Exponential Functions Top 10 Must Knows

Exponential Functions Cuemath I hope this video helps you learn the properties and rules associated with exponential functions. please consider subscribing if you enjoy the channel :)go t. Find an exponential function that passes through the points (− 2, 6) and (2, 1). solution. because we don’t have the initial value, we substitute both points into an equation of the form f(x) = abx, and then solve the system for a and b. substituting (− 2, 6) gives 6 = ab − 2. substituting (2, 1) gives 1 = ab2.
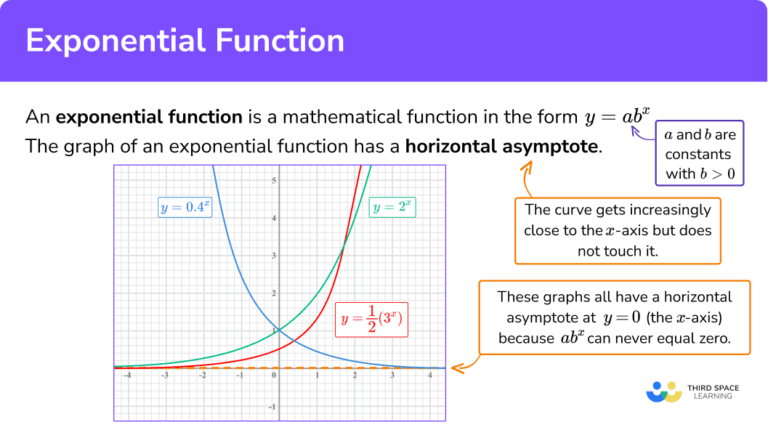
Exponential Function Gcse Maths Steps And Examples The exponential function is one of the most important functions in mathematics (though it would have to admit that the linear function ranks even higher in importance). to form an exponential function, we let the independent variable be the exponent. a simple example is the function. f(x) = 2x. f (x) = 2 x. as illustrated in the above graph of. Exponential functions have definitions of the form f(x) = bx where b> 0 and b ≠ 1. the domain consists of all real numbers (− ∞, ∞) and the range consists of positive numbers (0, ∞). also, all exponential functions of this form have a y intercept of (0, 1) and are asymptotic to the x axis. So far we have worked with rational bases for exponential functions. for most real world phenomena, however, e is used as the base for exponential functions. exponential models that use e e as the base are called continuous growth or decay models. we see these models in finance, computer science, and most of the sciences, such as physics. A function that models exponential growth grows by a rate proportional to the amount present. for any real number x and any positive real numbers a and b such that [latex]b\ne 1 [ latex], an exponential growth function has the form. [latex]\text { }f\left (x\right)=a {b}^ {x} [ latex] where. a is the initial or starting value of the function.

Exponential Function Formula Asymptotes Domain Range So far we have worked with rational bases for exponential functions. for most real world phenomena, however, e is used as the base for exponential functions. exponential models that use e e as the base are called continuous growth or decay models. we see these models in finance, computer science, and most of the sciences, such as physics. A function that models exponential growth grows by a rate proportional to the amount present. for any real number x and any positive real numbers a and b such that [latex]b\ne 1 [ latex], an exponential growth function has the form. [latex]\text { }f\left (x\right)=a {b}^ {x} [ latex] where. a is the initial or starting value of the function. In general, an exponential function is written as f (x) = a bx or as f (x) = a bcx, where a, b, and c are constants. previously, you have dealt with such functions as f (x) = x2, where the variable x was the base and the number 2 was the power. in the case of exponentials, however, you will be dealing with functions such as g(x) = 2x, where the. Contributed. an exponential function is a function of the form f (x)=a \cdot b^x, f (x) = a⋅bx, where a a and b b are real numbers and b b is positive. exponential functions are used to model relationships with exponential growth or decay. exponential growth occurs when a function's rate of change is proportional to the function's current value.
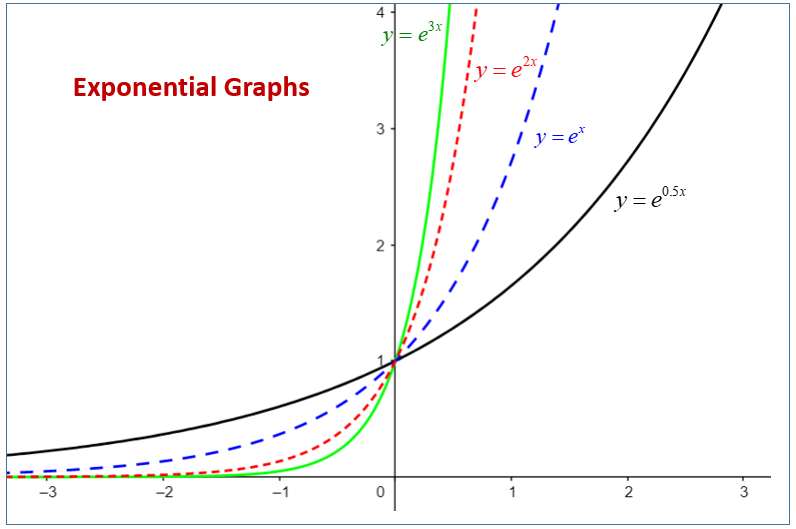
Exponential Functions Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Activities In general, an exponential function is written as f (x) = a bx or as f (x) = a bcx, where a, b, and c are constants. previously, you have dealt with such functions as f (x) = x2, where the variable x was the base and the number 2 was the power. in the case of exponentials, however, you will be dealing with functions such as g(x) = 2x, where the. Contributed. an exponential function is a function of the form f (x)=a \cdot b^x, f (x) = a⋅bx, where a a and b b are real numbers and b b is positive. exponential functions are used to model relationships with exponential growth or decay. exponential growth occurs when a function's rate of change is proportional to the function's current value.
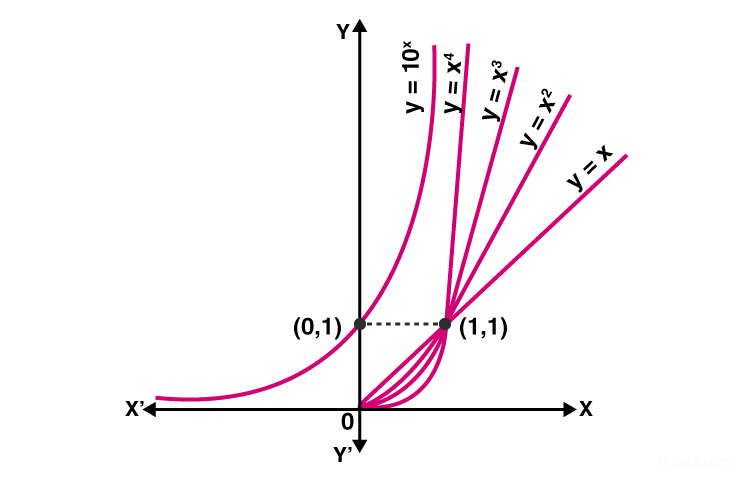
Exponential Functions Definition Formula Properties Rules

Comments are closed.