Carbon Oxygen Triple Bond Aldoqofrederick

Carbon Oxygen Triple Bond Aldoqofrederick A carbon–oxygen bond is a polar covalent bond between atoms of carbon and oxygen. [1][2][3]: 16–22 carbon–oxygen bonds are found in many inorganic compounds such as carbon oxides and oxohalides, carbonates and metal carbonyls, [4] and in organic compounds such as alcohols, ethers, and carbonyl compounds. [5]: 32–36 oxygen has 6 valence. Functional groups with a carbon–oxygen double bond (carbonyl groups) the carbonyl group c=o appears in several functional groups. aldehydes have at least one h atom bonded to the c=o, ketones have two carbon atoms bonded to the c=o, carboxylic acids have an oh group bonded to the c=o, thioesters have a sulfide like sulfur bonded to the c=o, amides have an amine like nitrogen bonded to the c.

Carbon Oxygen Triple Bond Aldoqofrederick Functional groups with a carbon–oxygen double bond (carbonyl groups) the carbonyl group, c=o c=o (pronounced car bo neel) is common to many of the families listed in table 3.1. carbonyl groups are present in a majority of organic compounds and in practically all biological molecules. these compounds therefore behave similarly in many. Hydrocarbons that are bonded together with only single bonds are alkanes. the simplest example is methane (shown below). when hydrocarbons have one or more double bonds, they are called alkenes. the simplest alkene is ethene (c 2 h 4) which contains a double bond between the two carbon atoms. ex. methane on left, ethene on right. However, these approaches rely on radical mechanisms that can be unselective. huang et al. present an alternative, nonradical activating paradigm in which a nickel catalyst cleaves the carbon oxygen bond of an ester and then excises carbon monoxide (co) rather than co 2. subtle ligand optimization was key to favoring this pathway. —jake s. yeston. Examples of double bonds are o 2 (oxygen, o=o), co 2 (carbon dioxide, o=c=o), and c 2 h 2 (ethylene, h c=c h). the double bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond. a pi bond forms by sideways overlapping of p orbitals. triple bond. a triple bond forms when two atoms share three electron pairs.

Carbon Oxygen Triple Bond Jaylinzebblair However, these approaches rely on radical mechanisms that can be unselective. huang et al. present an alternative, nonradical activating paradigm in which a nickel catalyst cleaves the carbon oxygen bond of an ester and then excises carbon monoxide (co) rather than co 2. subtle ligand optimization was key to favoring this pathway. —jake s. yeston. Examples of double bonds are o 2 (oxygen, o=o), co 2 (carbon dioxide, o=c=o), and c 2 h 2 (ethylene, h c=c h). the double bond consists of one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond. a pi bond forms by sideways overlapping of p orbitals. triple bond. a triple bond forms when two atoms share three electron pairs. By going through an analogous process for sp hybridization of nitrogen and oxygen we can arrive at the molecular structure of species containing carbon nitrogen and carbon oxygen triple bonds. notice that an oxygen containing a triple bond must also carry a positive charge in observance of the rules of covalent bonding. also notice that when. Triple bond. a triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order of three. the most common triple bond is in a nitrogen n 2 molecule; the second most common.
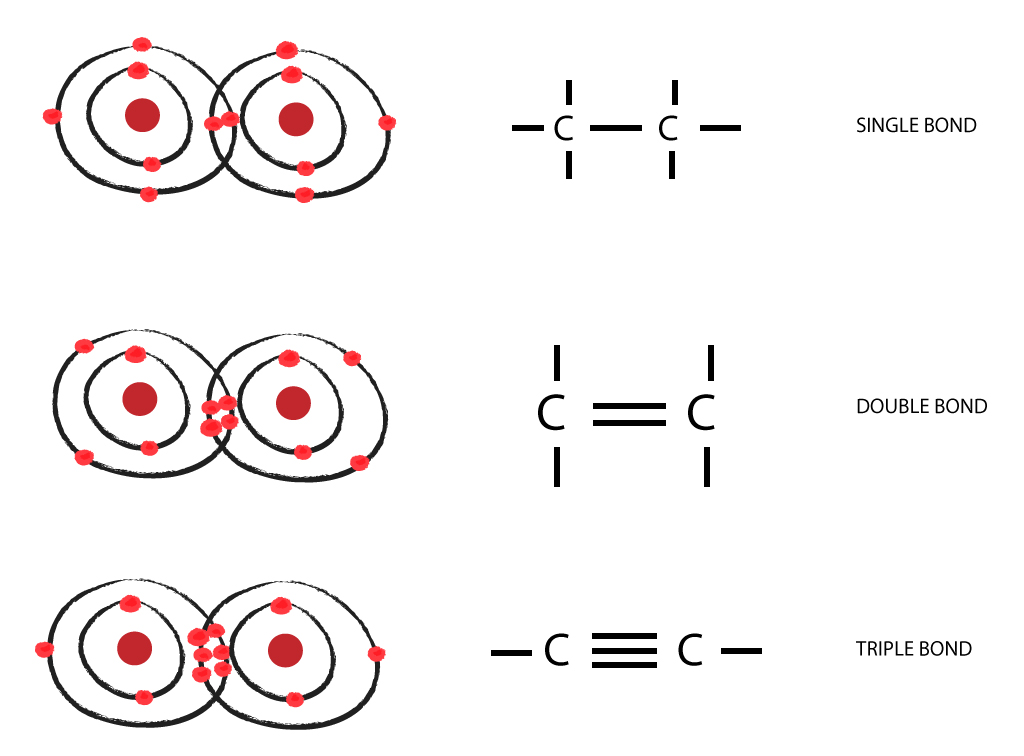
Carbon To Carbon Single Double Triple Bonds Surfguppy By going through an analogous process for sp hybridization of nitrogen and oxygen we can arrive at the molecular structure of species containing carbon nitrogen and carbon oxygen triple bonds. notice that an oxygen containing a triple bond must also carry a positive charge in observance of the rules of covalent bonding. also notice that when. Triple bond. a triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order of three. the most common triple bond is in a nitrogen n 2 molecule; the second most common.
Carbon Oxygen Triple Bond Adelaideaxharding

Comments are closed.