Diabetes Care Blood Sugar Monitoring And Control Nugenomics

Diabetes Care Blood Sugar Monitoring And Control Nugenomics If you have any more questions, please feel free to write to us at [email protected] or call us directly at 91 9176655912. you can also visit here to know more about how we can help you and make your life better. sources: cdc, webmd (1, 2), diabetes uk, niddk. The introduction of home blood glucose monitoring (bgm) in the late 1970s and regulatory clearance of the first meter for this purpose in 1980 revolutionized the self care of people with diabetes (pwd) (1 – 3). although often referred to as “self monitoring of blood (or plasma) glucose,” this form of glucose monitoring will be referred to.

Diabetes Care Blood Sugar Monitoring And Control Nugenomics Role of nutrigenomics in diabetes care. nutrigenomics holds immense potential for the effective management of diabetes mellitus. armed with the correct knowledge, healthcare providers can design customized nutrition plans that target the identified genetic predispositions. for instance, if an individual is found to have genetic variants. Any condition leading to deterioration in glycemic control necessitates more frequent monitoring of blood glucose; ketosis prone patients also require urine or blood ketone monitoring. if accompanied by ketosis, vomiting, or alteration in the level of consciousness, marked hyperglycemia requires temporary adjustment of the treatment regimen and. Self monitoring blood glucose improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetes without intensive treatment: a systematic review and meta analysis. diabetes res clin pract 2018; 142:173. danne t, nimri r, battelino t, et al. international consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. diabetes care 2017; 40:1631. In hospitalized critically ill and noncritically ill patients, point of care glucose monitoring remains the gold standard. before the coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19) pandemic, there were few studies on using real time continuous glucose monitoring (rtcgm) in hospitalized patients, but the pandemic escalated the need for minimizing patient contact and compelled us to explore rtcgm to.
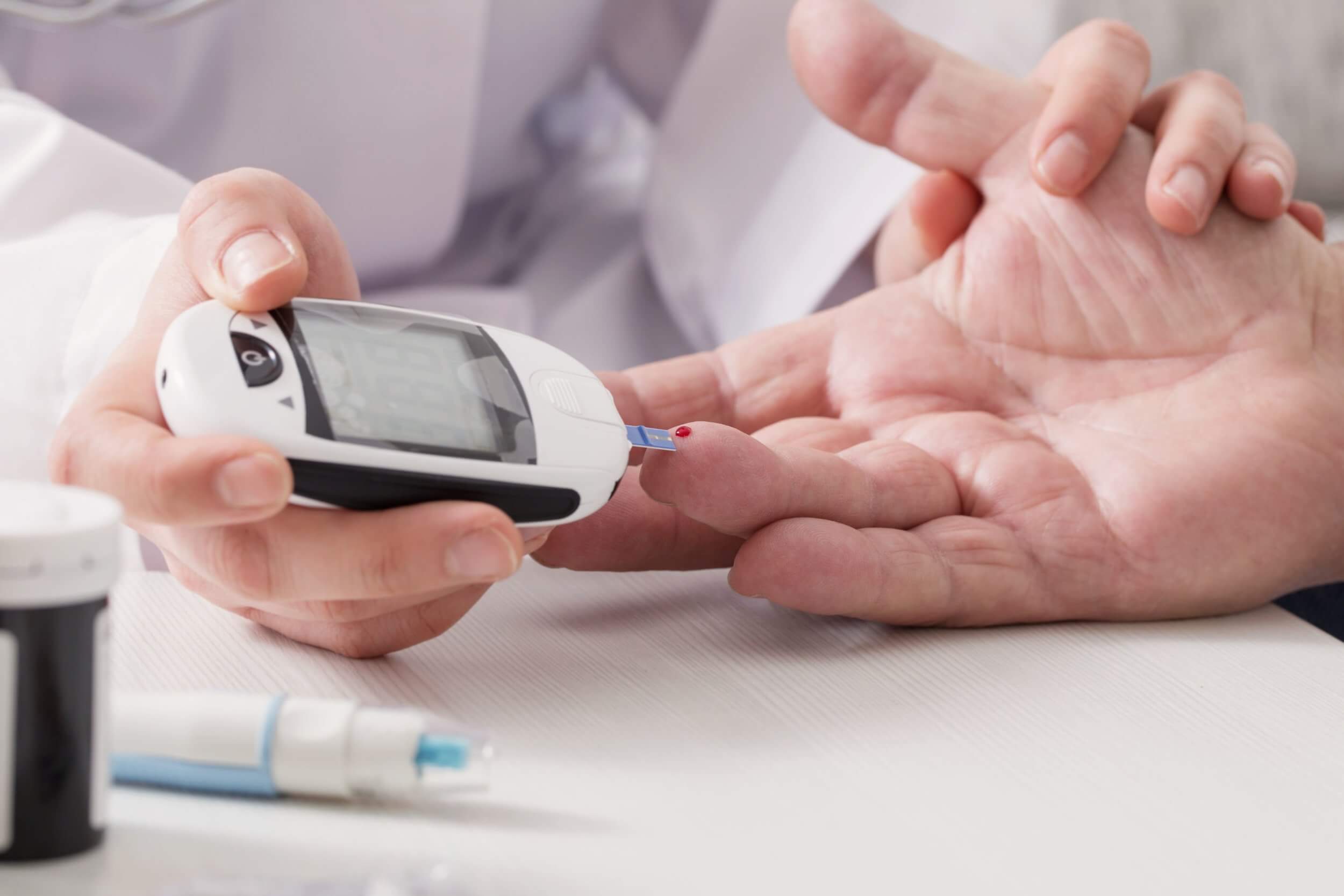
Continuous Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems Part 1 The Evolution Of Self monitoring blood glucose improves glycemic control in type 2 diabetes without intensive treatment: a systematic review and meta analysis. diabetes res clin pract 2018; 142:173. danne t, nimri r, battelino t, et al. international consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. diabetes care 2017; 40:1631. In hospitalized critically ill and noncritically ill patients, point of care glucose monitoring remains the gold standard. before the coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19) pandemic, there were few studies on using real time continuous glucose monitoring (rtcgm) in hospitalized patients, but the pandemic escalated the need for minimizing patient contact and compelled us to explore rtcgm to. The glucose monitoring field represents an essential component of the management of diabetes. beside self–blood glucose monitoring (sbgm), which primarily supported self management and medication adjustment of people with diabetes, continuous glucose monitoring (cgm) has emerged as a valuable tool to assess the effectiveness and safety of treatment in many patients with type 1 diabetes and. Below are steps to test your blood sugar: make sure the meter is charged and ready to use. wash your hands with soap and warm water, and dry well before each test. massage or shake out your hand to get blood into your finger. use a lance to prick your finger. squeezing from the base of the finger, gently place a small amount of blood onto the.

Comments are closed.