Climate Change Global Warming Natural Disaster Extreme Weather
Future Of Climate Change Climate Change Science Us Epa Climate change caused by the emission of greenhouse gases from human activities affects global temperature and precipitation.records from the intergovernmental panel on climate change indicate that the global average temperature has increased by at least 0.4 degrees celsius (0.72 degrees fahrenheit) since the 1970s, and that by 2100, it could increase to around 4 degrees celsius (7.2 degrees. Scientists use a combination of climate models (simulations) and land, air, sea, and space based observations to research how extreme weather events change over time. first, scientists examine historical records to determine the frequency and intensity of past events. many of these long term records date back to the 1950s, though some start in.

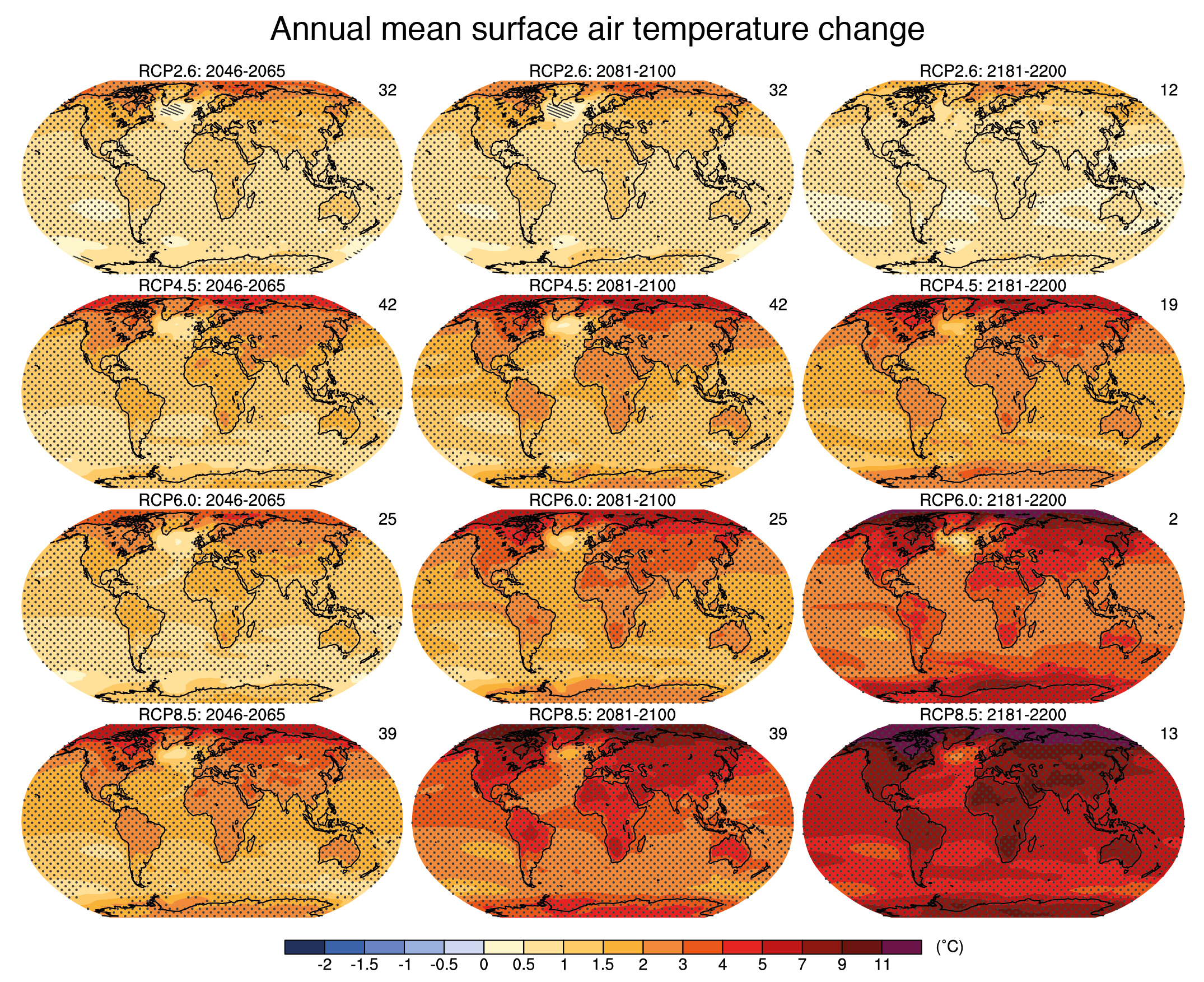
Extreme Weather Across Us Driven By Climate Change But climate change is making the weather conditions needed for wildfires to spread more likely, the ipcc says. extreme, long lasting heat draws more moisture out of soils and vegetation. Climate change and increasingly extreme weather events, have caused a surge in natural disasters over the past 50 years disproportionately impacting poorer countries, the world meteorological organization (wmo) and un office for disaster risk reduction (undrr) said on wednesday. Typically, these events are considered extreme if they are unlike 90% or 95% of similar weather events that happened before in that same area. global warming can contribute to the intensity of heat waves by increasing the chances of very hot days and nights. warming air also boosts evaporation, which can worsen drought. The ar6 assessment shows that every bit of global warming matters and that changes in global warming of 0.5°c lead to statistically significant changes in mean climate and climate extremes on global scale and for large regions (sections 4.6.2, 11.2.4, 11.3, 11.4, 11.6 and 11.9, figures 11.8 and 11.9, atlas and interactive atlas), as also assessed in ipcc sr1.5.

How Global Warming Fueled Five Extreme Weather Events The New York Times Typically, these events are considered extreme if they are unlike 90% or 95% of similar weather events that happened before in that same area. global warming can contribute to the intensity of heat waves by increasing the chances of very hot days and nights. warming air also boosts evaporation, which can worsen drought. The ar6 assessment shows that every bit of global warming matters and that changes in global warming of 0.5°c lead to statistically significant changes in mean climate and climate extremes on global scale and for large regions (sections 4.6.2, 11.2.4, 11.3, 11.4, 11.6 and 11.9, figures 11.8 and 11.9, atlas and interactive atlas), as also assessed in ipcc sr1.5. Many are spending up to a tenth of their budgets just managing extreme weather disasters. many of those extreme events are driven by the emissions of planet heating greenhouse gases, but africa is. The link between extreme weather and climate change has never been more clear. experts say drawing the direct connection from specific storms to the nebulous idea of climate change can help people.

Comments are closed.