Antarctic Food Web And Food Chains
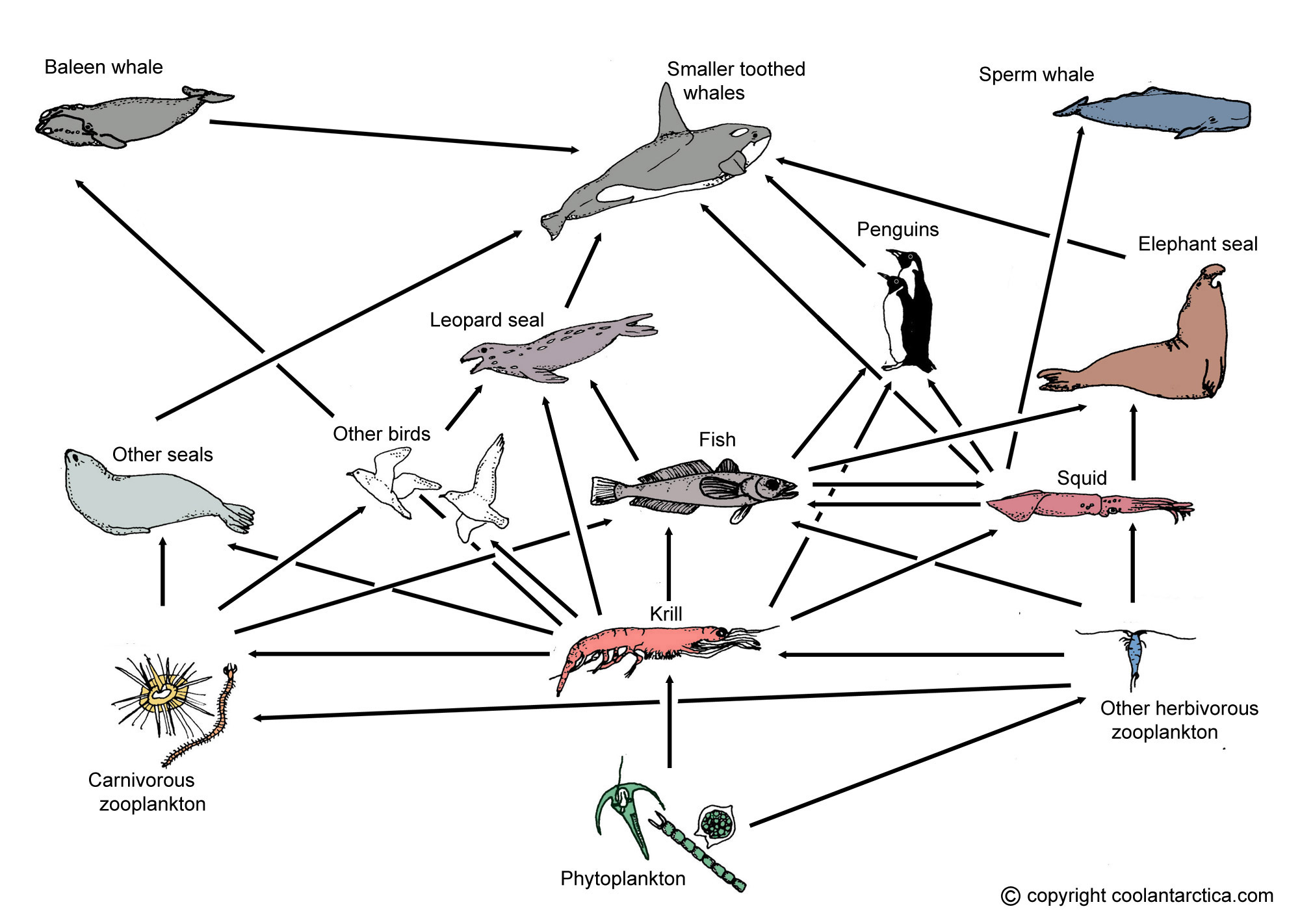
Antarctic Food Web And Food Chains The producers in antarctic food chains are tiny single celled plants known collectively as phytoplankton that float in the upper layer of the sea though they can grow at depths down to about 100m. assorted phytoplankton, these are about 20,000 larger than life size. there are many different species and types of phytoplankton, the two largest. The web is a complex network of food chains. food chains are often based on plants that provide food for other animals. some animals only eat plants and are called herbivores. others eat plants and animals and are called omnivores. animals that only eat other animals are called carnivores. food webs are finely balanced ecosystems.

A Diagram Of The Antarctic Food Web Download Scientific Diagram Ecosystems. antarctica is fascinating from an ecological point of view: despite the harshest environmental conditions on the surface of the planet, well adapted organisms are able to survive here. discover the antarctic food web and ecosystems plankton, krill, blue whales, leopard seals, penguins and killer whales, who is eating who?. This study examines for the first time the food web structure of antarctic benthic communities in medium deep waters, where most of the antarctic biodiversity lies 8, 31 and where the spatio. Antarctic biodiversity is affected by seasonal sea ice dynamics driving basal resource availability. to (1) determine the role of intraspecific dietary variability in structuring benthic food webs. Food web structure in natural ecosystems food web: natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what eats what in an ecological community. network formed by entirety of trophic interactions found in a given ecosystem. food webs are complex ecological networks, but a lot of that complexity can be summarized.
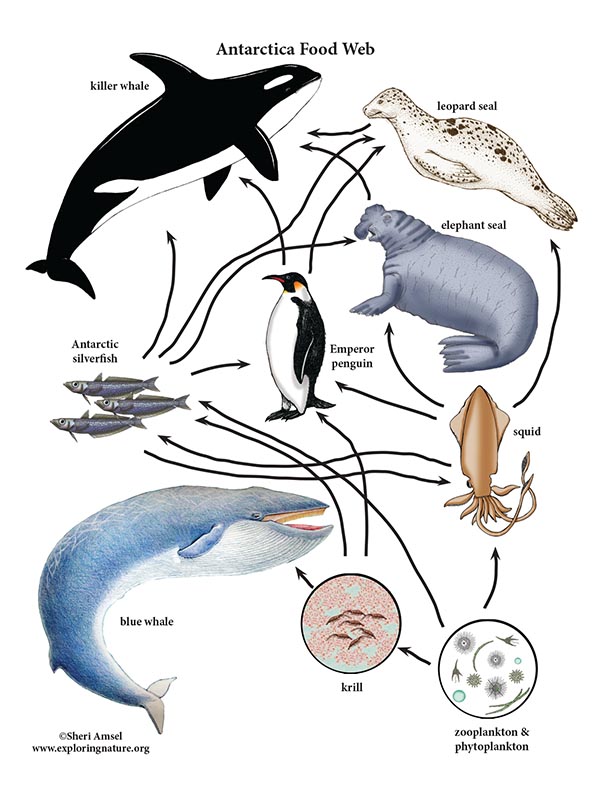
Antarctic Food Web Antarctic biodiversity is affected by seasonal sea ice dynamics driving basal resource availability. to (1) determine the role of intraspecific dietary variability in structuring benthic food webs. Food web structure in natural ecosystems food web: natural interconnection of food chains and a graphical representation of what eats what in an ecological community. network formed by entirety of trophic interactions found in a given ecosystem. food webs are complex ecological networks, but a lot of that complexity can be summarized. Foraging optimization by consumers led to a simpler food web, with lower potential competition and shorter food chains. however, basal resources and antarctic species such as the bivalve adamussium colbecki and the sea urchin sterechinus neumayeri were central and highly connected both before and after the sea ice break up, thus playing key. The ross sea is characterised by strong seasonality in sea ice cover and primary productivity, which produces marked spatio temporal variations in the availability of food 5, 7, 24, 58. the same seasonality is found in tnb 18, 27, 32, 59. sampling was carried out along a coastal tract located between adelie cove (southward) and tethys bay.

Learnz Foraging optimization by consumers led to a simpler food web, with lower potential competition and shorter food chains. however, basal resources and antarctic species such as the bivalve adamussium colbecki and the sea urchin sterechinus neumayeri were central and highly connected both before and after the sea ice break up, thus playing key. The ross sea is characterised by strong seasonality in sea ice cover and primary productivity, which produces marked spatio temporal variations in the availability of food 5, 7, 24, 58. the same seasonality is found in tnb 18, 27, 32, 59. sampling was carried out along a coastal tract located between adelie cove (southward) and tethys bay.

Comments are closed.