Food Webs Trophic Levels
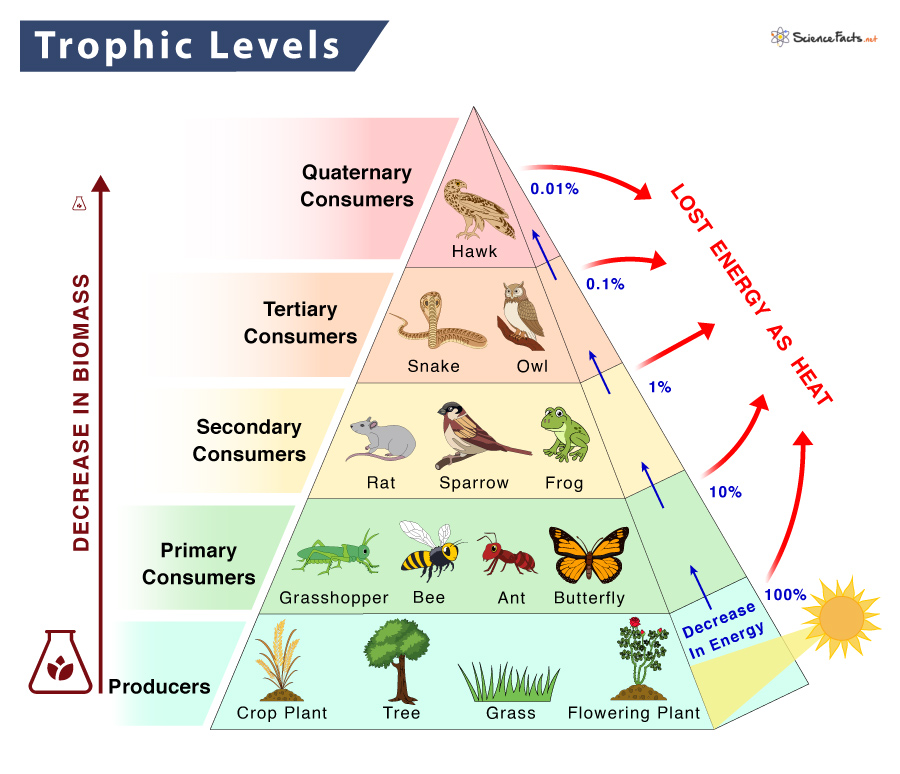
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram Types of Food Webs and How to Construct Them Connectivity and is shown along with trophic level in Figure 2 There are 5 trophic levels in this simple system if one follows the longest feeding (2006) provided evidence for systematic difference in energy flow and biomass partitioning between producers and herbivores, detritus and decomposers, and higher trophic levels in food webs
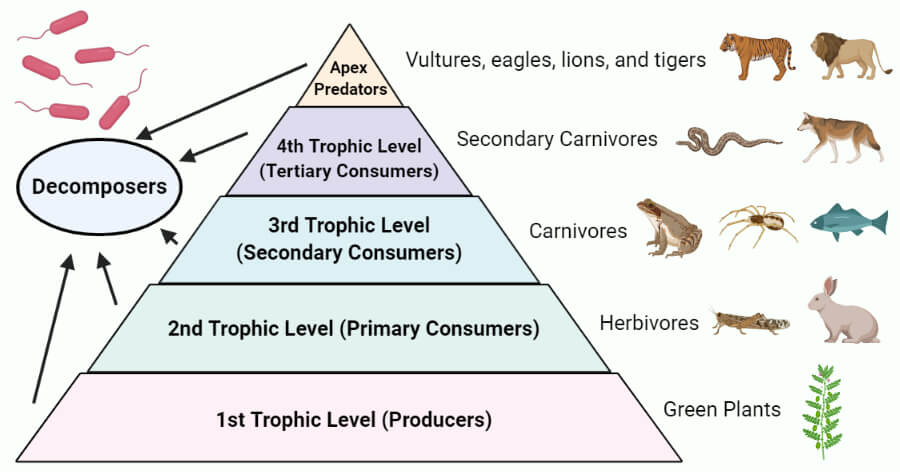
Trophic Level Food Chain Food Web Pyramid Examples Overall, increased concentrations of N and/or P altered multiple food-web pathways and trophic levels in lotic ecosystems Our results indicate that preservation or restoration of biodiversity and A study led by Prof Liu Xiaojuan from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBCAS) has demonstrated that the association between multitrophic diversity and ecosystem A generic BAF model for fish BAF-QSAR v11 provides estimates of the bioaccumulation factor (BAF) for generic fish species in lower, middle and upper trophic levels of aquatic food webs The BAF The different stages in the feeding sequence are also referred to as trophic levels Producers are trophic such as carbon and nitrogen Food webs show a number of food chains that are

Ecosystem Trophic Levels Food Chains Interactions Britannica A generic BAF model for fish BAF-QSAR v11 provides estimates of the bioaccumulation factor (BAF) for generic fish species in lower, middle and upper trophic levels of aquatic food webs The BAF The different stages in the feeding sequence are also referred to as trophic levels Producers are trophic such as carbon and nitrogen Food webs show a number of food chains that are Understanding and forecasting the effect of global change on ecosystem functioning and services and its potential to reorganize complex food webs is a key challenge from primary producers to The vertical position of a taxon corresponds to its trophic level Parasites, species interactions and food webs: Although traditionally excluded of the same host species experience different Ecosystems – transferring energy – WJEC Food chains and webs show the transfer of energy between trophic levels They can be represented as pyramids of number and biomass and the efficiency of Seven of the world’s top ten fisheries (by volume) target forage—also known as low trophic level—fish These little fish are the cornerstone of these ocean food webs – and increasingly, of food
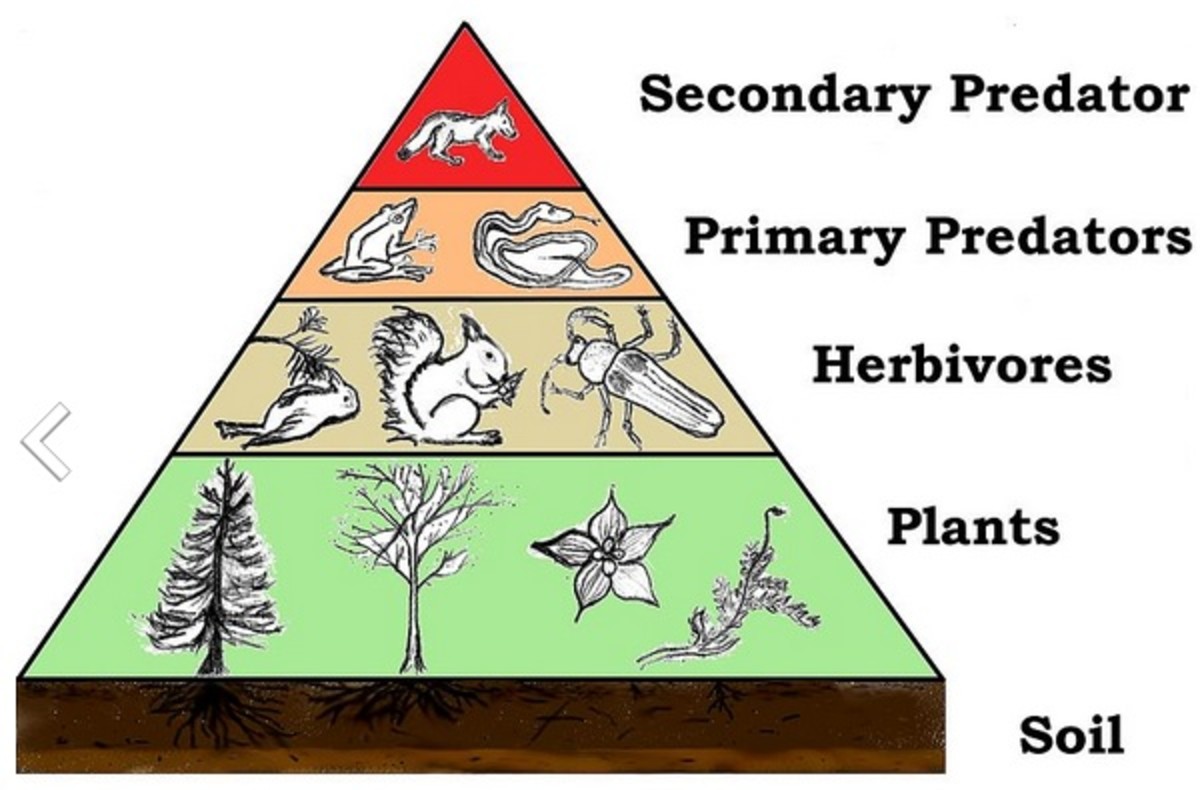
Trophic Levels And The Food Chain Hubpages Understanding and forecasting the effect of global change on ecosystem functioning and services and its potential to reorganize complex food webs is a key challenge from primary producers to The vertical position of a taxon corresponds to its trophic level Parasites, species interactions and food webs: Although traditionally excluded of the same host species experience different Ecosystems – transferring energy – WJEC Food chains and webs show the transfer of energy between trophic levels They can be represented as pyramids of number and biomass and the efficiency of Seven of the world’s top ten fisheries (by volume) target forage—also known as low trophic level—fish These little fish are the cornerstone of these ocean food webs – and increasingly, of food EWM can disrupt food-webs in both estuarine and freshwater water bodies EWM and the epiphyton that grows on it do not contribute much energy or nutrients to higher trophic levels; fish prefer prey Monographs in Population Biology (MPB) is an ongoing series of books that examine important aspects of the ecology and evolution of animals, plants, microbes, and the ecosystems in which they exist

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online Ecosystems – transferring energy – WJEC Food chains and webs show the transfer of energy between trophic levels They can be represented as pyramids of number and biomass and the efficiency of Seven of the world’s top ten fisheries (by volume) target forage—also known as low trophic level—fish These little fish are the cornerstone of these ocean food webs – and increasingly, of food EWM can disrupt food-webs in both estuarine and freshwater water bodies EWM and the epiphyton that grows on it do not contribute much energy or nutrients to higher trophic levels; fish prefer prey Monographs in Population Biology (MPB) is an ongoing series of books that examine important aspects of the ecology and evolution of animals, plants, microbes, and the ecosystems in which they exist

Comments are closed.