Food Chain Examples With Labels At Andrew Brown Blog
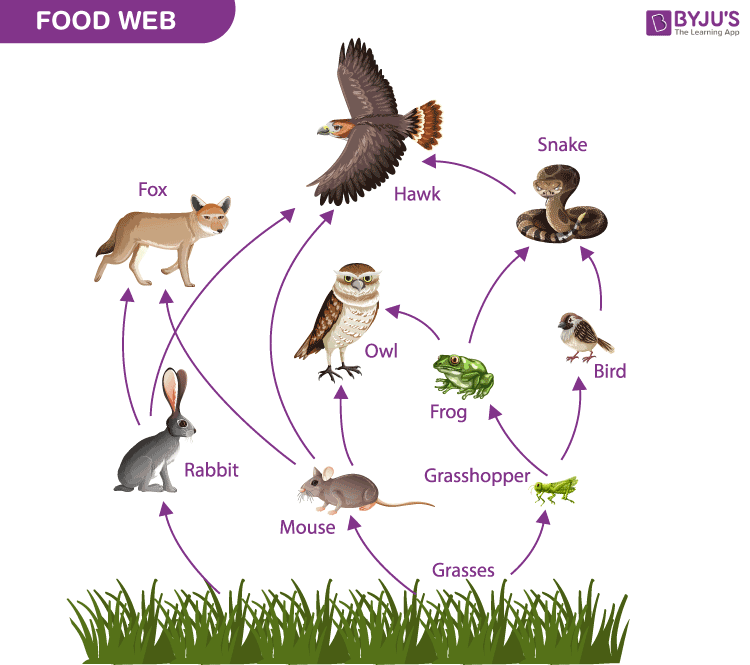
Food Chain With Labels Discover The Essential Components For A De 25 bedste idéer inden for food chains på pinterest food chain examples with labels a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. here is an example of a simple food chain: but a food shows different paths, where. grass → cow → human. the cow and human are. Maybe you’ve studied a little ecology and come across the terms “food chain” and “food web.” both help ecologists explain the ways that energy from food travels through an ecosystem. in this post, we will dive into the differences between food chains and food webs, and look at some examples of both!.

Food Chain Example With Labels At James Madera Blog Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. A food web can be composed of multiple food chains, some very short and others much longer. food chains follow the flow of energy as it moves through the chain. the starting point is the energy. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Food Chain Examples With Explanation A food web can be composed of multiple food chains, some very short and others much longer. food chains follow the flow of energy as it moves through the chain. the starting point is the energy. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Noun. one of three positions on the food chain: autotrophs (first), herbivores (second), and carnivores and omnivores (third). volcano. noun. an opening in the earth's crust, through which lava, ash, and gases erupt, and also the cone built by eruptions. the food chain describes who eats whom in the wild.

Food Chain Diagram With Labels A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Noun. one of three positions on the food chain: autotrophs (first), herbivores (second), and carnivores and omnivores (third). volcano. noun. an opening in the earth's crust, through which lava, ash, and gases erupt, and also the cone built by eruptions. the food chain describes who eats whom in the wild.

Food Chain With Labels Discover The Essential Components For A

Comments are closed.