Food Insecurity Inequality And Covid 19
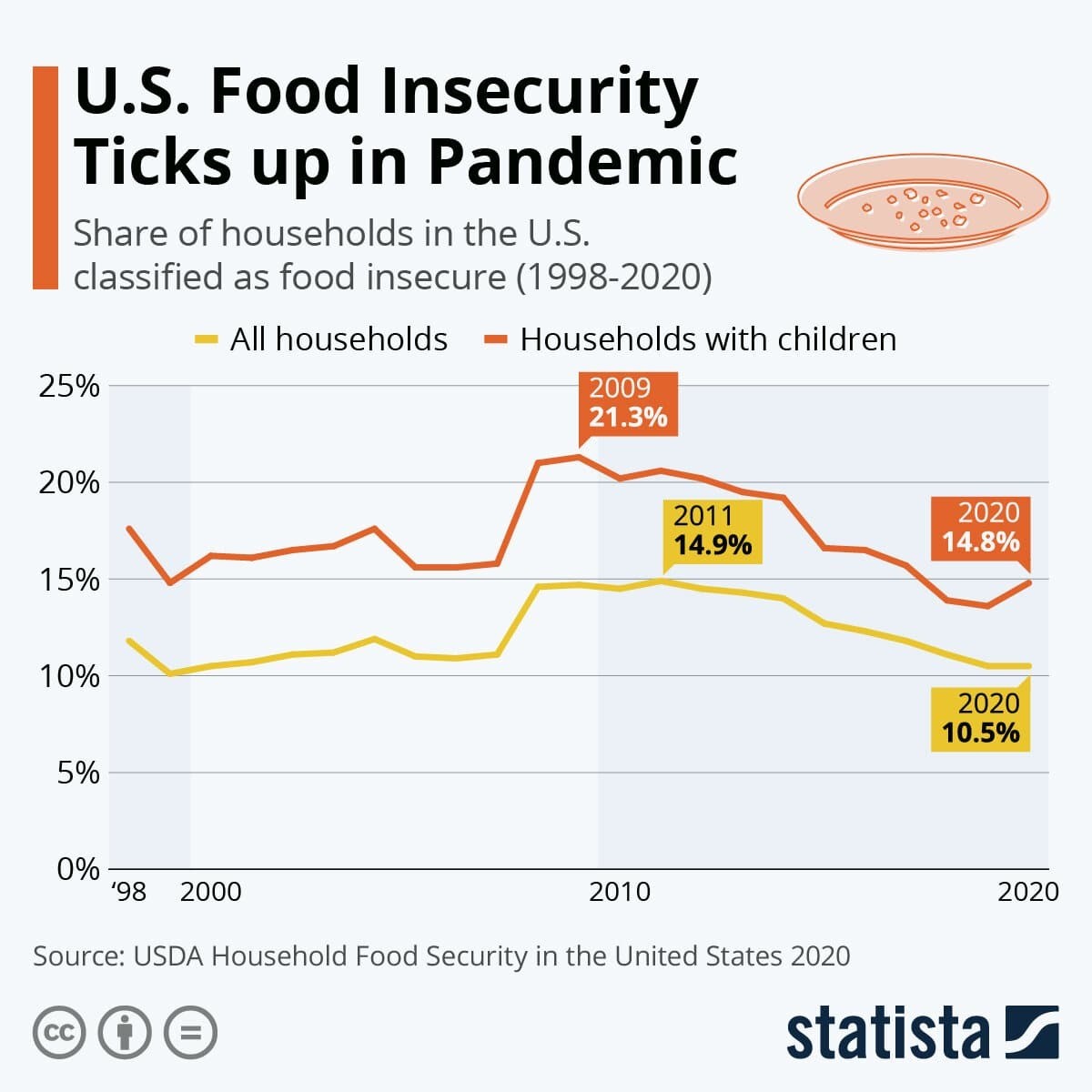
How Has Covid 19 Impacted Food Security In The Us World Economic Forum The impact of the covid 19 epidemic on food insecurity and poor health outcomes is due to previous economic and health inequalities, which are mainly driven by systemic racial discrimination.51, 66 before covid 19, black, hispanic, and low income households experienced food insecurity and chronic illness. 67 in 2018 the prevalence of food. The number of individuals in food insecure households also increased by 3 million, from 35.2 million in 2019 to 38.3 million in 2020. the cps fss includes a measure of food insecurity, based on ten to 18 questions about conditions and behaviors related to difficulty meeting food needs.
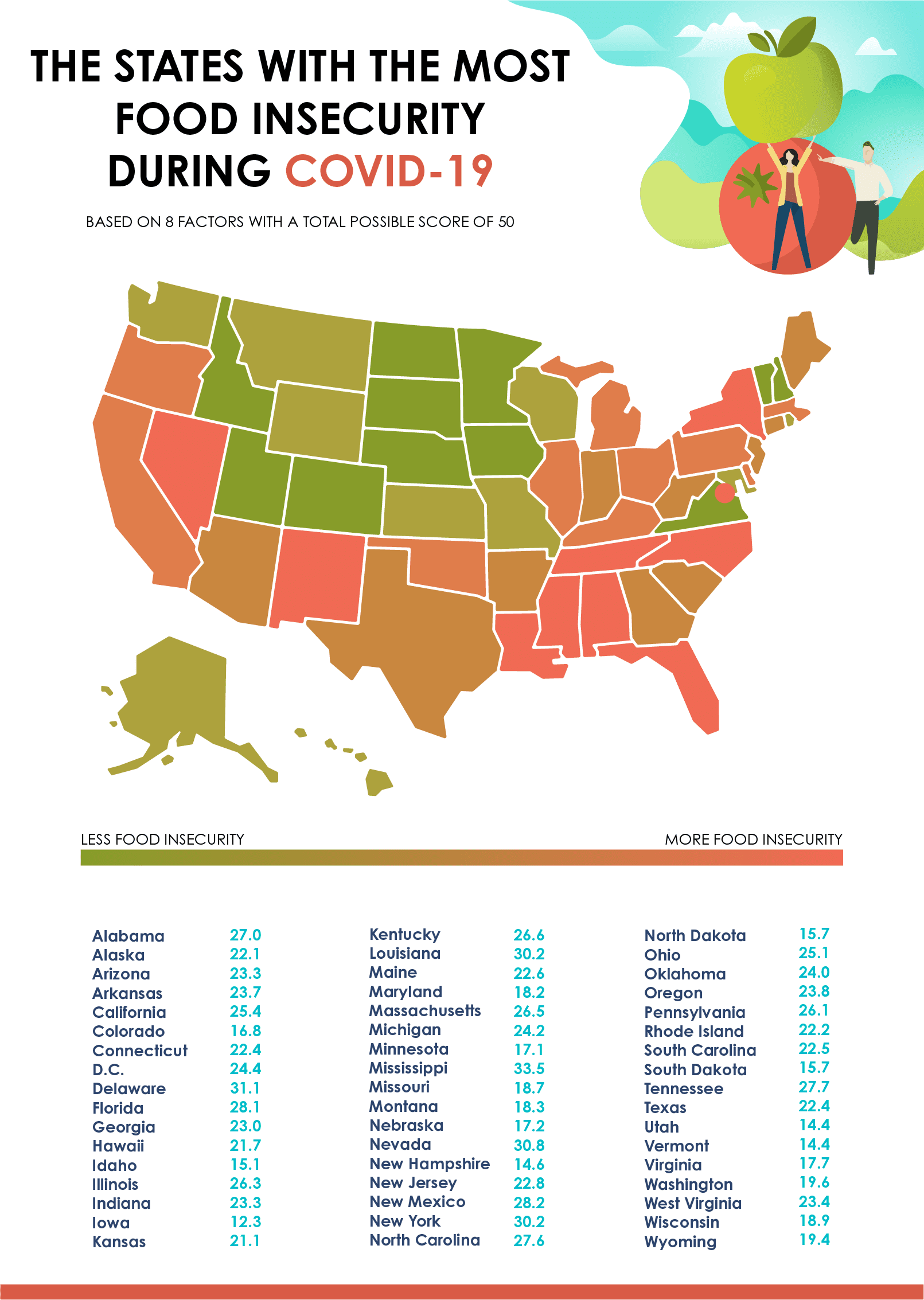
Food Insecurity By State Due To Covid 19 United Way Nca This is the current state of global food prices. the negative effects of the covid 19 pandemic on food security stayed behind those of the great depression between 2008 and 2011. image: statista. the report said that the lack of school lunches and the closure of businesses during coronavirus lockdowns made food insecurity more severe in 2020. The covid 19 pandemic has dramatically increased food insecurity in the united states (us). the objective of this study was to understand the early effects of the covid 19 pandemic among low income adults in the us as social distancing measures began to be implemented. on 19–24 march 2020 we fielded a national, web based survey (53% response. Food insecurity trajectories. in the early stages of the covid 19 pandemic, in april 2020, the prevalence of any food insecurity was as high as 20.4%. the prevalence decreased to 8.9% by march 2021, with most of the decline occurring in the early months, before leveling off in mid 2020 (figure 1). figure 1. Covid 19. 4. significant racial disparities in food insecurity which existed before covid 19 remain in the wake of the pandemic. feeding america projects that 21% of black individuals (1 in 5) may experience food insecurity in 2021, compared to 11% of white individuals (1 in 9). 5. it will likely take time for food insecurity levels to recover.
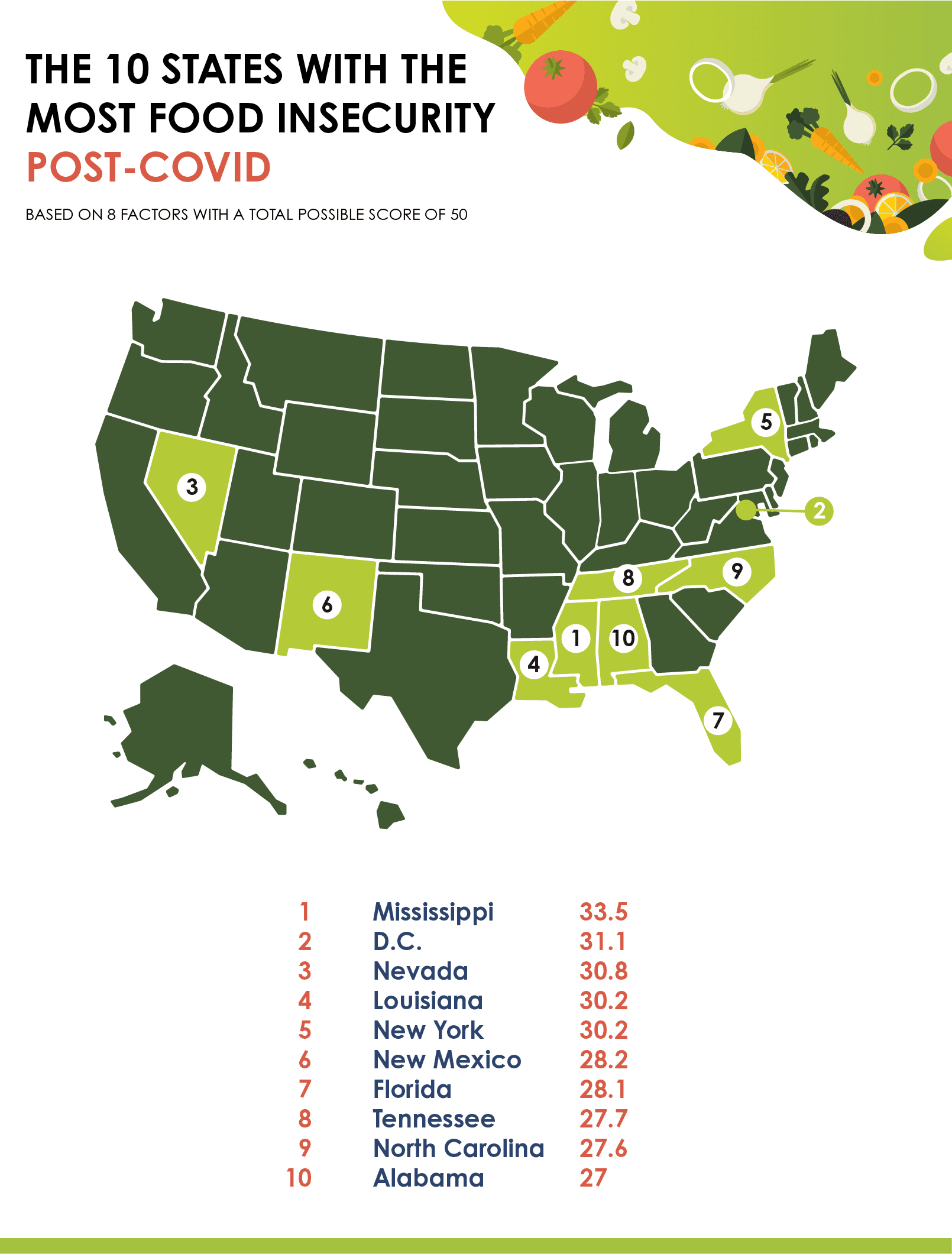
Food Insecurity By State Due To Covid 19 United Way Nca Food insecurity trajectories. in the early stages of the covid 19 pandemic, in april 2020, the prevalence of any food insecurity was as high as 20.4%. the prevalence decreased to 8.9% by march 2021, with most of the decline occurring in the early months, before leveling off in mid 2020 (figure 1). figure 1. Covid 19. 4. significant racial disparities in food insecurity which existed before covid 19 remain in the wake of the pandemic. feeding america projects that 21% of black individuals (1 in 5) may experience food insecurity in 2021, compared to 11% of white individuals (1 in 9). 5. it will likely take time for food insecurity levels to recover. This cross sectional study on household food insecurity during covid 19 used data from a nationally representative sample of us households through the 2020 household pulse survey (hps) (including all 50 states and the district of columbia, n = 74,413 households). six generalized estimating equation (gee) models were estimated, and the results. These findings are consistent with much of the literature on the socioeconomic determinants of food insecurity 22; and with 23 who highlight key socioeconomic inequalities in covid 19 related.

Covid 19 Pandemic Has Increased Food Security Risks In Asia And The Pacific This cross sectional study on household food insecurity during covid 19 used data from a nationally representative sample of us households through the 2020 household pulse survey (hps) (including all 50 states and the district of columbia, n = 74,413 households). six generalized estimating equation (gee) models were estimated, and the results. These findings are consistent with much of the literature on the socioeconomic determinants of food insecurity 22; and with 23 who highlight key socioeconomic inequalities in covid 19 related.

Comments are closed.