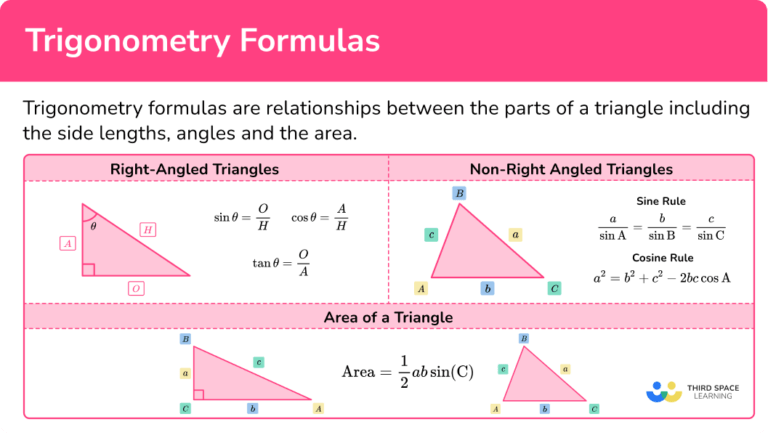
Gcse Trigonometry Sine Cosine Tangent Angles And Triangles Sin cos tan is a shortened description of the three trigonometric functions of sine, cosine, and tangent. these functions associate the ratio of two sides of a right angled triangle with an angle. to calculate using sin, cos and tan, we need to know their trigonometric ratios (remember that the ratio of two values is a division of these values. Sine, cosine and tangent. sine, cosine and tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: for a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is. to calculate them: divide the length of one side by another side. Example 1: find a side given the angle and the hypotenuse. abc is a right angle triangle. the size of angle acb = 60º and the length bc = 16cm. calculate the value of x. labelling the sides oah in relation to the angle 60º, we can use the hypotenuse, and we need to find the adjacent side. we therefore need to use the cosine function. The sine of the angle = the length of the opposite side. the length of the hypotenuse. the cosine of the angle = the length of the adjacent side. the length of the hypotenuse. the tangent of the angle = the length of the opposite side. the length of the adjacent side. so in shorthand notation: sin = o h cos = a h tan = o a.

Comments are closed.