Anatomy Facial Muscle Nerve
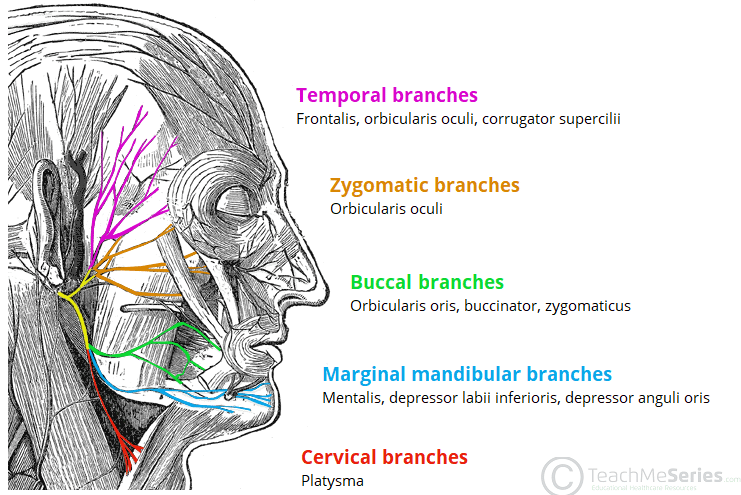
The Facial Nerve Cn Vii Course Functions Teachmeanatomy The facial nerve is associated with the derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch: motor – muscles of facial expression, posterior belly of the digastric, stylohyoid and stapedius muscles. sensory – a small area around the concha of the external ear. special sensory – provides special taste sensation to the anterior 2 3 of the tongue via. The facial nerve exits the skull via the stylomastoid foramen, after which it gives off the following branches: the posterior auricular nerve is the first extracranial branch to emerge which continues to provide motor innervation to the occipital belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle (occipital branch) and intrinsic auricular muscles (auricular branch).

The Facial Nerve Cn Vii Course Functions Teachmeanatomy Symptoms of facial nerve palsy (paralysis) vary depending on the cause and which part of the nerve is affected. the symptoms may be temporary or permanent. you may experience: facial muscle weakness in parts of or all of one side of your face. facial muscle spasms. drooping eyebrow and or eyelid. trouble closing your eyes or blinking. Introduction. the facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve. it contains the motor, sensory, and parasympathetic (secretomotor) nerve fibers, which provide innervation to many areas of the head and neck region. the facial nerve is comprised of three nuclei: the main motor nucleus. the parasympathetic nuclei. the sensory nucleus. Facial expression. the main function of the facial nerve is motor control of all the muscles of facial expression. it also innervates the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, the stylohyoid muscle, and the stapedius muscle of the middle ear. these skeletal muscles are developed from the second pharyngeal arch. The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve (cn vii). it arises from the brain stem and extends posteriorly to the abducens nerve and anteriorly to the vestibulocochlear nerve. it courses through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits through the stylomastoid foramen after which it divides into terminal branches at the posterior edge of the parotid gland. the facial nerve provides.

Face Nerve Supply Facial expression. the main function of the facial nerve is motor control of all the muscles of facial expression. it also innervates the posterior belly of the digastric muscle, the stylohyoid muscle, and the stapedius muscle of the middle ear. these skeletal muscles are developed from the second pharyngeal arch. The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve (cn vii). it arises from the brain stem and extends posteriorly to the abducens nerve and anteriorly to the vestibulocochlear nerve. it courses through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits through the stylomastoid foramen after which it divides into terminal branches at the posterior edge of the parotid gland. the facial nerve provides. Also, this nerve innervates facial muscles, controlling how to contract and produce facial expressions. during its course, cn7 splits into several branches. the greater petrosal nerve serves the. Cranial nerve vii is the facial nerve. it supplies motor, sensory and parasympathetic innervation to various structures of the head and neck. in this article, we discuss the embryology, structure and course of the facial nerve and the brainstem nuclei associated with it. check out our summary of the cranial nerves here.
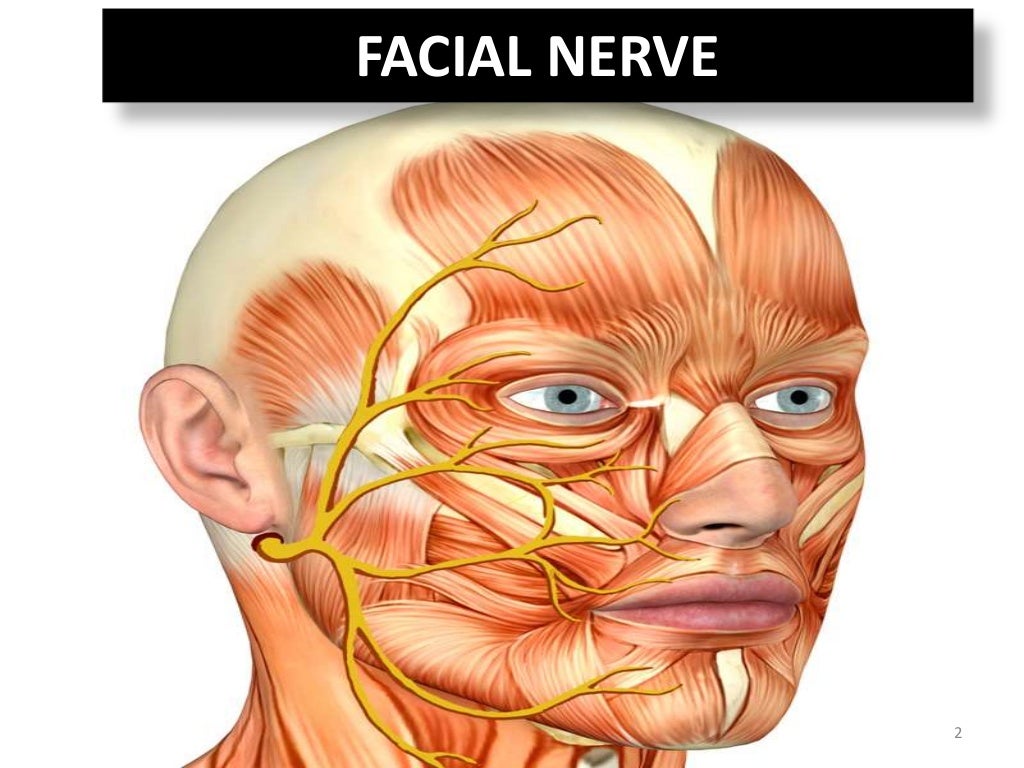
Facial Nerve Also, this nerve innervates facial muscles, controlling how to contract and produce facial expressions. during its course, cn7 splits into several branches. the greater petrosal nerve serves the. Cranial nerve vii is the facial nerve. it supplies motor, sensory and parasympathetic innervation to various structures of the head and neck. in this article, we discuss the embryology, structure and course of the facial nerve and the brainstem nuclei associated with it. check out our summary of the cranial nerves here.
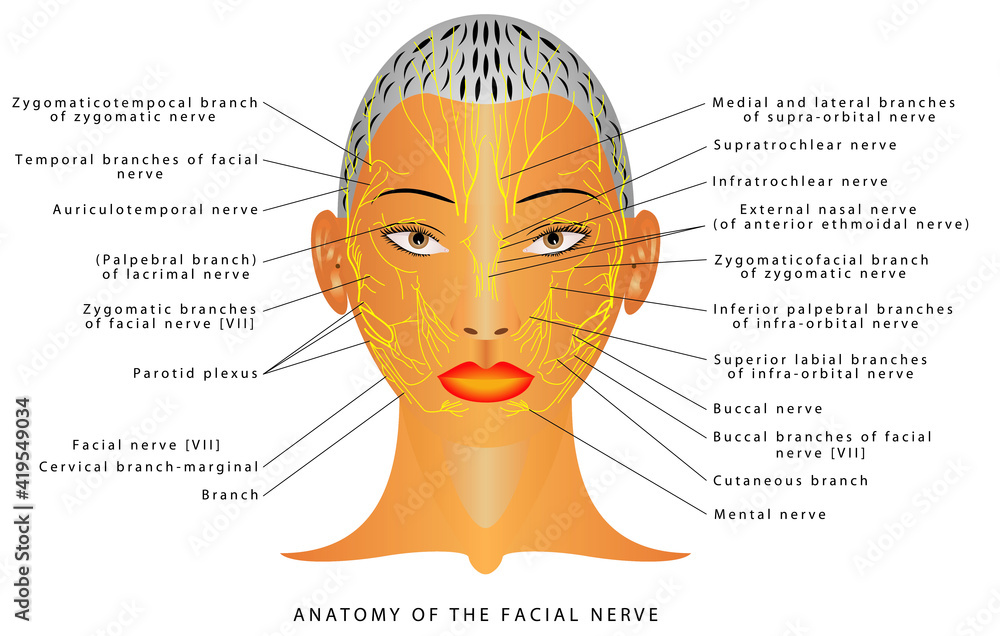
Anatomy Of The Facial Nerve The Mandibular Nerve And Other Nerves Of

Comments are closed.