Can Not Peeing Cause Kidney Stones Healthykidneyclub
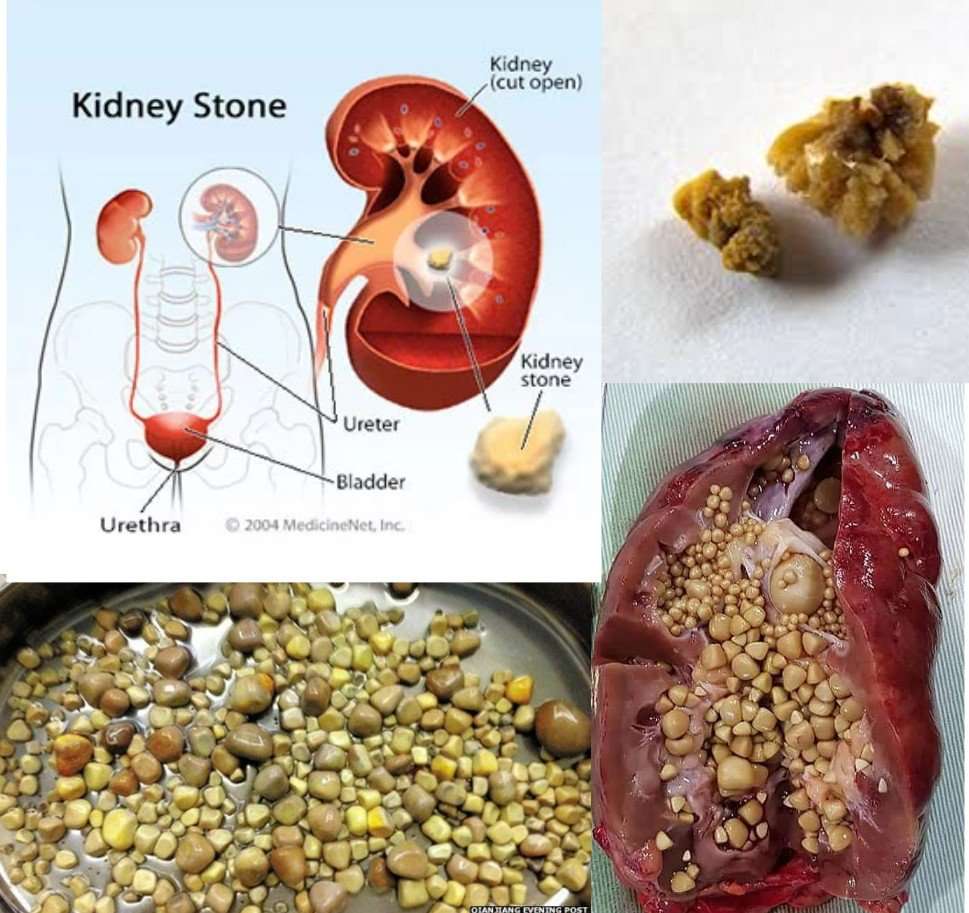
Can Not Peeing Cause Kidney Stones Healthykidneyclub Kidney stones are much more likely to develop if you do not drink enough fluid. as the urethra is smaller than the stone, passing a kidney stone can be a painful process. some kidney stones of a large stone will not pass without the help of a physician. people with kidney stones also often experience the following symptoms: pain in the lower. A kidney stone usually will not cause symptoms until it moves around within the kidney or passes into one of the ureters. the ureters are the tubes that connect the kidneys and bladder. if a kidney stone becomes lodged in the ureters, it may block the flow of urine and cause the kidney to swell and the ureter to spasm, which can be very painful.
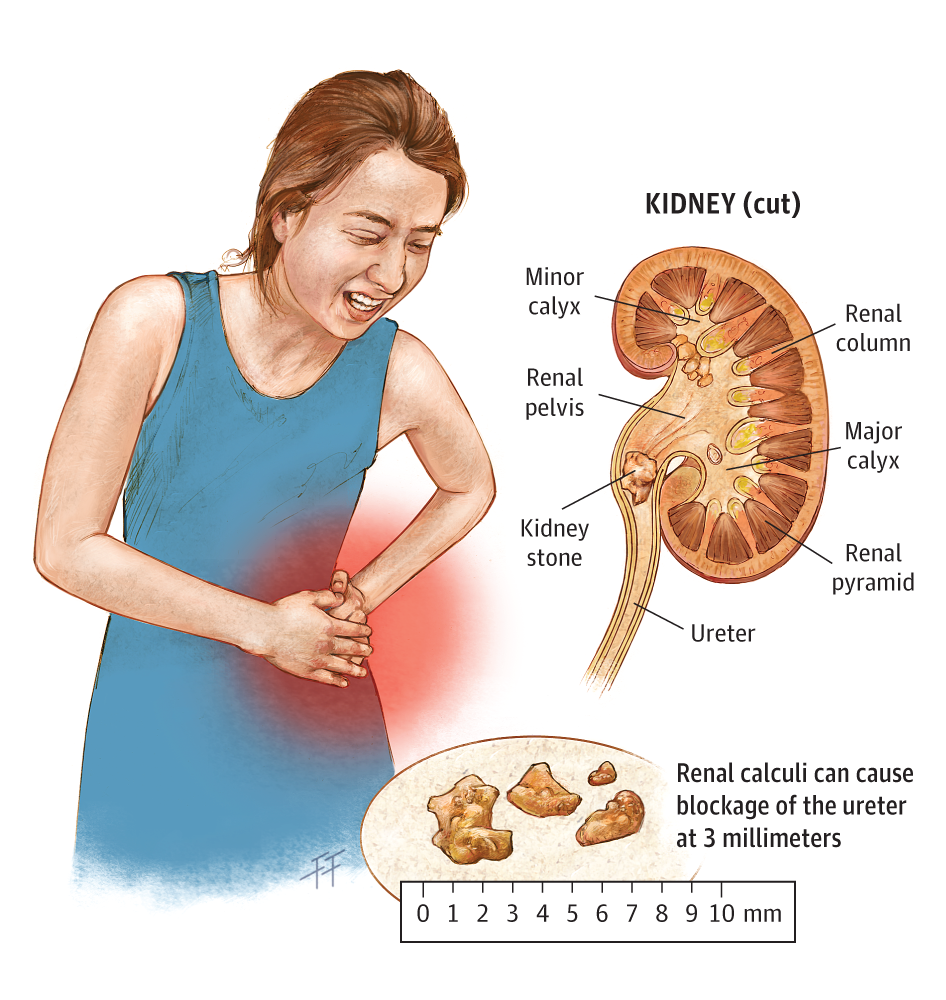
What Does Kidney Stones Feel Like Symptoms Healthykidneyclub Blood. blood in your urine is a sign that your kidney stone is getting worse. if the pain and nausea haven’t moved you to seek medical help, blood is a serious cause for concern. it occurs from either the pressure on your ureters or the damage incurred when the stone pushes against the walls of your kidneys. blood can appear pink, red, or brown. The consequences of kidney stones can be very serious. kidney stones are tiny stones that form in the kidneys as a result of excess sodium or calcium. consequently, if these mineral deposits are not regularly expelled via the urine the stones will try to leave the body via the urinary tract. the resulting pain can be unbearable. causes of. If a stone is interrupting your urine passage, your body will try to tell you in a number of ways. you should not ignore these symptoms: a burning feeling when you urinate. bad smelling and or cloudy pee. blood in your urine. discomfort or pain on your sides or lower back, below the rib cage. Weight loss surgery: weight loss surgery can change the mineral composition of urine, which can lead to kidney stones. it can also cause low urine volume, making urine more concentrated.

Do You Poop Or Pee Out Kidney Stones Healthykidneyclub If a stone is interrupting your urine passage, your body will try to tell you in a number of ways. you should not ignore these symptoms: a burning feeling when you urinate. bad smelling and or cloudy pee. blood in your urine. discomfort or pain on your sides or lower back, below the rib cage. Weight loss surgery: weight loss surgery can change the mineral composition of urine, which can lead to kidney stones. it can also cause low urine volume, making urine more concentrated. Usually, the pain starts when a stone moves into the narrow ureter. this causes a blockage, which causes pressure to build up in the kidney. the pressure activates nerve fibers that transmit pain signals to the brain. kidney stone pain often starts suddenly. as the stone moves, the pain changes location and intensity. Kidney stones can put you at risk for: a blockage that backs pee up into your kidney, causing it to swell (hydronephrosis). kidney infection (pyelonephritis). acute kidney injury (a type of kidney failure that can be reversible). frequent urinary tract infections (utis). chronic kidney disease (ckd).
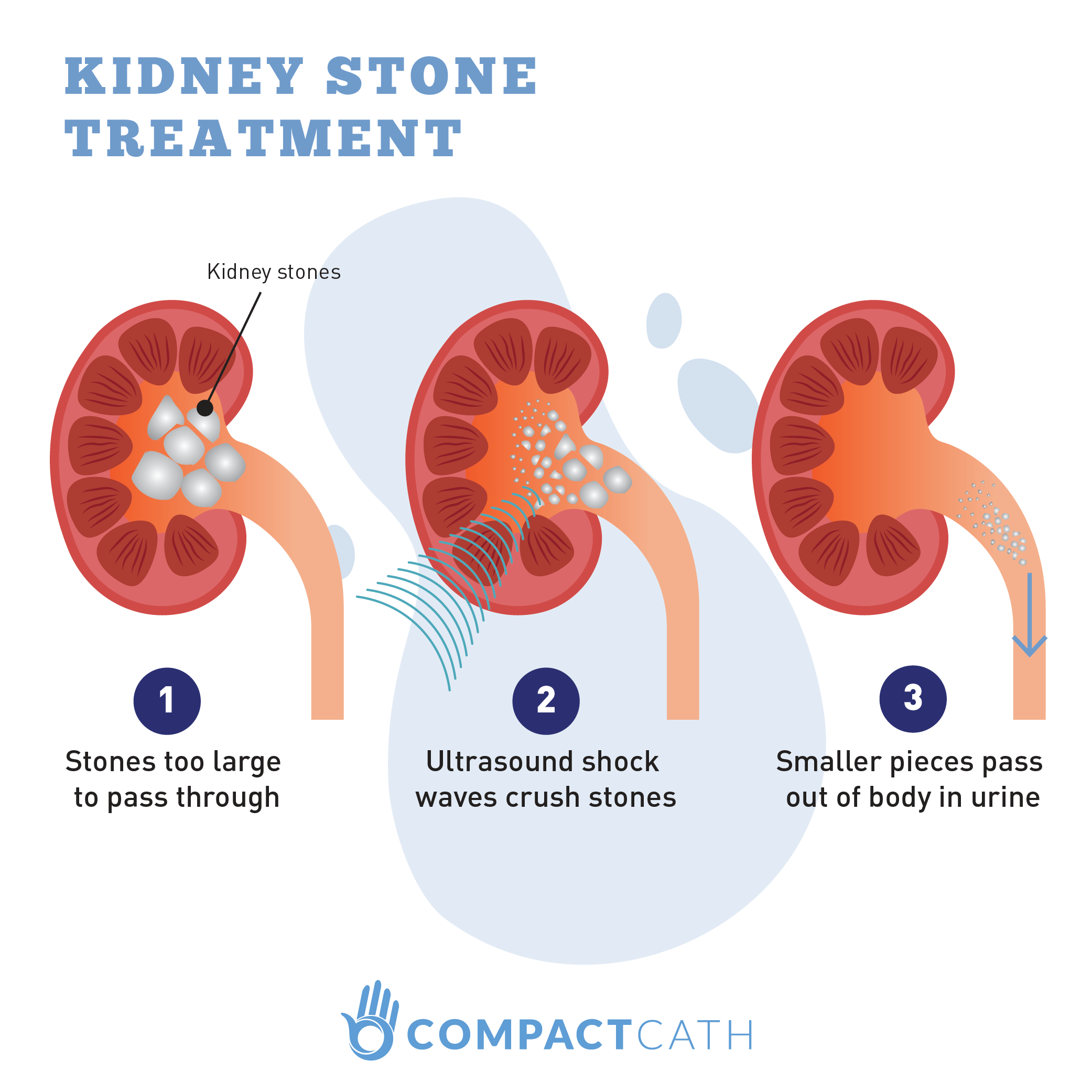
Why Do Kids Get Kidney Stones Healthykidneyclub Usually, the pain starts when a stone moves into the narrow ureter. this causes a blockage, which causes pressure to build up in the kidney. the pressure activates nerve fibers that transmit pain signals to the brain. kidney stone pain often starts suddenly. as the stone moves, the pain changes location and intensity. Kidney stones can put you at risk for: a blockage that backs pee up into your kidney, causing it to swell (hydronephrosis). kidney infection (pyelonephritis). acute kidney injury (a type of kidney failure that can be reversible). frequent urinary tract infections (utis). chronic kidney disease (ckd).

Comments are closed.