Energy Level Hydrogen Atom Bohr Model Hydrogen Spectral ођ

Energy Level Hydrogen Atom Bohr Model Spectral Series Tran The electron’s speed is largest in the first bohr orbit, for n = 1, which is the orbit closest to the nucleus. the radius of the first bohr orbit is called the bohr radius of hydrogen, denoted as a0. its value is obtained by setting n = 1 in equation 6.5.6: a0 = 4πϵ0 ℏ2 mee2 = 5.29 × 10 − 11m = 0.529 Å. From their sizes to their spectra, much was known about atoms, but little had been explained in terms of the laws of physics. bohr’s theory explained the atomic spectrum of hydrogen and established new and broadly applicable principles in quantum mechanics. figure \ (\pageindex {1}\). niels bohr, danish physicist, used the planetary model of.
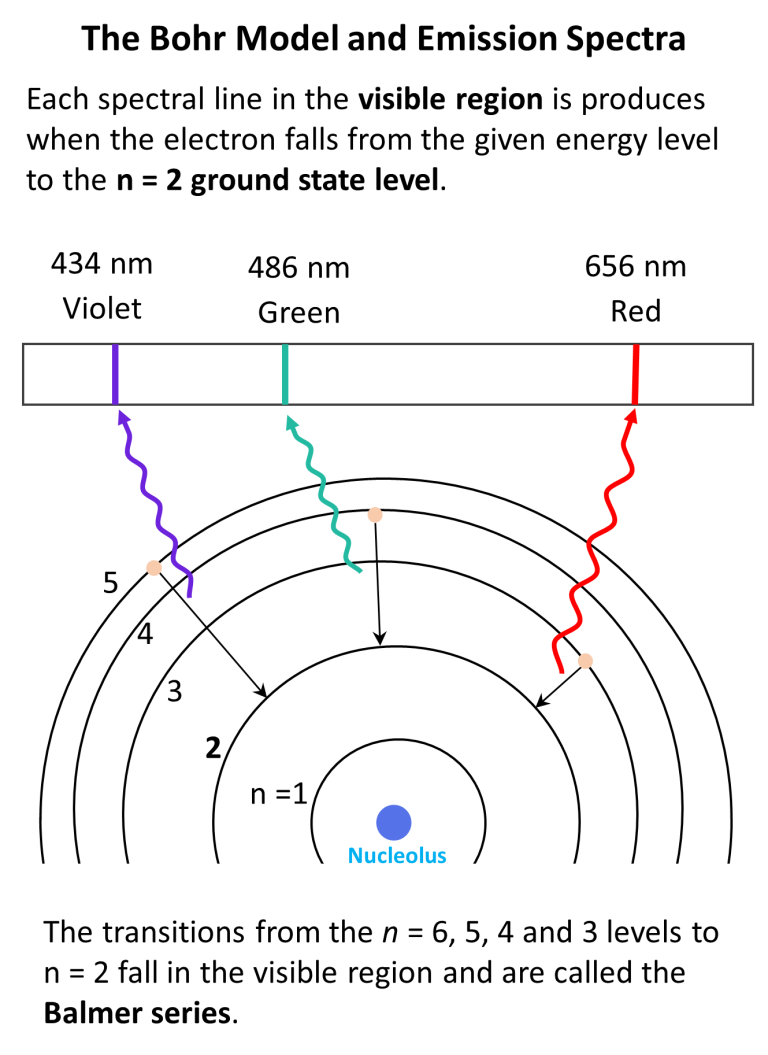
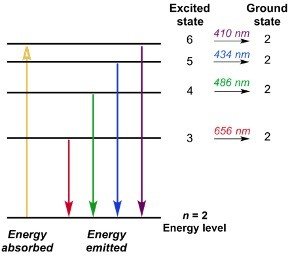
Bohr Model Of The Hydrogen Atom Chemistry Steps Historically, bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the very first model of atomic structure that correctly explained the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen. the model has a special place in the history of physics because it introduced an early quantum theory, which brought about new developments in scientific thought and later culminated in. An energy level diagram has energy plotted on the vertical axis with a horizontal line drawn to locate each energy level (figure 1.8.4 ). figure 1.8.4 : energy levels predicted by the bohr model of hydrogen (\(z=1\)). (cc by nc; Ümit kaya via libretexts) these turn out to be the correct energy levels, apart from small corrections that cannot. Bohr calculated the energy of an electron in the nth level of hydrogen by considering the electrons in circular, quantized orbits as: \ (\begin {array} {l}e (n)= \frac {1} {n^2}\times 13.6\,ev\end {array} \) where, 13.6 ev is the lowest possible energy of a hydrogen electron e (1). the energy obtained is always a negative number and the ground. The bohr model was later replaced by quantum mechanics in which the electron occupies an atomic orbital rather than an orbit, but the allowed energy levels of the hydrogen atom remained the same as in the earlier theory. spectral emission occurs when an electron transitions, or jumps, from a higher energy state to a lower energy state.
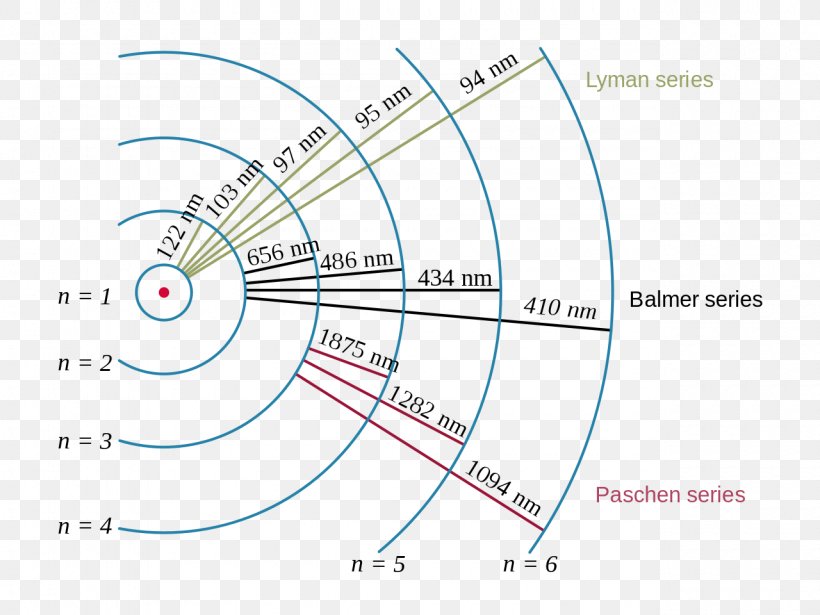
Energy Level Hydrogen Atom Bohr Model Hydrogen Spectral Bohr calculated the energy of an electron in the nth level of hydrogen by considering the electrons in circular, quantized orbits as: \ (\begin {array} {l}e (n)= \frac {1} {n^2}\times 13.6\,ev\end {array} \) where, 13.6 ev is the lowest possible energy of a hydrogen electron e (1). the energy obtained is always a negative number and the ground. The bohr model was later replaced by quantum mechanics in which the electron occupies an atomic orbital rather than an orbit, but the allowed energy levels of the hydrogen atom remained the same as in the earlier theory. spectral emission occurs when an electron transitions, or jumps, from a higher energy state to a lower energy state. Bohr used the planetary model to develop the first reasonable theory of hydrogen, the simplest atom. atomic and molecular spectra are quantized, with hydrogen spectrum wavelengths given by the formula. 1 λ = r(1 n2 f − 1 n2 i), where λ is the wavelength of the emitted em radiation and r is the rydberg constant, which has the value. Historically, bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the very first model of atomic structure that correctly explained the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen. the model has a special place in the history of physics because it introduced an early quantum theory, which brought about new developments in scientific thought and later culminated in.
Bohr Model Of Hydrogen Atom Definition And Properties Bohr used the planetary model to develop the first reasonable theory of hydrogen, the simplest atom. atomic and molecular spectra are quantized, with hydrogen spectrum wavelengths given by the formula. 1 λ = r(1 n2 f − 1 n2 i), where λ is the wavelength of the emitted em radiation and r is the rydberg constant, which has the value. Historically, bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the very first model of atomic structure that correctly explained the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen. the model has a special place in the history of physics because it introduced an early quantum theory, which brought about new developments in scientific thought and later culminated in.

Bohr Model Energy Levels Diagram

Comments are closed.