Disparities In Greenspace Associated With Sleep Duration Amo

Disparities In Greenspace Associated With Sleep Duration Amo Urban environmental exposures are becoming recognized as another important factor that can have an influence on sleep. 10,11 for example, residing in a noisier neighborhood has been associated with later sleep onset and shorter sleep duration. 10 air pollution has been associated with both obstructive sleep apnea 12 and sleep disordered. Residing in urban neighborhoods of greater greenness was associated with improved sleep duration among children of low ses but not higher ses. these findings support the importance of widely reported disparities in exposure and access to greenspace in socioeconomically disadvantaged populations.

Pdf Disparities In Greenspace Associated With Sleep Duration Among The most commonly examined neighborhood exposure was low socioeconomic status (40 studies), which was associated with sleep outcomes in 58% of studies (primarily shorter sleep duration, later. Background: more than half of adolescent children do not get the recommended 8 hours of sleep necessary for optimal growth and development. in adults, several studies have evaluated effects of urban stressors including lack of greenspace, air pollution, noise, nighttime light, and psychosocial stress on sleep duration. little is known about these effects in adolescents, however, it is known. Proximity to green space, natural water, and greater tree canopy has been associated with better sleep. 33 more recreational areas and a better walking environment are also associated with weight loss and greater physical activity, 34 which themselves are associated with improved sleep quality, latency, and duration. 35 community gardens may. Physical environment and adult sleep health. exposure to a natural physical environment has been associated with better sleep health. observational studies have shown that adults living in neighborhoods with access to green space or natural water features have a lower likelihood of insufficient sleep. 6, 7 green vegetation has been associated with better cardiovascular biomarkers and lower.
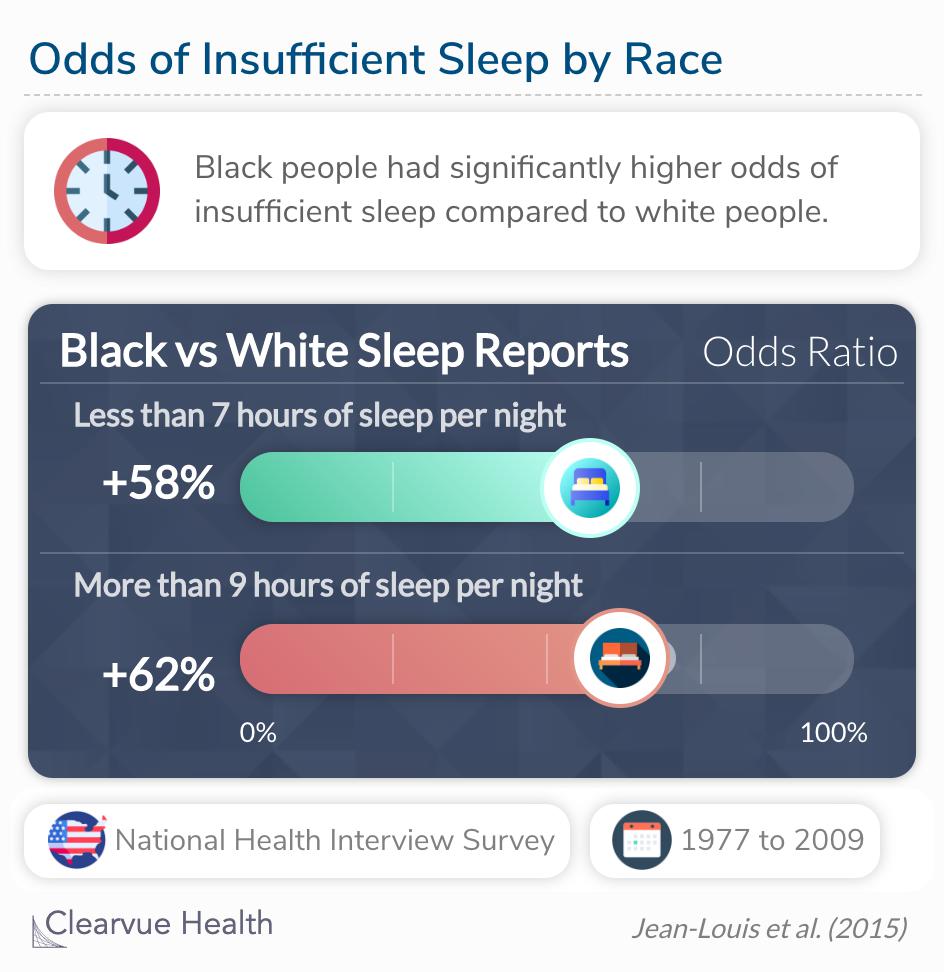
3 Charts Racial Disparities In Sleep Proximity to green space, natural water, and greater tree canopy has been associated with better sleep. 33 more recreational areas and a better walking environment are also associated with weight loss and greater physical activity, 34 which themselves are associated with improved sleep quality, latency, and duration. 35 community gardens may. Physical environment and adult sleep health. exposure to a natural physical environment has been associated with better sleep health. observational studies have shown that adults living in neighborhoods with access to green space or natural water features have a lower likelihood of insufficient sleep. 6, 7 green vegetation has been associated with better cardiovascular biomarkers and lower. Low moderate greenspace was also marginally associated with a higher prevalence of short sleep duration (pr=1.01 [0.98 1.05]), insomnia symptoms (pr=1.03 [0.99 1.07]), and comorbid short sleep. A systematic review. evidence indicates that exposure to particulate matter, secondhand smoke, dioxins and dioxin like compounds, lead, mercury, pesticides, solvents, and exposures related to the gulf war are associated with worse sleep health and disorders. expand.

Stages Of Sleep Introduction To Psychology Low moderate greenspace was also marginally associated with a higher prevalence of short sleep duration (pr=1.01 [0.98 1.05]), insomnia symptoms (pr=1.03 [0.99 1.07]), and comorbid short sleep. A systematic review. evidence indicates that exposure to particulate matter, secondhand smoke, dioxins and dioxin like compounds, lead, mercury, pesticides, solvents, and exposures related to the gulf war are associated with worse sleep health and disorders. expand.

Comments are closed.