Double Angle Formula Equations

The Complete Guide To The Trigonometry Double Angle Formulas Using double angle formulas to find exact values. in the previous section, we used addition and subtraction formulas for trigonometric functions. now, we take another look at those same formulas. the double angle formulas are a special case of the sum formulas, where \(\alpha=\beta\). deriving the double angle formula for sine begins with the. Examples using double angle formulas. example 1: if tan a = 3 4, find the values of sin 2a, cos 2a, and tan 2a. solution: since the value of tan a is given, we use the double angle formulas for finding each of sin 2a, cos 2a, and tan 2a in terms of tan. sin2a= 2tana 1 tan2a = 2(3 4) 1 (3 4)2 = 24 25 sin 2 a = 2 tan a 1 tan 2 a = 2 (3 4) 1.
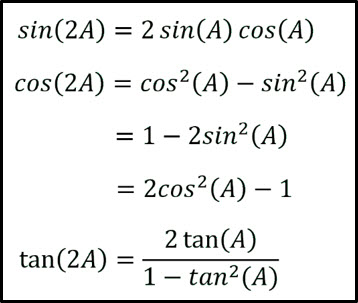
Double Angle Formula Equations Trigonometric identities. formulas expressing trigonometric functions of an angle 2x in terms of functions of an angle x, sin (2x) = 2sinxcosx (1) cos (2x) = cos^2x sin^2x (2) = 2cos^2x 1 (3) = 1 2sin^2x (4) tan (2x) = (2tanx) (1 tan^2x). (5) the corresponding hyperbolic function double angle formulas are sinh (2x) = 2sinhxcoshx (6) cosh (2x. Using double angle formulas to find exact values. in the previous section, we used addition and subtraction formulas for trigonometric functions. now, we take another look at those same formulas. the double angle formulas are a special case of the sum formulas, where α = β. α = β. deriving the double angle formula for sine begins with the. Deriving the double angle formula for sine begins with the sum formula, sin(α β) = sin α cos β cos α sinβ. if we let α = β = θ, then we have. sin(θ θ) = sin θcos θ cos θ sin θ sin(2θ) = 2sin θ cos θ. deriving the double angle for cosine gives us three options. first, starting from the sum formula, cos(α β) = cos α. The trigonometric double angle formulas give a relationship between the basic trigonometric functions applied to twice an angle in terms of trigonometric functions of the angle itself. tips for remembering the following formulas: we can substitute the values (2x) (2x) into the sum formulas for \sin sin and \cos. cos.

Comments are closed.