Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infections Lesson 1

Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infections Lesson 1 An overview of a practical classification scheme for pathological fungi, as well as a summary of their microscopic structure. differences between yeast and. Fungal infections on or in your skin can look red, swollen or bumpy. they can look like a rash or you might be able to see a lump under your skin. fungal infections in your nails can make them discolored (yellow, brown or white), thick or cracked. fungal infections in your mouth or throat can cause a white coating or patches.
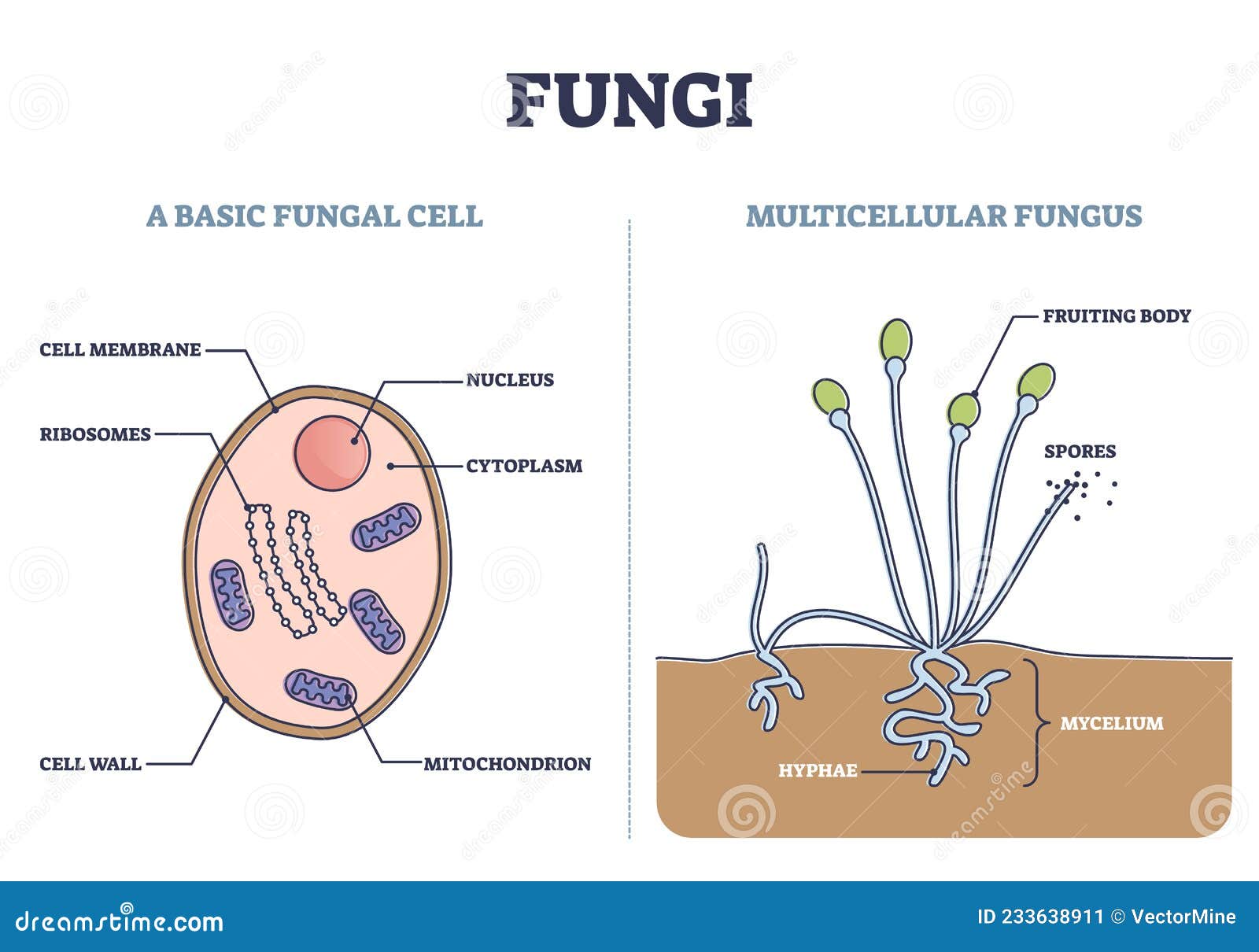
Structure Of Fungal Cell With Diagram Fungi Fungal classification, or taxonomy, is a way of organizing the vast diversity within the fungal kingdom. historically, fungi were classified based on their morphology, reproduction, and growth patterns. with advances in molecular biology, though, the focus has shifted to dna sequencing, offering more accurate insights into evolutionary. Fungi can occur as yeasts, molds, or as a combination of both forms. some fungi are capable of causing superficial, cutaneous, subcutaneous, systemic or allergic diseases. yeasts are microscopic fungi consisting of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds, in contrast, occur in long filaments known as hyphae, which grow by apical extension. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that exist as yeast, molds, or both forms. yeasts consist of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds occur in filaments, also known as hyphae, which extend by apical elongation. dimorphic fungi grow as mold in the environment and as yeast cells or spherules (sac like cells that are the reproductive form of. These fungi may produce a range of infections from superficial to subcutaneous to deep (visceral) infection characterized by the presence of dematiaceous hyphal and or yeast like cells in tissue. such deep infections due to dematiaceous fungi are termed phaeohyphomycosis. sporotrichosis is the third general class of subcutaneous mycoses.

Classification And Structure Of Fungi Fungal Infectio Vrogue Co Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that exist as yeast, molds, or both forms. yeasts consist of solitary cells that reproduce by budding. molds occur in filaments, also known as hyphae, which extend by apical elongation. dimorphic fungi grow as mold in the environment and as yeast cells or spherules (sac like cells that are the reproductive form of. These fungi may produce a range of infections from superficial to subcutaneous to deep (visceral) infection characterized by the presence of dematiaceous hyphal and or yeast like cells in tissue. such deep infections due to dematiaceous fungi are termed phaeohyphomycosis. sporotrichosis is the third general class of subcutaneous mycoses. 1.7 million (2020) [12] fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. [5][13] different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. [3][6] superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet. Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that belong to the kingdom of fungi. these are eukaryotic, non photosynthetic creatures that take nourishment from their surroundings by absorbing organic materials. fungi can live in many different places, including soil, water, plants, and animals. importance of fungal classification.
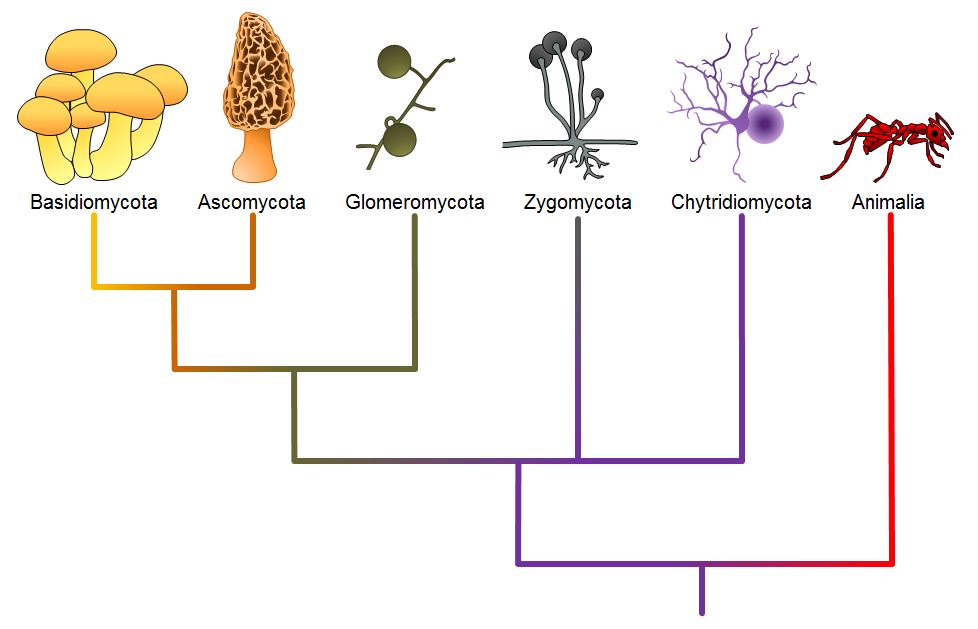
Classifications Of Fungi вђ Introductory Biology Evolutionary And 1.7 million (2020) [12] fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. [5][13] different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. [3][6] superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet. Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that belong to the kingdom of fungi. these are eukaryotic, non photosynthetic creatures that take nourishment from their surroundings by absorbing organic materials. fungi can live in many different places, including soil, water, plants, and animals. importance of fungal classification.

Comments are closed.