Energy Relations Between Different Trophic Levels Biology Lecture

Trophic Levels And Energy Flow Energy flow is the flow of energy through a food chain and food webthis video is about: energy relations between different trophic levels. subscribe to our y. Ecological efficiency: the transfer of energy between trophic levels. as illustrated in figure 46.1.7, large amounts of energy are lost from the ecosystem from one trophic level to the next level as energy flows from the primary producers through the various trophic levels of consumers and decomposers. the main reason for this loss is the.
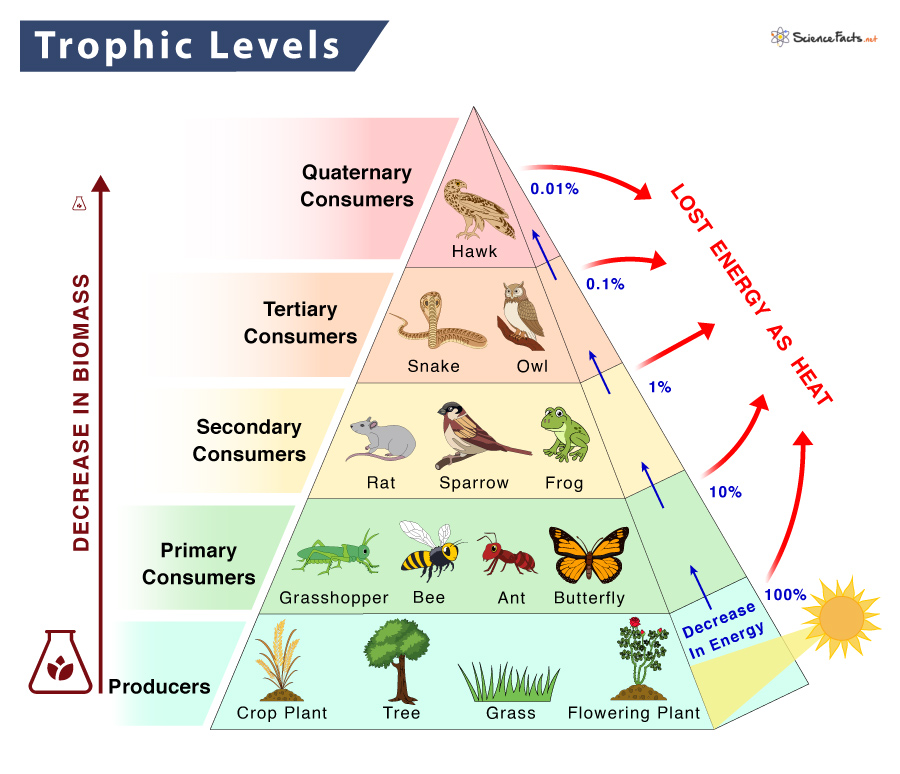
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram One major factor that limits the number of steps in a food chain is energy. energy is lost at each trophic level and between trophic levels as heat and in the transfer to decomposers (figure 20.5). thus, after a limited number of trophic energy transfers, the amount of energy remaining in the food chain may not be great enough to support viable. Figure 10.2.2 10.2. 2: ecological pyramids depict the (a) biomass, (b) number of organisms, and (c) energy in each trophic level. test your understanding 10.2.1 10.2. 1. pyramids depicting the number of organisms or biomass may be inverted, upright, or even diamond shaped. energy pyramids, however, are always upright. Ecological efficiency: the transfer of energy between trophic levels. as illustrated in (figure 46.8), as energy flows from primary producers through the various trophic levels, the ecosystem loses large amounts of energy. the main reason for this loss is the second law of thermodynamics, which states that whenever energy is converted from one. A cell is a complex chemical system, and all of those chemical reactions occurring within cells make up a large portion of the energy that’s lost in the transfer between trophic levels. 5b. some food energy isn’t absorbed. here’s a second reason why energy transfer between trophic levels is so inefficient.
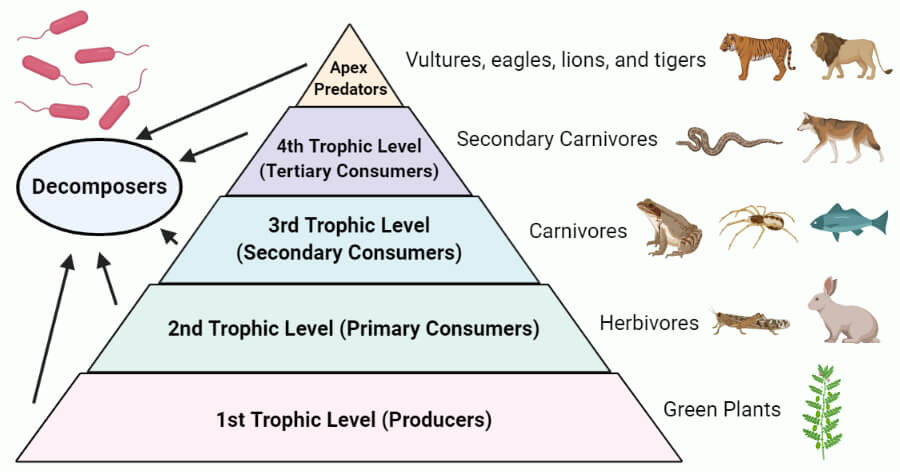
Trophic Levels Study Guide Inspirit Ecological efficiency: the transfer of energy between trophic levels. as illustrated in (figure 46.8), as energy flows from primary producers through the various trophic levels, the ecosystem loses large amounts of energy. the main reason for this loss is the second law of thermodynamics, which states that whenever energy is converted from one. A cell is a complex chemical system, and all of those chemical reactions occurring within cells make up a large portion of the energy that’s lost in the transfer between trophic levels. 5b. some food energy isn’t absorbed. here’s a second reason why energy transfer between trophic levels is so inefficient. Energy transfer and the 10 percent rule. not all food chains and food webs consist of five trophic levels. however, five is the maximum number of trophic levels most ecosystems can support. this is because of inefficiencies in energy flow, which begin with photosynthesis. of all the solar energy that reaches earth, only a small percentage lands. Summary of part 2, higher trophic levels. only a fraction of the energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level; the fractions can vary between 1 15%, with an average value of 10%. typically the numbers and biomass of organisms decreases as one ascends the food chain.

Comments are closed.