Food Chain Ocean Animals
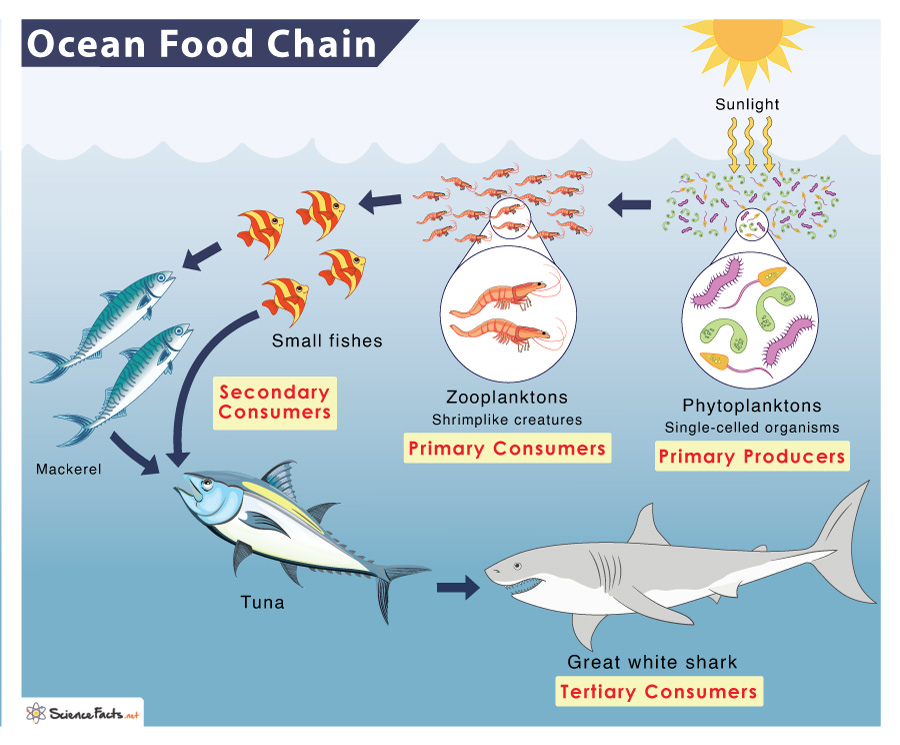
Ocean Marine Food Chain Examples And Diagram Example. a typical example of the ocean food chain is sharks eating tunas, which eat small fish. the small fishes consume plankton and crustacean, which feed on the microscopic, single celled organism. ocean food chain. like terrestrial food chains, the primary ocean food chain also has different levels. The next level of the marine food chain is made up of animals that feast on the sea's abundant plant life. on the ocean's surface waters, microscopic animals— zooplankton, which include jellyfish and the larval stages of some fish, barnacles, and mollusks—drift across the sea, grazing opportunistically. larger herbivores include surgeonfish.

Food Chain For Ocean Animals The food chain of the ocean. by ana diaz maqueda, biologist specialized in ethology. may 2, 2023. oceanic food chains contain some of the largest organisms in the world, such as whales, feeding on some of the smallest organisms, such as phytoplankton. we know this thanks to the great work of many marine biologists, but the difficulties in. A food web is a system of interconnected food chains. a food chain is a top to bottom set of animals and plants. they are linked to each other because those on top eat those below. level one: photo autotrophs the bottom level of the ocean's food chain is largely invisible. it is made up of billions of one celled organisms, called phytoplankton. Directions. 1. define the role of marine microbes. explain to students that, in a single drop of salt water, thousands of microbes (tiny organisms), including bacteria and phytoplankton (tiny floating plants), are interacting to form the base of the food web for the entire ocean. Sea creatures at this level of the food chain include crabs, sea urchins, and parrotfish. these are usually eaten in large quantities by the carnivores of the ocean. finally, we reach the bottom of the food chain where the photoautotrophs sit. these mostly provide food for herbivores, although carnivores will sometimes add these to their diets.

Phytoplankton Food Chain In The Ocean Animals World Directions. 1. define the role of marine microbes. explain to students that, in a single drop of salt water, thousands of microbes (tiny organisms), including bacteria and phytoplankton (tiny floating plants), are interacting to form the base of the food web for the entire ocean. Sea creatures at this level of the food chain include crabs, sea urchins, and parrotfish. these are usually eaten in large quantities by the carnivores of the ocean. finally, we reach the bottom of the food chain where the photoautotrophs sit. these mostly provide food for herbivores, although carnivores will sometimes add these to their diets. There are around 300,000 known ocean species. a species is a particular kind of animal or plant. ocean species are also called marine species. most marine species are part of a food chain. a food chain is a top to bottom set of animals and plants. they are connected to each other because those on top eat those below. A video that provides explains the four levels of the ocean food chain. 0:00 intro0:32 level 1: plants and phytoplankton1:17 level 2: herbivores and om.

Ocean Food Web Science Project Education There are around 300,000 known ocean species. a species is a particular kind of animal or plant. ocean species are also called marine species. most marine species are part of a food chain. a food chain is a top to bottom set of animals and plants. they are connected to each other because those on top eat those below. A video that provides explains the four levels of the ocean food chain. 0:00 intro0:32 level 1: plants and phytoplankton1:17 level 2: herbivores and om.

Comments are closed.