Cancers Free Full Text Primary And Acquired Resistance To
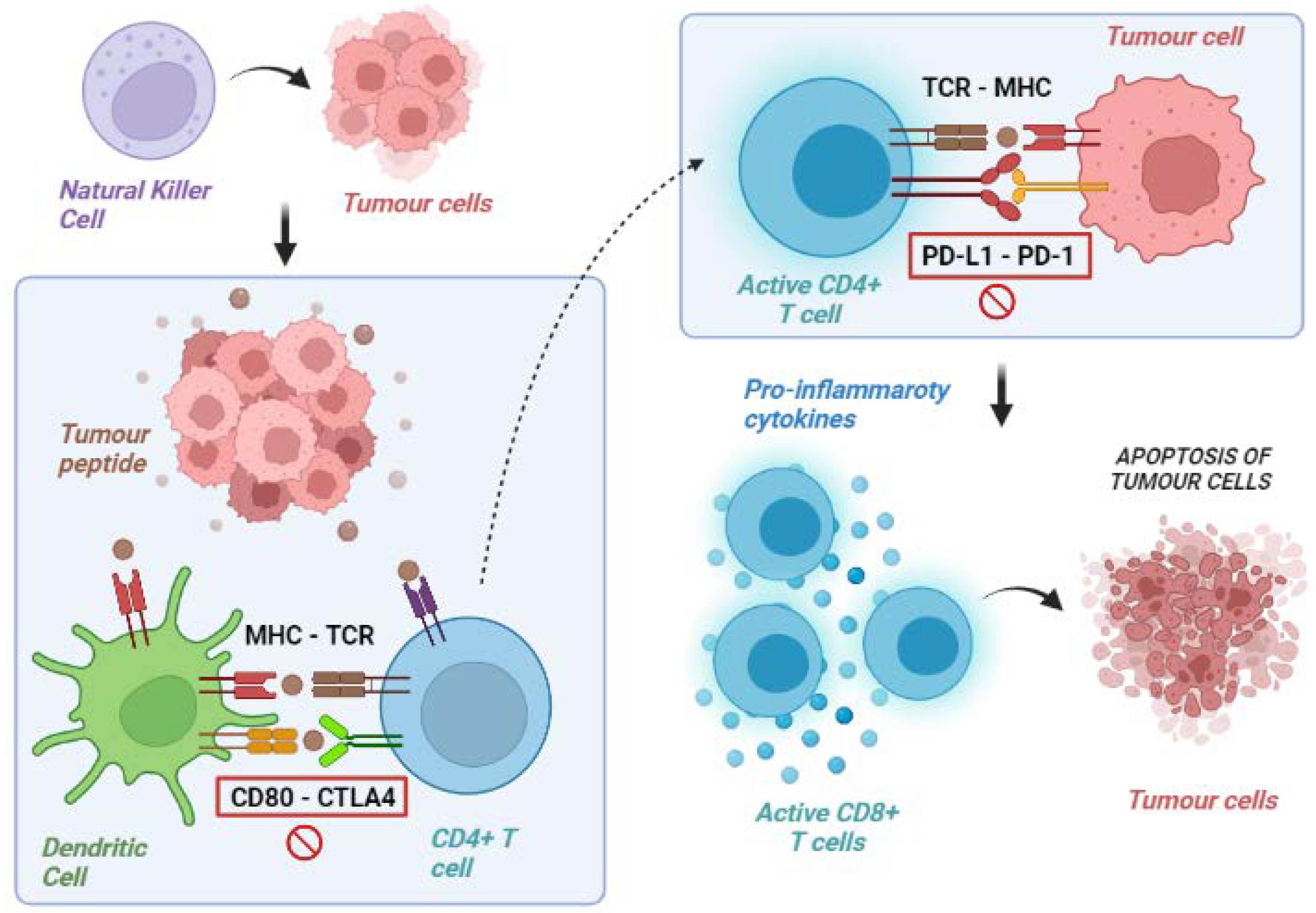
Cancers Free Full Text Mechanisms Of Primary And Acquired Immune checkpoint inhibitors have emerged as the treatment landscape of advanced non small cell lung cancer (nsclc) in recent years. however, approximately 80% of nsclc patients do not benefit from icis due to primary resistance (no initial response) or acquired resistance (tumor relapse after an initial response). in this review, we highlight the mechanisms of primary and secondary resistance. We agree with the reviewer on this point, and we have changes the manuscript title to “primary and acquired resistance to immunotherapy in lung cancer: unveiling the mechanisms underlying of immune checkpoint blockade therapy” 2: in subsec.4, in addition to chemotherapy, there are many other effective combination immunotherapy approaches.
Cancers Free Full Text Primary And Acquired Resistance To Adaptive immune resistance. a mechanism of resistance where a cancer is recognized by the immune system but it protects itself by adapting to the immune attack. given the evolving nature of the immune cancer cell interaction, this could clinically manifest as primary resistance, mixed responses or acquired resistance. Memon et al. demonstrate the relationship between persistent and upregulated interferon signaling and acquired resistance in tumors from patients with nsclc who have developed acquired resistance to pd (l)1 blockade. these findings inform approaches for overcoming acquired resistance, which occurs in >60% of patients with nsclc who initially respond to pd (l)1 blockade. Abstract. immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of patients with advanced stage metastatic melanoma, as well as patients with many other solid cancers, yielding long lasting responses and improved survival. however, a subset of patients who initially respond to immunotherapy, later relapse and develop therapy resistance (termed “acquired resistance”), whereas. Figure 1. clinical scenarios of primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to immunotherapy. (a) patient’s tumor is resistant to immunotherapy with no active immune response. (b) patient’s tumor is resistant to immunotherapy; active anti tumor immune response, but turned off by checkpoints or other adaptive resistance mechanisms.

Cancers Free Full Text Primary And Acquired Resistance Aga Abstract. immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized the treatment of patients with advanced stage metastatic melanoma, as well as patients with many other solid cancers, yielding long lasting responses and improved survival. however, a subset of patients who initially respond to immunotherapy, later relapse and develop therapy resistance (termed “acquired resistance”), whereas. Figure 1. clinical scenarios of primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to immunotherapy. (a) patient’s tumor is resistant to immunotherapy with no active immune response. (b) patient’s tumor is resistant to immunotherapy; active anti tumor immune response, but turned off by checkpoints or other adaptive resistance mechanisms. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) have rapidly altered the treatment landscape for multiple tumor types, providing unprecedented survival in some patients. despite the characteristic durability of response to ici, unfortunately many patients with initial response will later develop acquired resistance. the current understanding of mechanisms of acquired resistance to icis is remarkably. These therapeutic failures arise from innate (primary), adaptive, and acquired resistance mechanisms that depend on cancer cell features, tumor heterogeneity, tme, immune system, and other host.
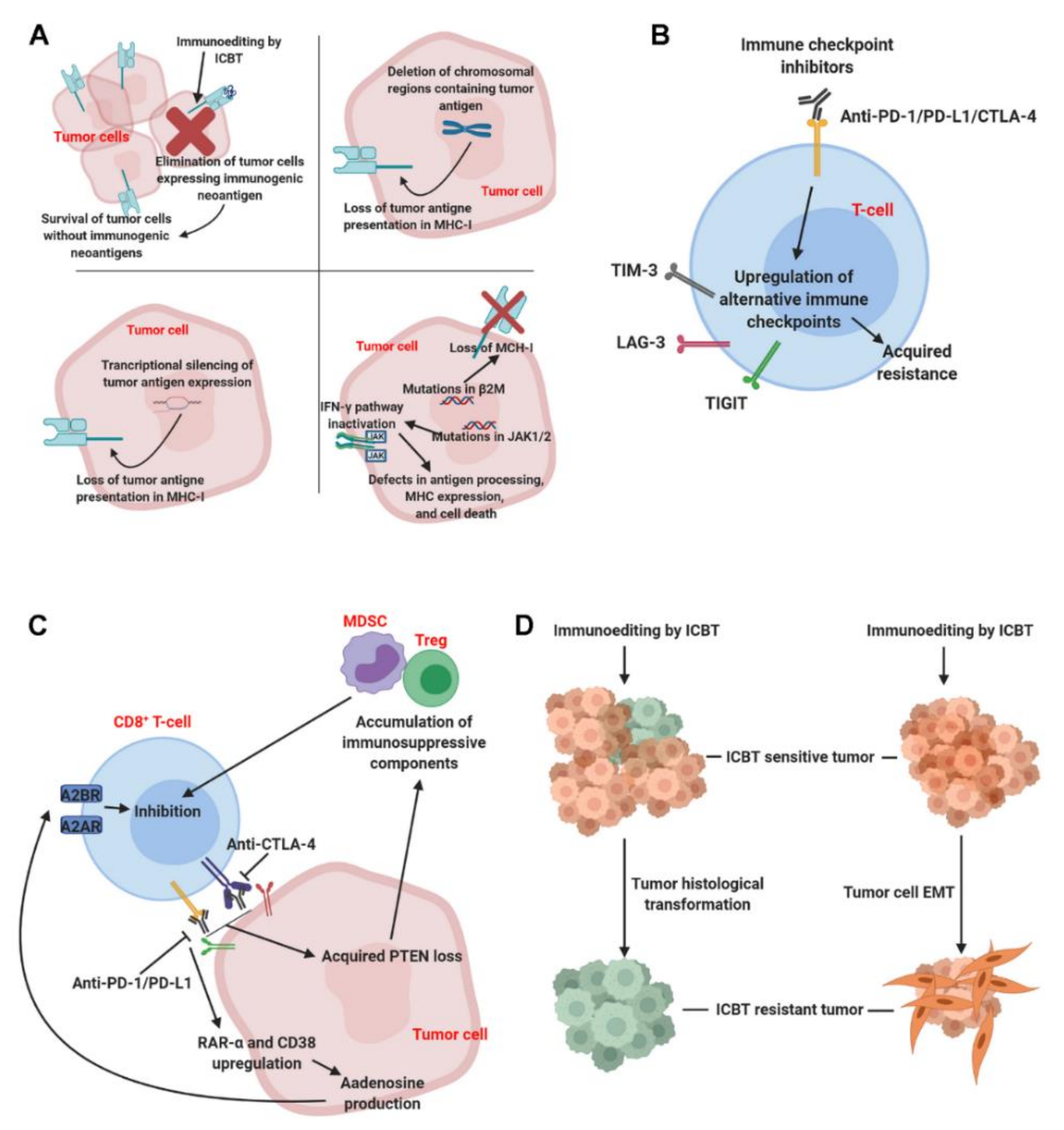
Cancers Free Full Text Acquired Resistance To Immune Checkpoint Immune checkpoint inhibitors (icis) have rapidly altered the treatment landscape for multiple tumor types, providing unprecedented survival in some patients. despite the characteristic durability of response to ici, unfortunately many patients with initial response will later develop acquired resistance. the current understanding of mechanisms of acquired resistance to icis is remarkably. These therapeutic failures arise from innate (primary), adaptive, and acquired resistance mechanisms that depend on cancer cell features, tumor heterogeneity, tme, immune system, and other host.
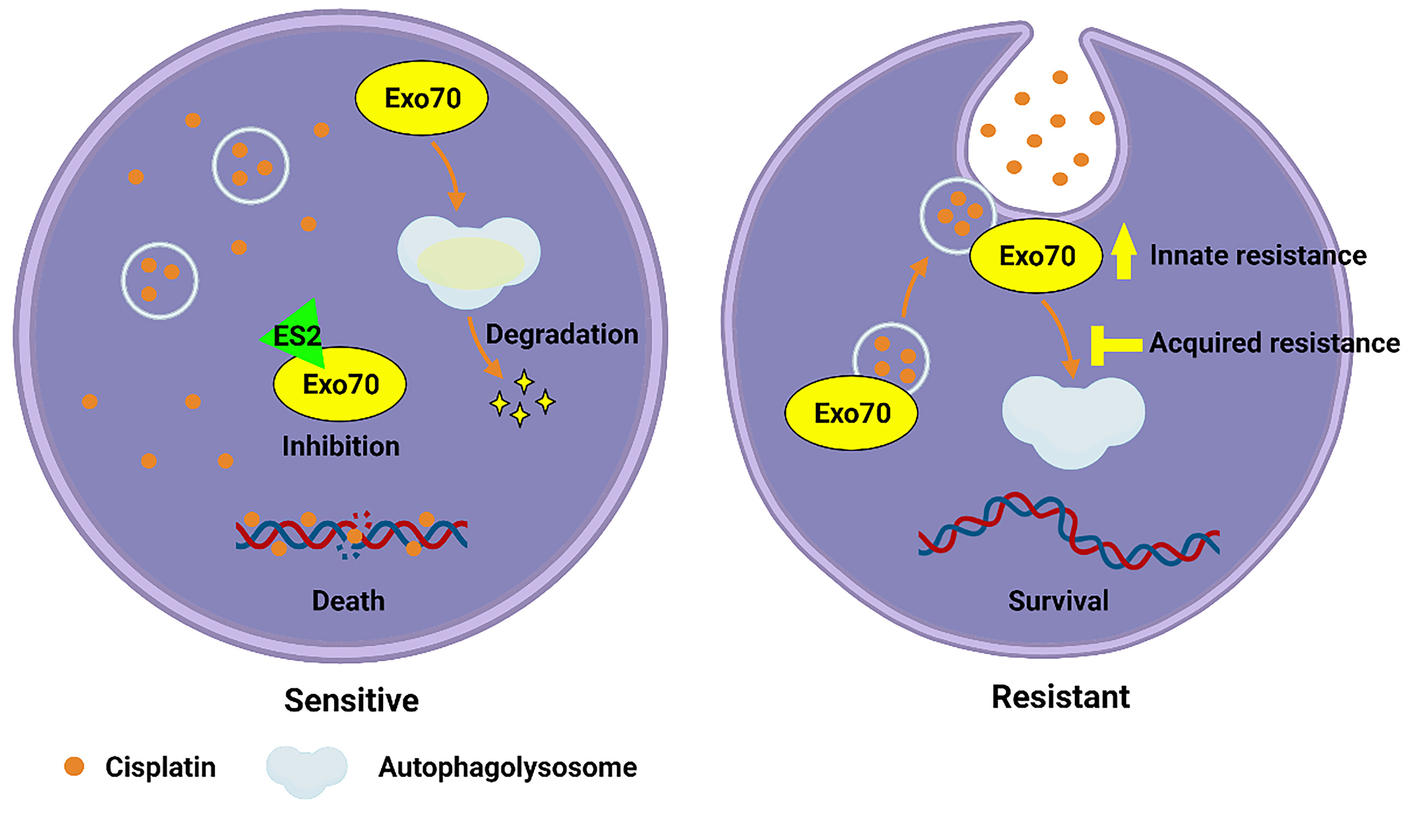
Cancers Free Full Text Deregulation Of Exo70 Facilitates Innate And

Comments are closed.