Education Sciences Free Full Text Leading Inclusive Learning
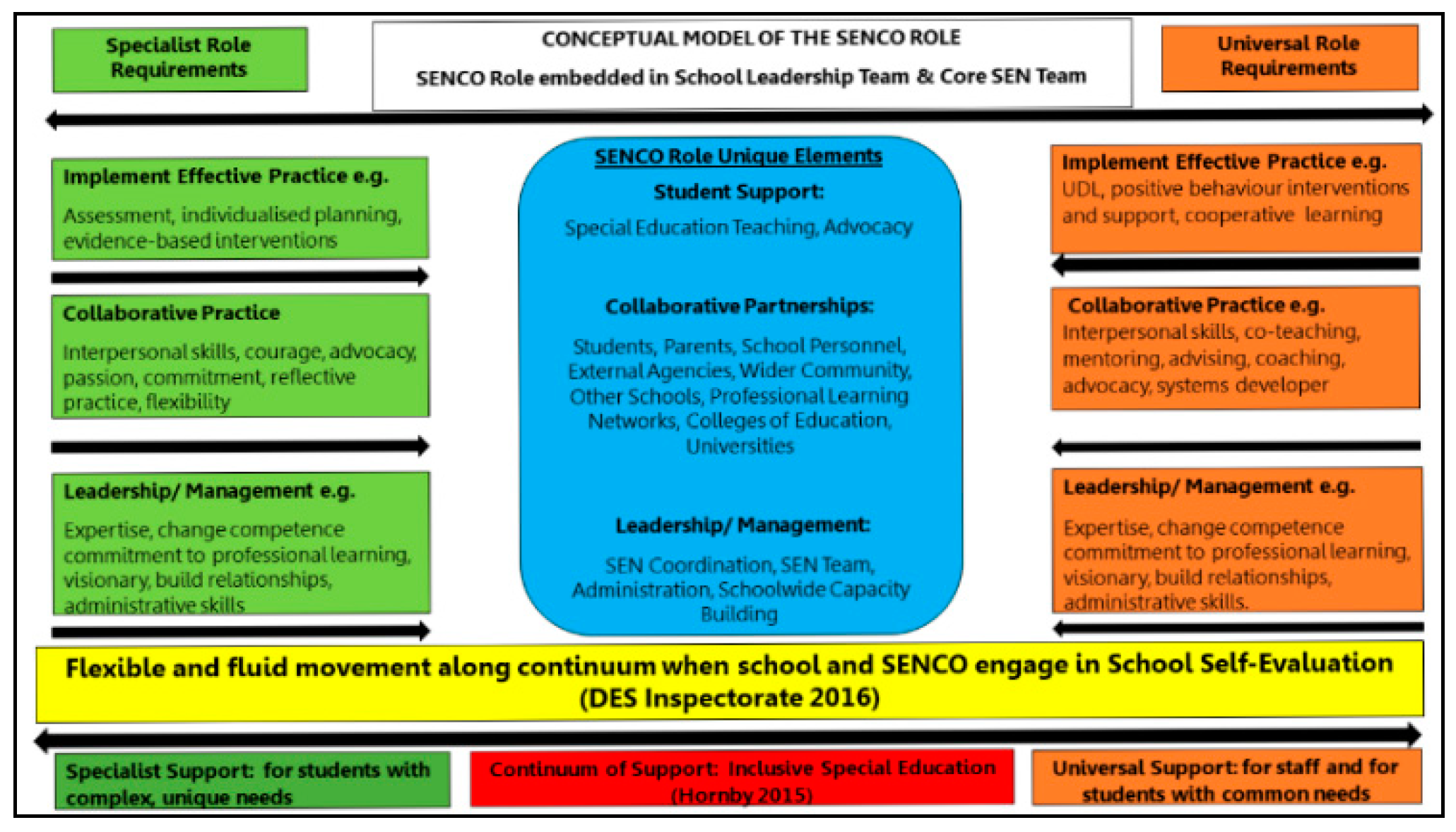
Education Sciences Free Full Text Leading Inclusive Learning This paper details a cross cultural study of inclusive leadership practices within a basic education context in each of the following countries: australia, canada, and colombia. each school was selected after district educational leaders identified the school as being inclusive of students with diverse learning needs over an extended period of time. the researchers were particularly interested. Inclusive values are integral to early childhood education and care (ecec) policies, promoting equal participation opportunities and individual support for all children. play serves as a method for meaningful engagement, mutual cultural knowledge creation, and learning within ecec. pedagogical play entails teachers’ observation, interaction, support, and guidance. this study investigates.
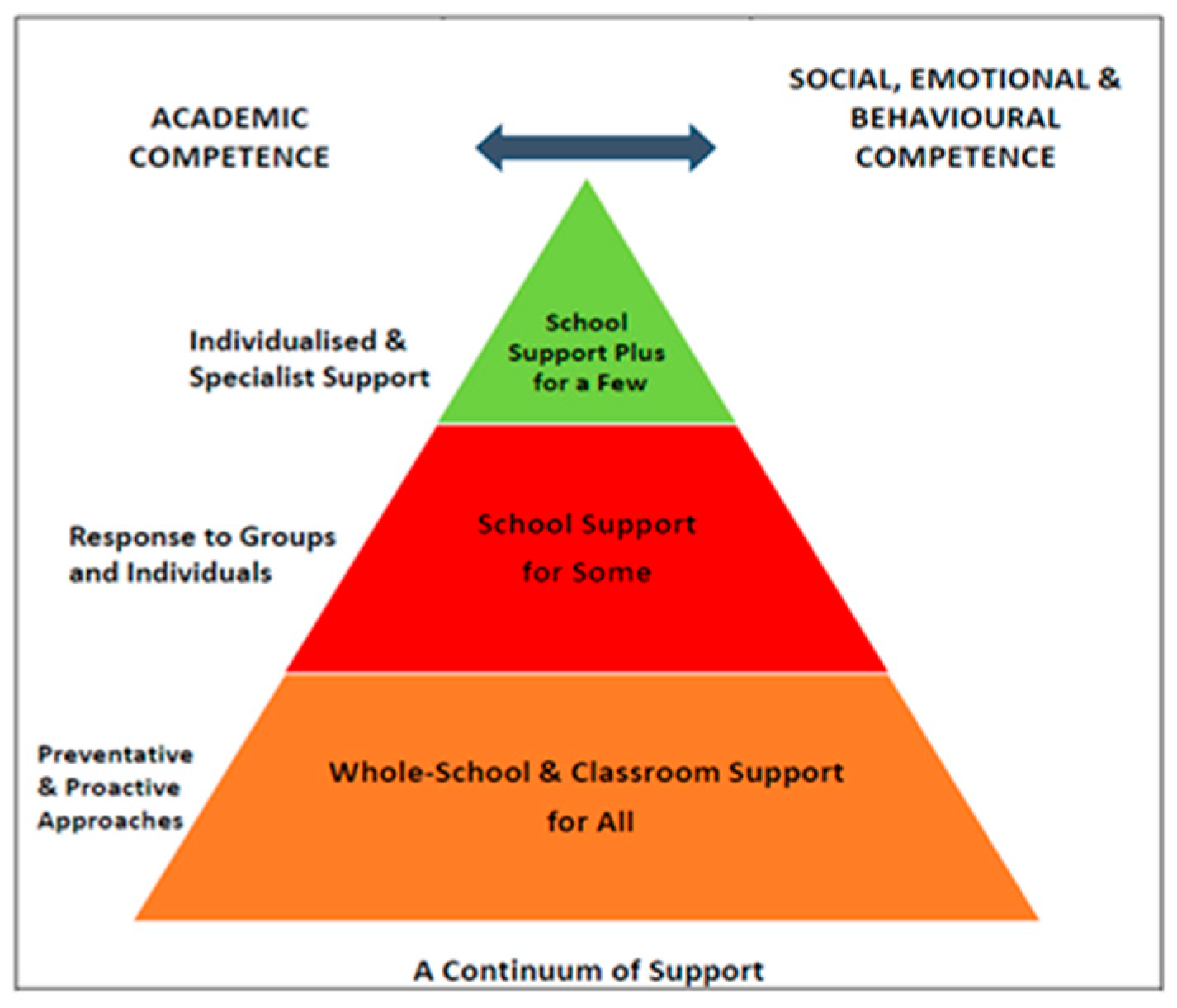
Education Sciences Free Full Text Leading Inclusive Learning Inclusive educational practices demand social justice where all students with special educational needs have the same right to access education, irrespective of their special needs. increasingly, across the world, teachers are supporting and defending the inclusion of students with disabilities in mainstream schools and classrooms. this is also the case in pakistan, the site of this study. Inclusive education is not just a goal; it is a commitment to making sure that every student, regardless of their unique needs, can learn, grow, and thrive in a diverse classroom. however, as we explore the world of inclusive practices, it becomes evident that there are challenges to overcome, but also innovative solutions to celebrate. Ing practices of inclusive education in schools and in the community, a commitment to the principle of inclusion from policy makers, uni versities, schools, ngos, parents and others involved are necessary. the system of inclusive education in ar meniawas officiallyembraced in 2003 as a. national policy. so far, many local and interna. The purpose of this systematic review was to investigate the learning, social, and psychological outcomes of students with moderate, severe, and complex disabilities (mscd) in inclusive settings.

Science Education Towards Inclusion вђ Nova Science Publishers Ing practices of inclusive education in schools and in the community, a commitment to the principle of inclusion from policy makers, uni versities, schools, ngos, parents and others involved are necessary. the system of inclusive education in ar meniawas officiallyembraced in 2003 as a. national policy. so far, many local and interna. The purpose of this systematic review was to investigate the learning, social, and psychological outcomes of students with moderate, severe, and complex disabilities (mscd) in inclusive settings. 3. observable indicators. feedback informs a student and teacher about the student’s performance relative to learning goals, allowing the student to align e orts, actions and behaviours to achieve the learning goals. the teacher consistently provides feedback that is positive, useful, and timely to complete the task. Since the salamanca statement, efforts for inclusive education have continued. the sustainable development goals adopted in 2015 and specifically goal 4 recognizes the urgent need to provide equitable and inclusive quality education for all learners from the early years through compulsory schooling, technical and vocational education and training, higher education and lifelong learning.

Comments are closed.