Blog Basics Copyright And Fair Use
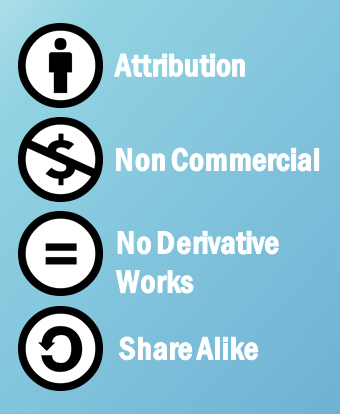
Blog Basics Copyright And Fair Use As you learned earlier, you generally need to license copyrighted material in order to use it, which often costs money. the exception to this is a rule called fair use. fair use means you can use copyrighted material without a license only for certain purposes. these include: commentary. Fair use is a legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission, under certain conditions. the dmca is a u.s. law that addresses digital copyright issues. it includes provisions for safe harbor and protects online service providers from liability for user generated content.

Blog Basics Copyright And Fair Use Page 1 Fair Use Fair Basic Using copyrighted material. as you learned earlier, you generally need to license copyrighted material in order to use it, which often costs money. the exception to this is a rule called fair use. fair use means you can use copyrighted material without a license only for certain purposes. these include: commentary. In certain situations, it’s legal to use copyrighted works without seeking permission. the uk government has published a page outlining the various situations in which this might be considered fair dealing, which you can read in full here. purposes that are probably most relevant to bloggers include: criticism, review and reporting current. You can place it directly beneath the image or in a credits section at the end of your blog post. format matters: pay attention to the format of your attribution. while there isn’t a strict rule, it should be clear and concise. for example: “image by [creator’s name] under cc by 3.0.”. If the work was created, but not published, before 1978, the copyright lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years. however, even if the author died over 70 years ago, the copyright in an unpublished work lasted until december 31, 2002. and if such a work was published before december 31, 2002, the copyright will last until december 31, 2047.
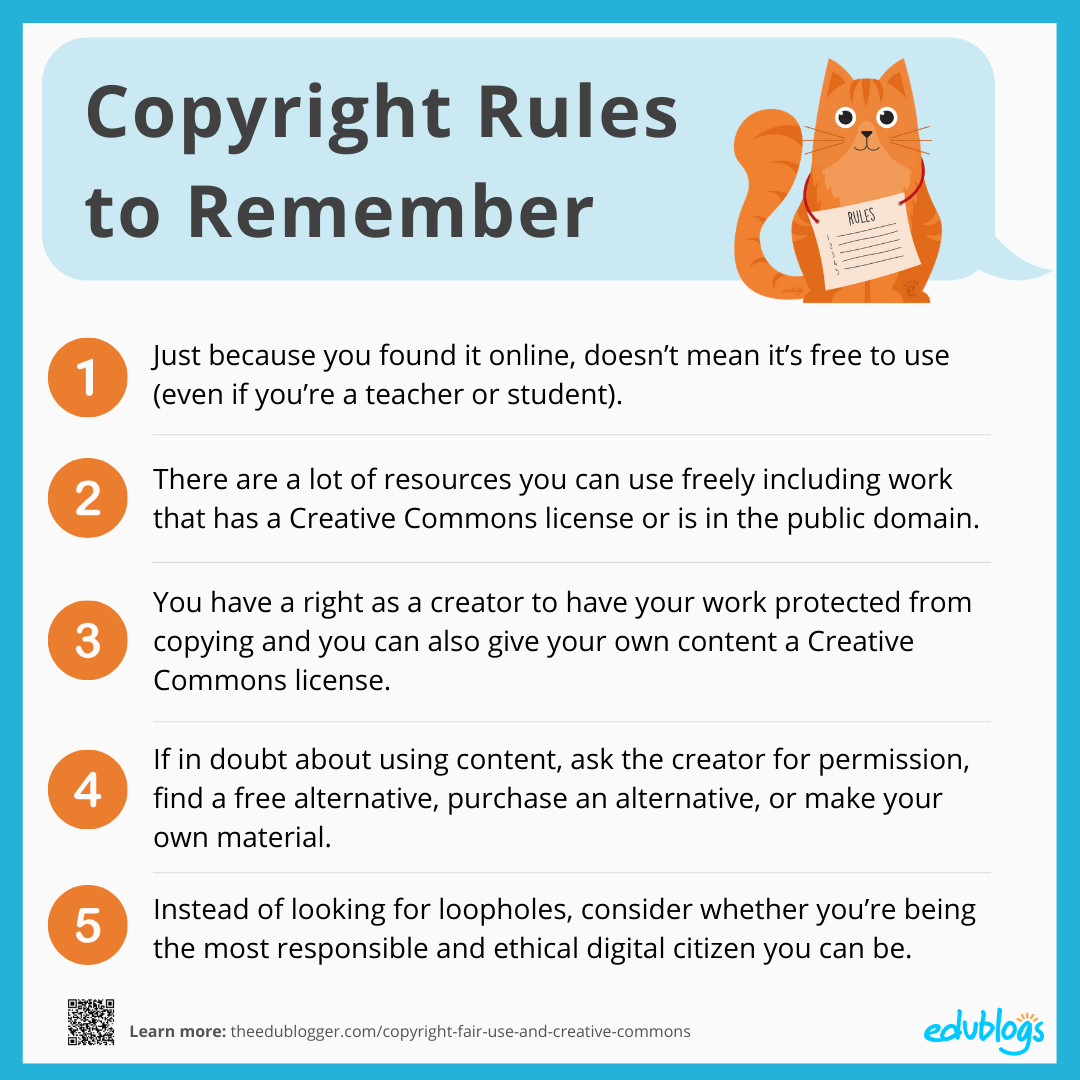
The Ultimate Guide To Copyright Creative Commons And Fair Use For You can place it directly beneath the image or in a credits section at the end of your blog post. format matters: pay attention to the format of your attribution. while there isn’t a strict rule, it should be clear and concise. for example: “image by [creator’s name] under cc by 3.0.”. If the work was created, but not published, before 1978, the copyright lasts for the life of the author plus 70 years. however, even if the author died over 70 years ago, the copyright in an unpublished work lasted until december 31, 2002. and if such a work was published before december 31, 2002, the copyright will last until december 31, 2047. Doing the analysis may lower the risks associated with copyrighted infringement, but ultimately, only a court can decide if a use is fair. in many instances, it can be important to conduct a fair use analysis before using a work that is under copyright. if the owner of a work sues you for copyright infringement, the fact that you conducted a. Fair use is a balancing test. to determine whether a use is or is not a fair use, always keep in mind that you need to apply all four factors. for example, do not jump to a conclusion based simply on whether your use is educational or commercial. you still need to evaluate, apply, and weigh in the balance the nature of the copyrighted work, the.

Copyright And Fair Use Guidelines Infographics Pdf Doing the analysis may lower the risks associated with copyrighted infringement, but ultimately, only a court can decide if a use is fair. in many instances, it can be important to conduct a fair use analysis before using a work that is under copyright. if the owner of a work sues you for copyright infringement, the fact that you conducted a. Fair use is a balancing test. to determine whether a use is or is not a fair use, always keep in mind that you need to apply all four factors. for example, do not jump to a conclusion based simply on whether your use is educational or commercial. you still need to evaluate, apply, and weigh in the balance the nature of the copyrighted work, the.

Comments are closed.