Domain And Range Math Algebra Functions F If 1 Showme
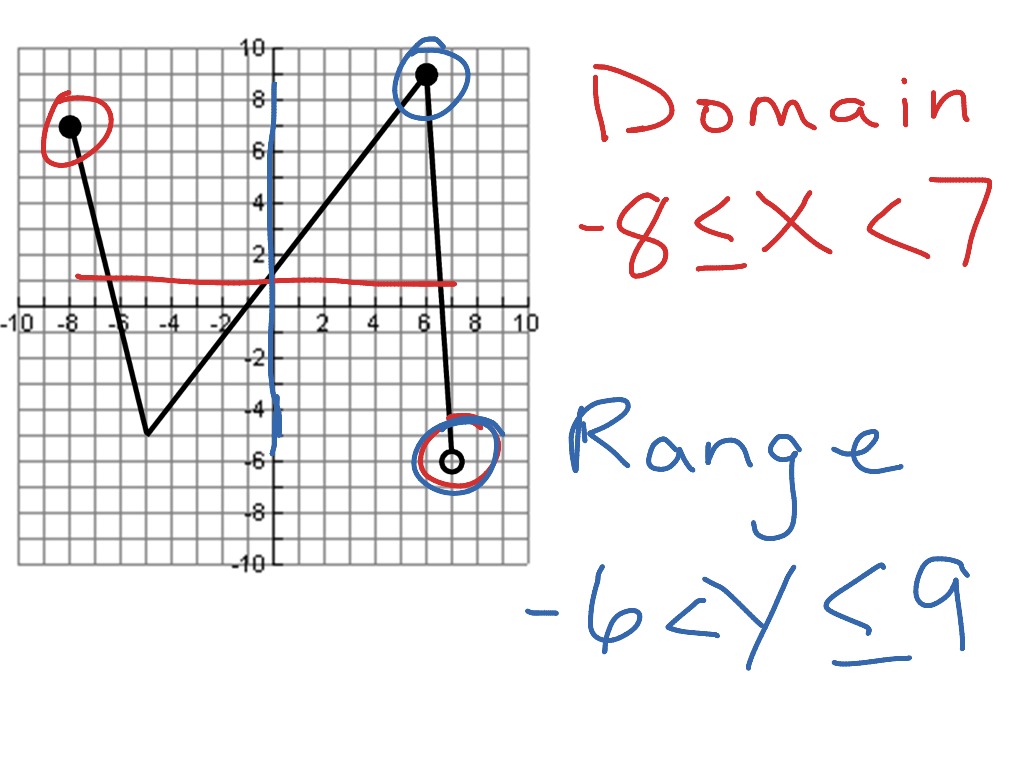
Domain And Range Math Algebra Functions F If 1 Showme Domain and range by kerisha tillmom september 8, 2012 math; algebra; functions; f.if.1; you should do so only if this showme contains inappropriate content. Identify and write domain and range by lindsay chatel february 1, 2012 math; algebra; functions; f.if.1; you should do so only if this showme contains.

Domain And Range Math Algebra Functions F If 1 Showme The domain and range of a function is all the possible values of the independent variable, x, for which y is defined. the range of a function is all the possible values of the dependent variable y. in other words, the domain is the set of values that we can plug into a function that will result in a real y value; the range is the set of values. The range also excludes negative numbers because the square root of a positive number x is defined to be positive, even though the square of the negative number − √x also gives us x. figure 3.3.20: cube root function f(x) = 3√x. for the cube root function f(x) = 3√x, the domain and range include all real numbers. Can there be functions in which the domain and range do not intersect at all? yes. for example, the function f (x) = − 1 x f (x) = − 1 x has the set of all positive real numbers as its domain but the set of all negative real numbers as its range. as a more extreme example, a function’s inputs and outputs can be completely different. The range is the set of all second elements of ordered pairs (y coordinates). only the elements "used" by the relation or function constitute the range. domain: all x values that are to be used (independent values). range: all y values that are used (dependent values).
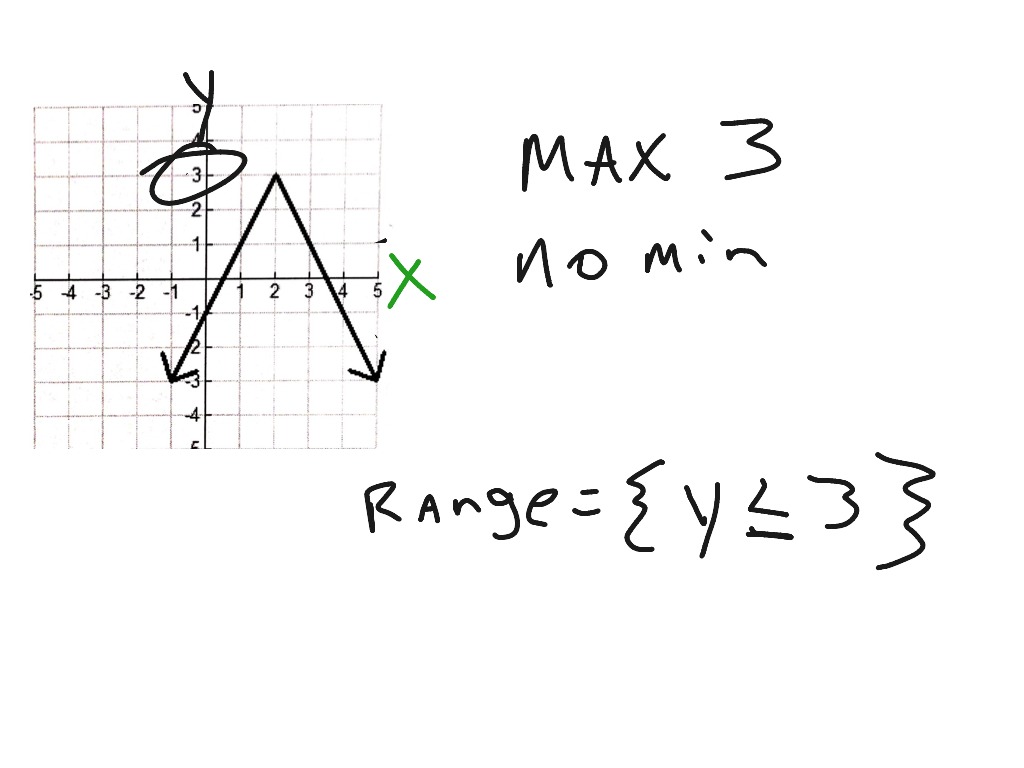
Domain And Range Video 7 Math Algebra Functions F If 1 Can there be functions in which the domain and range do not intersect at all? yes. for example, the function f (x) = − 1 x f (x) = − 1 x has the set of all positive real numbers as its domain but the set of all negative real numbers as its range. as a more extreme example, a function’s inputs and outputs can be completely different. The range is the set of all second elements of ordered pairs (y coordinates). only the elements "used" by the relation or function constitute the range. domain: all x values that are to be used (independent values). range: all y values that are used (dependent values). Using the tree table above, determine a reasonable domain and range. solution. we could combine the data provided with our own experiences and reason to approximate the domain and range of the function \(h = f(c)\). for the domain, possible values for the input circumference \(c\), it doesn’t make sense to have negative values, so \(c > 0\). Domain. the domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable. in plain english, this definition means: the domain is the set of all possible x values which will make the function "work", and will output real y values. when finding the domain, remember: the denominator (bottom) of a fraction cannot be zero.
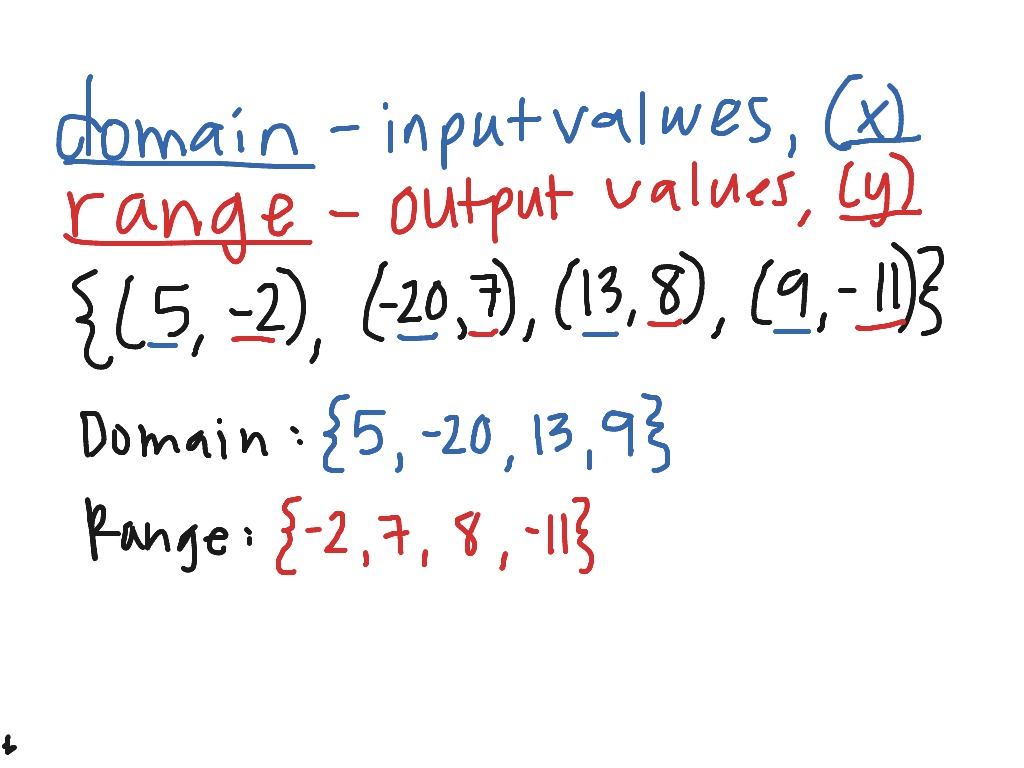
Identify And Write Domain And Range Math Algebra Functions F Using the tree table above, determine a reasonable domain and range. solution. we could combine the data provided with our own experiences and reason to approximate the domain and range of the function \(h = f(c)\). for the domain, possible values for the input circumference \(c\), it doesn’t make sense to have negative values, so \(c > 0\). Domain. the domain of a function is the complete set of possible values of the independent variable. in plain english, this definition means: the domain is the set of all possible x values which will make the function "work", and will output real y values. when finding the domain, remember: the denominator (bottom) of a fraction cannot be zero.

Comments are closed.