Food Chain Energy Flow Diagram Science School Example Ecosystem Vec

Premium Vector Food Chain Energy Flow Diagram A food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. Each food chain is a descriptive diagram including a series of arrows, each pointing from one species to another, representing the flow of food energy from one feeding group of organisms to another.

Ecosystem Trophic Levels Food Chains Interactions Britannica Figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: a (a) tidal pool ecosystem in matinicus island, maine, is a small ecosystem, while the (b) amazon rainforest in brazil is a large ecosystem. (credit a: modification of work by jim kuhn; credit b: modification of work by ivan mlinaric) there are three broad categories of ecosystems based on their general environment. Food chains. a food chain is a simple diagram that shows one way energy flows through an ecosystem. pictured below is an example of a food chain (figure below). producers form the base of all food chains. the consumers that eat producers are called primary consumers. the consumers that eat primary consumers are secondary consumers. this chain. Figure 4.4.2.1 4.4.2. 1: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the border with the united states. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae at the bottom to the top of the food chain: the chinook salmon. one major factor that limits the length of food chains is energy. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those.

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online Figure 4.4.2.1 4.4.2. 1: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the border with the united states. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae at the bottom to the top of the food chain: the chinook salmon. one major factor that limits the length of food chains is energy. Definition of food chain. a food chain shows energy pathways in ecosystems. each ecosystem on the planet has food chains of organisms ranging from producers to consumers. the producers are on the lowest level of the food chain, while the consumers that eat those producers are called primary consumers. higher level consumers who eat those. Typically, a food chain is represented by a diagram where arrows show the direction of energy and nutrients flow. many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. all interconnected to make a food web. The food chain would be: a food chain cannot continue to go on and on. for example the food chain could not be: food chains only have 4 or 5 total levels. therefore, a chain has only 3 or 4 levels for energy transfer. figure 12.18.1 12.18. 1: this food chain includes producers and consumers.

Food Chain Energy Flow Diagram Science School Exampleођ Typically, a food chain is represented by a diagram where arrows show the direction of energy and nutrients flow. many herbivores eat grass, and deer can eat other plants besides grass. even a tiger can eat many types of animals and plants. thus, each animal is part of multiple food chains. all interconnected to make a food web. The food chain would be: a food chain cannot continue to go on and on. for example the food chain could not be: food chains only have 4 or 5 total levels. therefore, a chain has only 3 or 4 levels for energy transfer. figure 12.18.1 12.18. 1: this food chain includes producers and consumers.
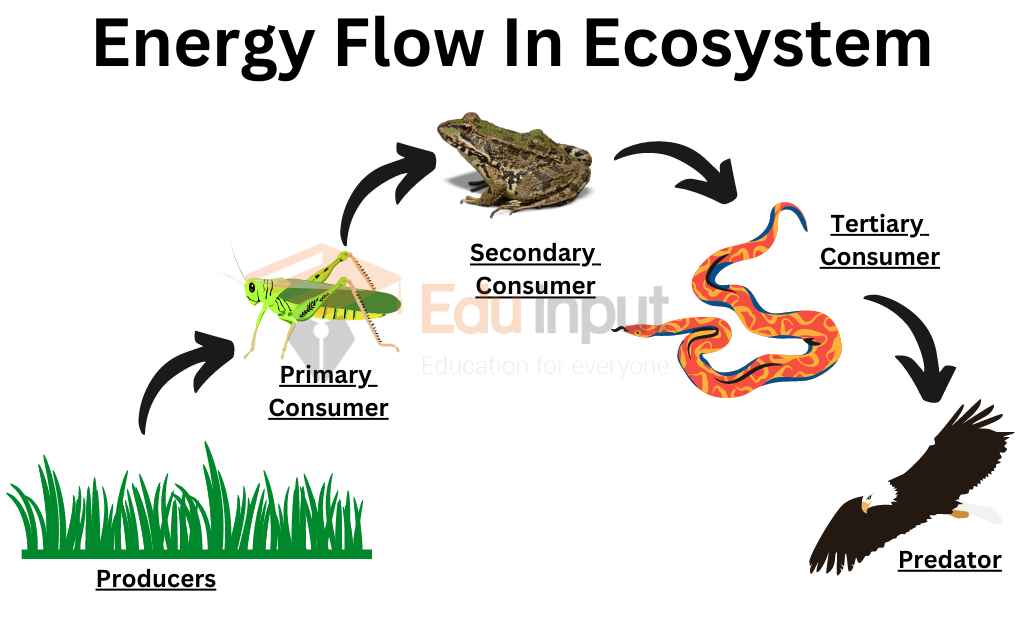
Energy Flow In Ecosystem

Comments are closed.