Double Angle Formulas What Are Double Angle Formulas Examples

The Complete Guide To The Trigonometry Double Angle Formulas Let us see the applications of the double angle formulas in the section below. examples using double angle formulas. example 1: if tan a = 3 4, find the values of sin 2a, cos 2a, and tan 2a. solution: since the value of tan a is given, we use the double angle formulas for finding each of sin 2a, cos 2a, and tan 2a in terms of tan. Using double angle formulas to find exact values. in the previous section, we used addition and subtraction formulas for trigonometric functions. now, we take another look at those same formulas. the double angle formulas are a special case of the sum formulas, where \(\alpha=\beta\). deriving the double angle formula for sine begins with the.
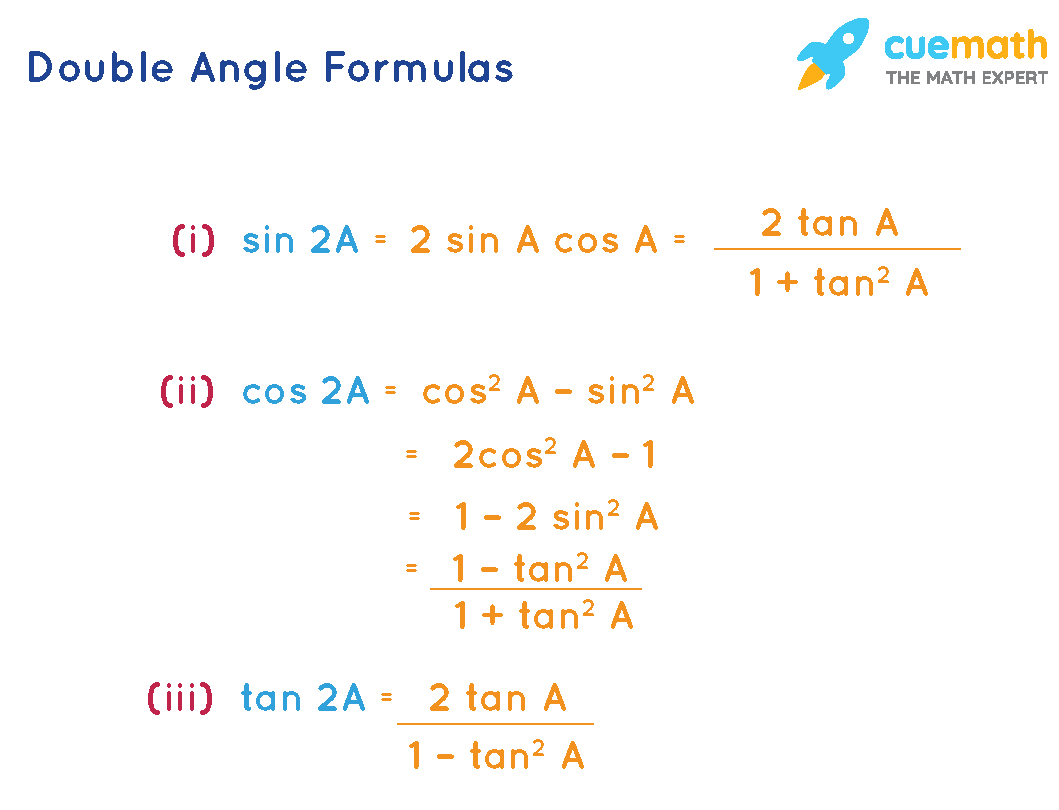
Double Angle Formulas What Are Double Angle Formulas Examples These formulas are especially important in higher level math courses, calculus in particular. also called the power reducing formulas, three identities are included and are easily derived from the double angle formulas. we can use two of the three double angle formulas for cosine to derive the reduction formulas for sine and cosine. The double angle formula for sine is: $2sinxcosx$. tangent double angle formula. it is possible to write the double angle formulas for the other trigonometric functions in terms of sine and cosine. for example, the tangent double angle formula is: $\frac{2tanx}{1 tan^2x}$. the proof for this formula is in example 1 below. examples. Prove trigonometry identities using double angles. trigonometry identities double angles (1) example: (1 − cos 2x) sin 2x = tan x. show video lesson. trigonometry identities double angle (2) example: prove tan x cos x = 2 cosec 2x. show video lesson. Esson: the double angle formulas: sine, cosine, and tangent. here are the double formulas. the next sections of this lesson will derive the double angle formulas using the sum angle formulas. double angle formula for sine. we will start by looking at a sum and difference angle formula for sine. we can use the formula to find a sum, but we will.

Double Angle Formula Equations Prove trigonometry identities using double angles. trigonometry identities double angles (1) example: (1 − cos 2x) sin 2x = tan x. show video lesson. trigonometry identities double angle (2) example: prove tan x cos x = 2 cosec 2x. show video lesson. Esson: the double angle formulas: sine, cosine, and tangent. here are the double formulas. the next sections of this lesson will derive the double angle formulas using the sum angle formulas. double angle formula for sine. we will start by looking at a sum and difference angle formula for sine. we can use the formula to find a sum, but we will. Also called the power reducing formulas, three identities are included and are easily derived from the double angle formulas. we can use two of the three double angle formulas for cosine to derive the reduction formulas for sine and cosine. let’s begin with [latex]\cos \left (2\theta \right)=1 2 {\sin }^ {2}\theta [ latex]. Cos2θ = cos²θ − sin²θ. the double angle formulas can be quickly derived from the angle sum formulas. here's a reminder of the angle sum formulas: sin (a b) = sinacosb cosasinb. cos (a b) = cosacosb − sinasinb. if you let θ = a = b in the double angle identities then you get. a b = 2θ.

The Complete Guide To The Trigonometry Double Angle Formulas Also called the power reducing formulas, three identities are included and are easily derived from the double angle formulas. we can use two of the three double angle formulas for cosine to derive the reduction formulas for sine and cosine. let’s begin with [latex]\cos \left (2\theta \right)=1 2 {\sin }^ {2}\theta [ latex]. Cos2θ = cos²θ − sin²θ. the double angle formulas can be quickly derived from the angle sum formulas. here's a reminder of the angle sum formulas: sin (a b) = sinacosb cosasinb. cos (a b) = cosacosb − sinasinb. if you let θ = a = b in the double angle identities then you get. a b = 2θ.

5 5 Double Angle Formulas I Double Angle Formulas A B C Ppt

Comments are closed.