Example Of Producers And Consumers

Consumer Biology Britannica Examples of producers and consumers in science are all around the world. explore the different plant and animal examples of producers and consumers. Producers and consumers. workers at a factory produce clothes that consumers will buy. a society’s economy is based on creating wealth through selling and buying. the people who do the selling and buying are producers and consumers. producers create, or produce, goods and provide services, and consumers buy those goods and services with money.
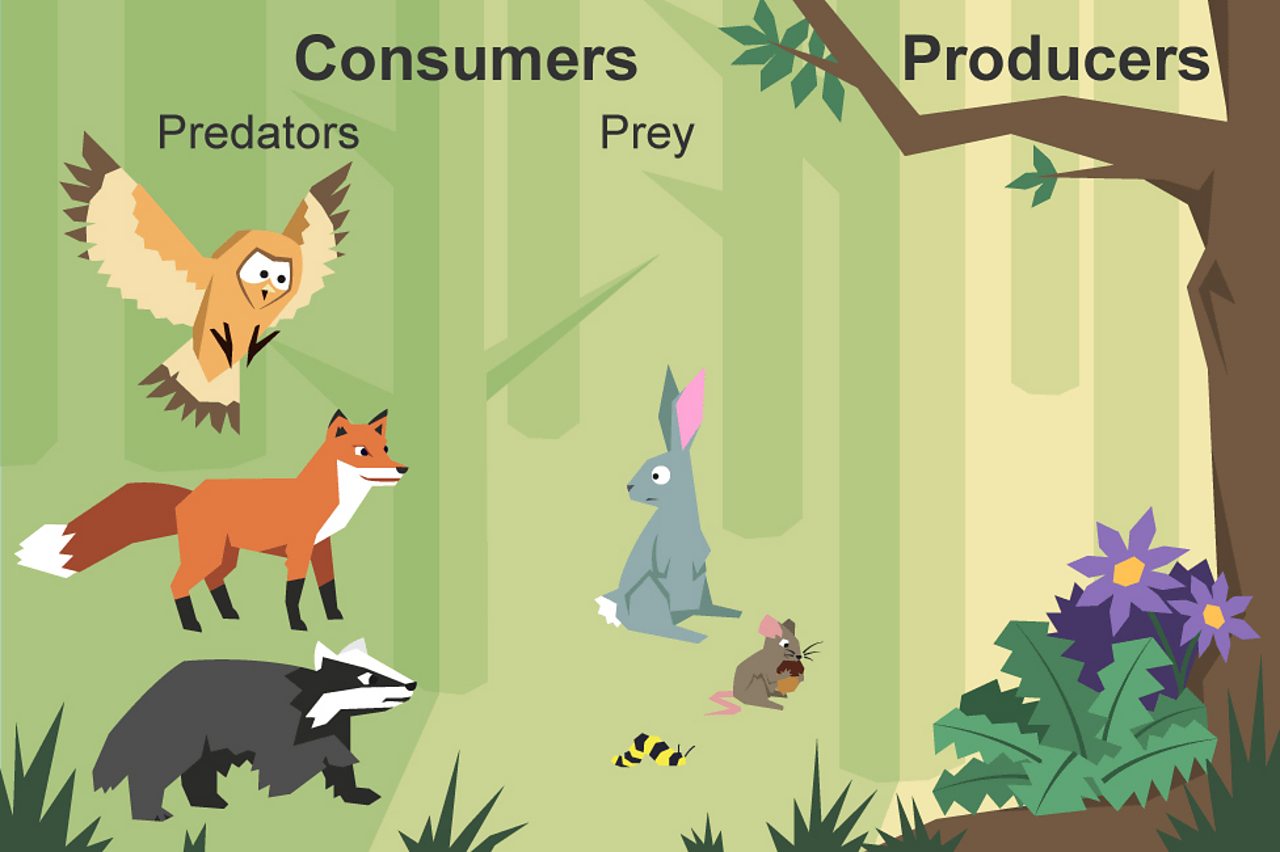
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Meaning. producers are those organisms capable of creating their own food in the form of simple sugars by using the elementary components of nature like sunlight, water, co2 etc. consumers are the living organisms that are not capable of synthesising their own food instead they consume the food made by producers. examples. The producer definition in biology is an organism that makes its own food. an organism is any living thing, whether plant, animal, bacteria, fungi, etc. while plants are definitely producers. Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Organisms that manufacture their own food are known as producers or autotrophs. energy from the sun or chemicals is one of the major ingredients of this food. with the help of water, producers convert this energy into sugar or food, which are usable forms of energy. producers are largely green plants, which use sunlight and water to generate.
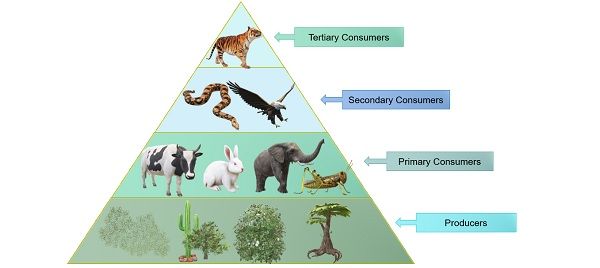
Difference Between Producers And Consumers With Examples And Producers are also called autotrophs. auto means self, while troph means food. they are organisms that create their food from inorganic molecules such as water, co2, nitrogen, and phosphate. most. Organisms that manufacture their own food are known as producers or autotrophs. energy from the sun or chemicals is one of the major ingredients of this food. with the help of water, producers convert this energy into sugar or food, which are usable forms of energy. producers are largely green plants, which use sunlight and water to generate. For example, bacteria living in active volcanoes use sulfur compounds to produce their own food. this process is called chemosynthesis. the second trophic level consists of organisms that eat the producers. these are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the. Producers are the foundation of every food web in every ecosystem—they occupy what is called the first tropic level of the food web. the second trophic level consists of primary consumers —the herbivores, or animals that eat plants. at the top level are secondary consumers —the carnivores and omnivores who eat the primary consumers.
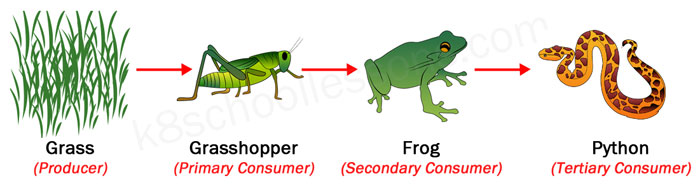
Producers And Consumers Food Chain 4th Grade Science For example, bacteria living in active volcanoes use sulfur compounds to produce their own food. this process is called chemosynthesis. the second trophic level consists of organisms that eat the producers. these are called primary consumers, or herbivores. deer, turtles, and many types of birds are herbivores. secondary consumers eat the. Producers are the foundation of every food web in every ecosystem—they occupy what is called the first tropic level of the food web. the second trophic level consists of primary consumers —the herbivores, or animals that eat plants. at the top level are secondary consumers —the carnivores and omnivores who eat the primary consumers.

Comments are closed.