E003 Functions Of Ecosystem Ecological Succession Primary Secondary Succession Homeostasis

E003 Functions Of Ecosystem Ecological Succession Primary Pmf ias environment video seriesvideo 003 explains chapter 04 — functions of an ecosystem — of pmf ias environment hardcopy.extra 10% discount on pmf ias pdf. Ecological functions in the food chain include the exchange of energy and nutrients. in general, ecosystems maintain a balance of producers, consumers, and decomposers. ecological succession is a key concept in ecology. ecological succession refers to the process through which the species and environment mix in a given area and change over time.
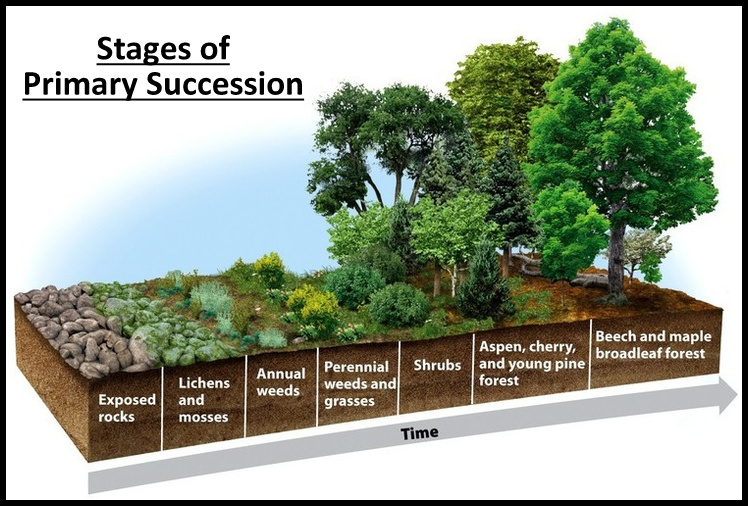
Ecological Succession Primary Secondary Succession Study Wrap Functions of ecosystem. the process by which communities of plant and animal species in an area are replaced or changed into another over a period of time is known as ecological succession. succession is a universal process of directional change in vegetation, on an ecological time scale. 19.5 summary. ecological succession is an orderly process of changes in community structure and function in an ecosystem with time mediated through the modifications in physical environment ultimately leading to a stable community over that area. it is a directional, continuous process and predictable. Figure 10.5.1 10.5. 1: secondary succession in the forest: secondary succession is shown in an oak and hickory forest after a forest fire. those organisms that could not escape are killed, but their bodies decompose, adding nutrients to the soil. these nutrients provide the basis for new plants to grow. Ecological succession was formerly seen as having a stable end stage called the climax, sometimes referred to as the 'potential vegetation' of a site, and shaped primarily by the local climate figure 4.3.4.5 4.3.4. 5. this idea has been largely abandoned by modern ecologists in favor of non equilibrium ideas of ecosystem dynamics.

Functions Of Ecosystem Ecological Succession Homeostasis Figure 10.5.1 10.5. 1: secondary succession in the forest: secondary succession is shown in an oak and hickory forest after a forest fire. those organisms that could not escape are killed, but their bodies decompose, adding nutrients to the soil. these nutrients provide the basis for new plants to grow. Ecological succession was formerly seen as having a stable end stage called the climax, sometimes referred to as the 'potential vegetation' of a site, and shaped primarily by the local climate figure 4.3.4.5 4.3.4. 5. this idea has been largely abandoned by modern ecologists in favor of non equilibrium ideas of ecosystem dynamics. Succession. the change in an ecosystem over time is called succession. succession describes the sequential change in species in a community over time. there are two types of succession: primary succession. secondary succession. the ecosystem that results from succession is called the climax community. Ecological succession is the process by which natural communities replace (or "succeed") one another over time. for example, when an old farm field in the midwestern u.s. is abandoned and left.

Comments are closed.