Examples Of Commensalism Mutualism And Parasitism
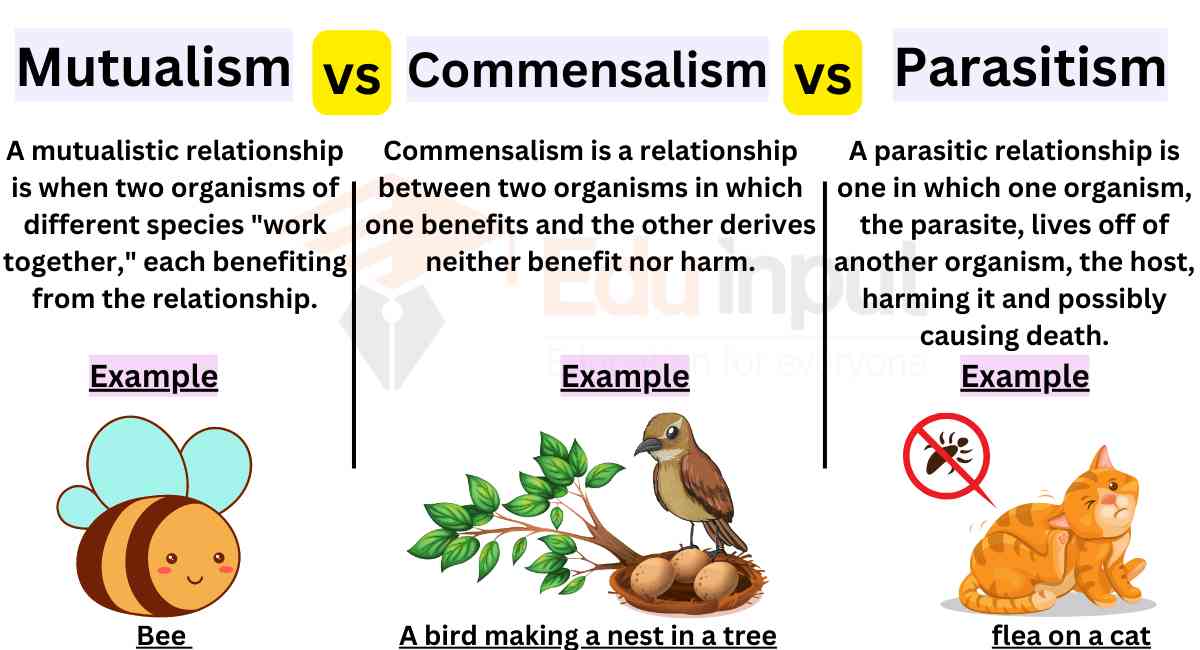
Differences Between Mutualism And Commensalism And Parasitism Commensalism, mutualism, and parasitism are the three main categories of symbiosis found in nature. commensalism. in a commensal relationship, one species benefits and there is a neutral effect on the other—it neither benefits nor is harmed. an example of this relationship is birds building nests in trees. Mutualism: both organisms involved benefit. obligate: the symbiosis is essential to the survival of both organisms. facultative: the symbiosis benefits both organisms, but isn’t necessary to their survival. commensalism: one organism benefits, the other is unharmed. inquilinism: one organism uses the other for permanent shelter.
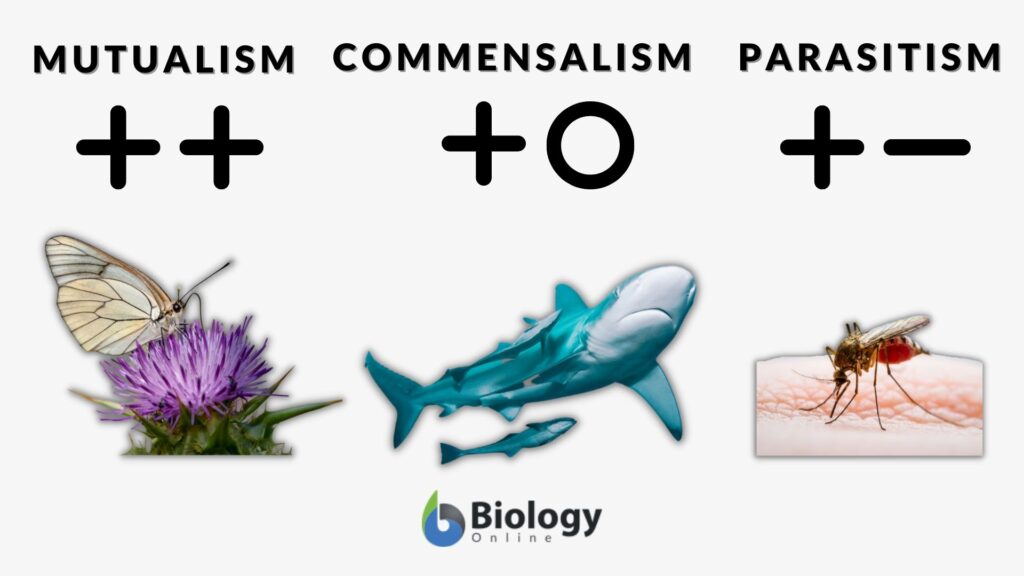
Commensalism Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Commensalism examples. another example of commensalism is one organism using another as a means of transportation. a lot of insects, fish, and other animals use each other in this way, but a good example is the remora. this is a type of suckerfish that will attach itself to sharks and other big fish to catch an underwater ride. In some cases, the species are entirely dependent on each other (obligate mutualism) and in others, they derive benefits from their relationship but could survive without each other (facultative mutualism). here are eight examples of mutualistic relationships. 1. pistol shrimps and gobies. A big thanks to all current and future patrons who are helping fund this science communication outreach via patreon: bit.ly 2sfmkphsymbiosis is close. In other words, it is a win neutral situation. the best example of commensalism is sea barnacles attached to the skin of whales. unlike parasitism, where one organism benefits at the expense of the other, and mutualism, where both organisms benefit, commensalism involves an unequal partnership. the organism benefiting is the commensal, while.

Examples Of Commensalism Mutualism And Parasitism A big thanks to all current and future patrons who are helping fund this science communication outreach via patreon: bit.ly 2sfmkphsymbiosis is close. In other words, it is a win neutral situation. the best example of commensalism is sea barnacles attached to the skin of whales. unlike parasitism, where one organism benefits at the expense of the other, and mutualism, where both organisms benefit, commensalism involves an unequal partnership. the organism benefiting is the commensal, while. There are four main symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. to explore these relationships, let’s consider a natural ecosystem such as the ocean. oceanic environments are known for their species diversity. imagine you are on a diving expedition to explore the worlds beneath the waves. Symbiosis, any of several living arrangements between members of two different species, including mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. both positive (beneficial) and negative (unfavourable to harmful) associations are therefore included, and the members are called symbionts. any association between two species populations that live together.

Mutualism Definition And Examples In Biology There are four main symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, and competition. to explore these relationships, let’s consider a natural ecosystem such as the ocean. oceanic environments are known for their species diversity. imagine you are on a diving expedition to explore the worlds beneath the waves. Symbiosis, any of several living arrangements between members of two different species, including mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. both positive (beneficial) and negative (unfavourable to harmful) associations are therefore included, and the members are called symbionts. any association between two species populations that live together.

Comments are closed.