Digestive System Learn Anatomy
Digestive System Learn Anatomy Anatomy & physiology of digestion: 10 facts that explain how the body absorbs nutrients. what does the digestive system do? the digestive system is a kind of processing plant inside the body. it pulls in food and pushes it through organs and structures where the processing happens. the fuels we need are extracted, and the digestive system. Extending from the mouth to the anus, the digestive tract is one of the largest systems in the human body. it contains organs that regulate food intake, its digestion and absorbtion of the useful materia that it contains. in addition to this, the digestive system also eliminates the waste products from food and products from various endogenous.

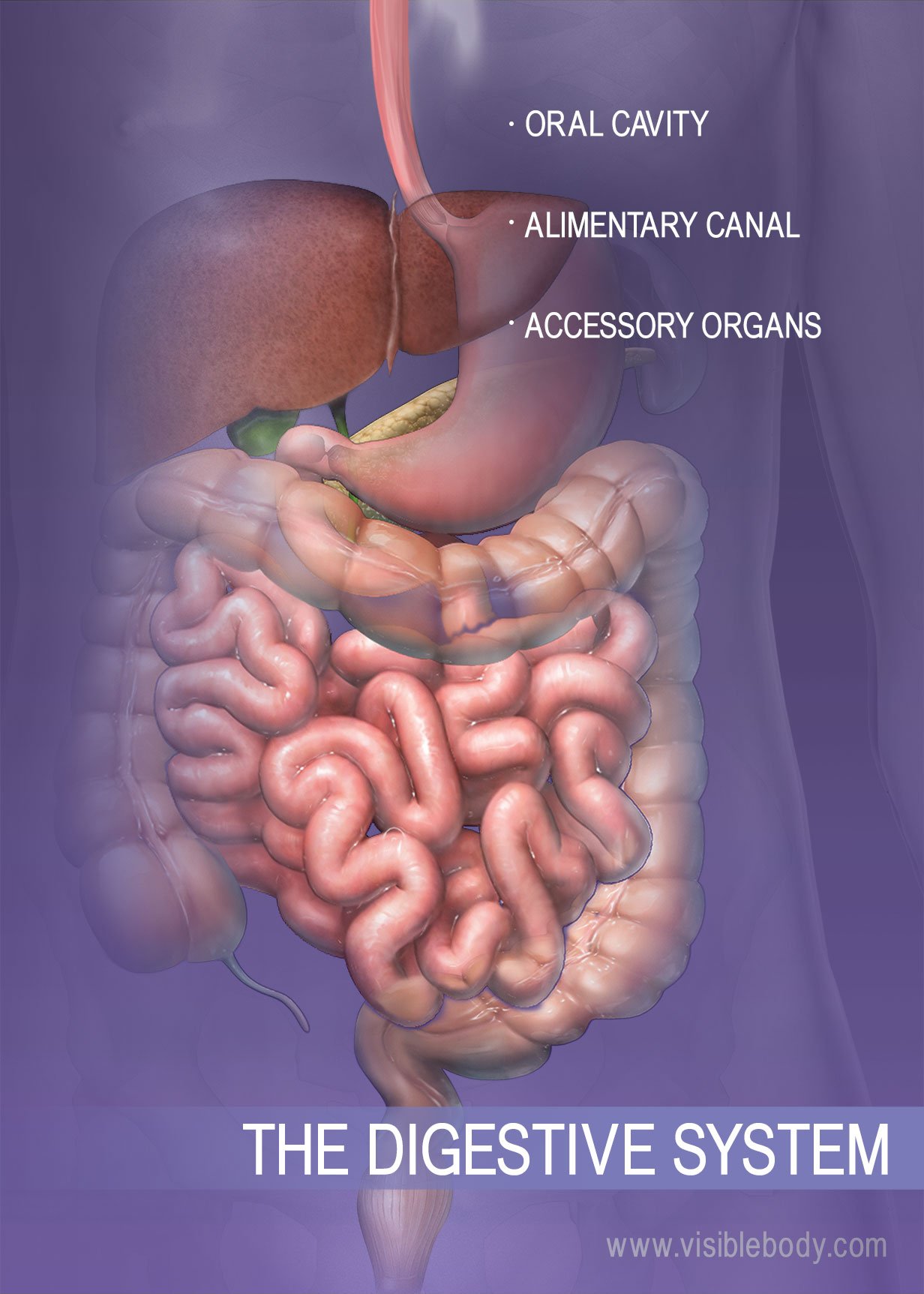
Digestive System Structure Of Digestive System The main organs that make up your digestive system are the organs known as your gastrointestinal tract. they are: your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus. assisting your gi organs along the way are your pancreas, gallbladder and liver. here’s how these organs work together in your digestive system. The digestive system use our 3d models and detailed descriptions to learn all about the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower digestive tract as well as the accessory digestive organs like the teeth, tongue, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system, also known as the gastrointestinal system, regulates food intake, enables the digestion and absorption of nutrients and enables waste elimination. 1. this digestive system is responsible for transforming the variety of foods consumed into usable energy and building blocks for bodily functions, growth and repair. 1,2. Hormones secreted by several endocrine glands, as well as endocrine cells of the pancreas, the stomach, and the small intestine, contribute to the control of digestion and nutrient metabolism. in turn, the digestive system provides the nutrients to fuel endocrine function. table 23.1 gives a quick glimpse at how these other systems contribute.

File Digestive System For Kids Png Wikimedia Commons The digestive system, also known as the gastrointestinal system, regulates food intake, enables the digestion and absorption of nutrients and enables waste elimination. 1. this digestive system is responsible for transforming the variety of foods consumed into usable energy and building blocks for bodily functions, growth and repair. 1,2. Hormones secreted by several endocrine glands, as well as endocrine cells of the pancreas, the stomach, and the small intestine, contribute to the control of digestion and nutrient metabolism. in turn, the digestive system provides the nutrients to fuel endocrine function. table 23.1 gives a quick glimpse at how these other systems contribute. The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. although the small intestine is the workhorse of the system, where the majority of digestion occurs, and where most of the released nutrients are absorbed into the blood or lymph, each of the digestive system organs makes a vital contribution to this. The human digestive system is the means by which tissues and organs receive nutrients to function. learn more about the hilum. we'll go over the main differences and dive into the anatomy.

Comments are closed.