Energy Transfer In Food Chains
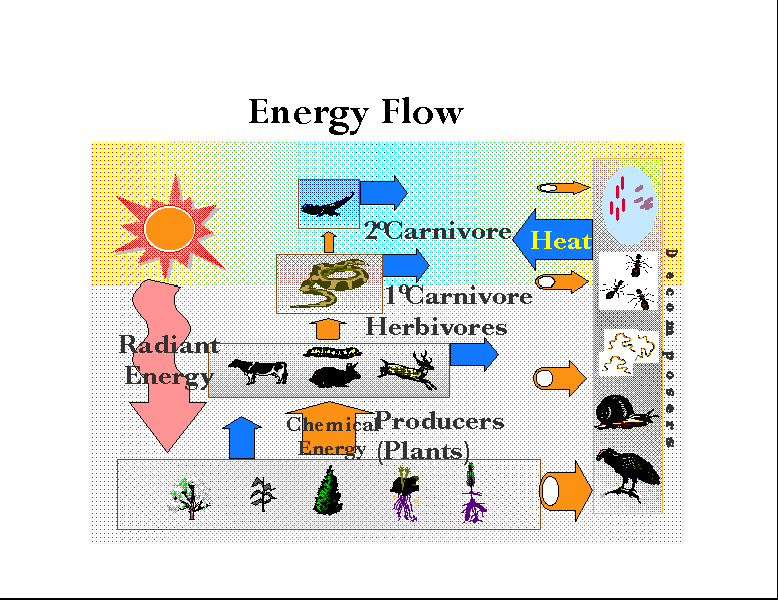
Energy Flow Through An Ecosystem Diagram Energy cannot be created from nothing, so it must be transferred through the ecosystem. the primary source of energy for almost every ecosystem on earth is the sun. primary producers use energy from the sun to produce their own food in the form of glucose, and then primary producers are eaten by primary consumers who are in turn eaten by. Food chains and webs show the transfer of energy between trophic levels. they can be represented as pyramids of number and biomass and the efficiency of these transfers can be calculated.
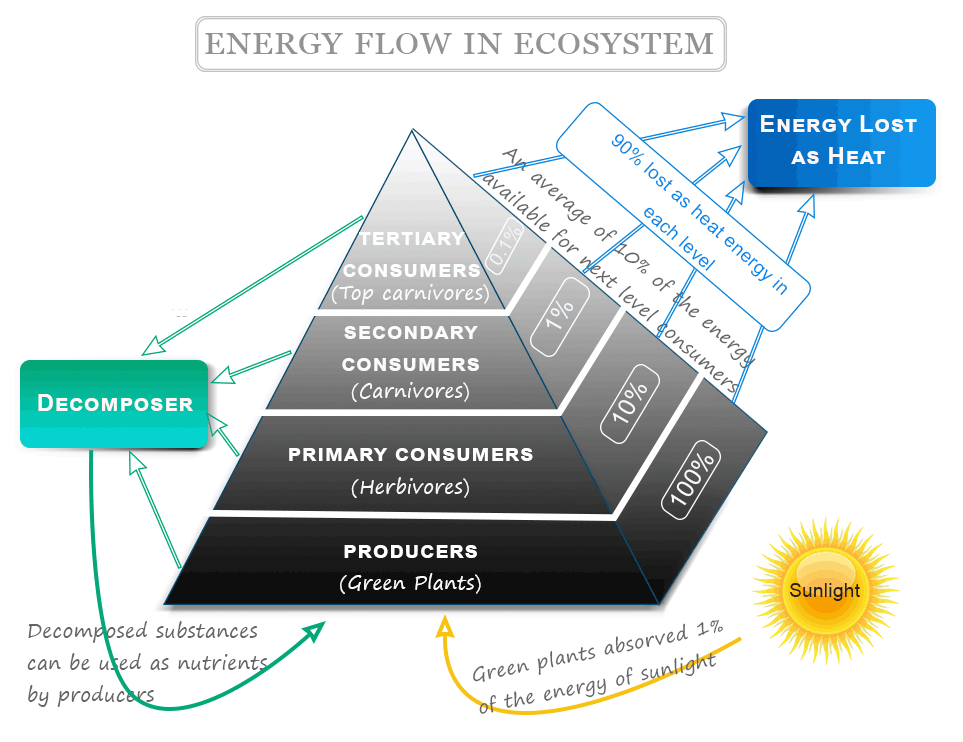
Ecosystem Definition Diversity Examples Types Structure A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. each organism in a food chain occupies a specific trophic level (energy level), its position in the food chain. the first trophic level in the food chain is the producers. Trophic level transfer efficiency (tlte) measures the amount of energy that is transferred between trophic levels. a food chain can usually sustain no more than six energy transfers before all the energy is used up. net production efficiency (npe) measures how efficiently each trophic level uses and incorporates the energy from its food into. It also implies the transfer of food energy from its source in plants through herbivores to carnivores (krebs 2009). each food chain is a descriptive diagram including a series of arrows, each. Figure 15.5.6: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the united states–canada border. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae (producers) at the base to the primary consumers, which are mollusks, or snails. the secondary consumers are small fish called slimy sculpin.

Topic 5 Energy Transfers In And Between Organisms Model Answer Revision It also implies the transfer of food energy from its source in plants through herbivores to carnivores (krebs 2009). each food chain is a descriptive diagram including a series of arrows, each. Figure 15.5.6: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario at the united states–canada border. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae (producers) at the base to the primary consumers, which are mollusks, or snails. the secondary consumers are small fish called slimy sculpin. Energy transfer and the 10 percent rule. not all food chains and food webs consist of five trophic levels. however, five is the maximum number of trophic levels most ecosystems can support. this is because of inefficiencies in energy flow, which begin with photosynthesis. of all the solar energy that reaches earth, only a small percentage lands. Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and consumers, and those producers and consumers can further be organized into a food chain. [2][3] each of the levels within the food chain is a trophic level. [1] in order to more efficiently show the quantity.

Comments are closed.