Alkali Metals Chemistry

Chemistry 4 Students Alkali Metals Group 1 Elements Alkali metal, any of the six elements of group 1 (ia) of the periodic table—lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, and francium. the alkali metals are so called because reaction with water forms alkalies (i.e., strong bases capable of neutralizing acids). All of the alkali metals like to give up their single valence electron," says dr. chip nataro, chemistry professor at lafayette college in easton, pennsylvania. "as electrons have a charge of 1, losing an electron causes the atom to have a charge of 1.
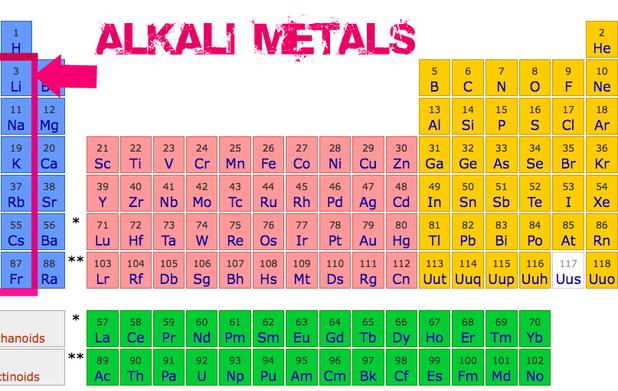
Wjec Chemistry C2 Online Revision Reactions Of Alkali Metals And Halogens The alkali metals are potent reductants whose chemistry is largely that of ionic compounds containing the m ion. alkali metals have only a weak tendency to form complexes with simple lewis bases. the first alkali metals to be isolated (na and k) were obtained by passing an electric current through molten potassium and sodium carbonates. Where are the alkali metals located on the periodic table. these are found in group 1 (the first column from left) of the periodic table. all the alkali metals lie in the s block since the electron on the outermost shell of their atom (valence electron) is in the s orbital [2, 3] alkali metals on the priodic table. The chemistry of alkali metal germanides, involving the germanide ion ge 4− and other cluster ions such as ge 2− 4, ge 4− 9, ge 2− 9, and [(ge 9) 2] 6−, is largely analogous to that of the corresponding silicides. Further, as can be seen from the data in table 8.3.1 8.3. 1, both the melting and boiling points decrease down the alkali metal group. this decrease in melting and boiling points reflects a decrease in metallic bonding strength as the atomic size (and consequently average electron nucleus distance) increases down the group. table 8.3.1 8.3.
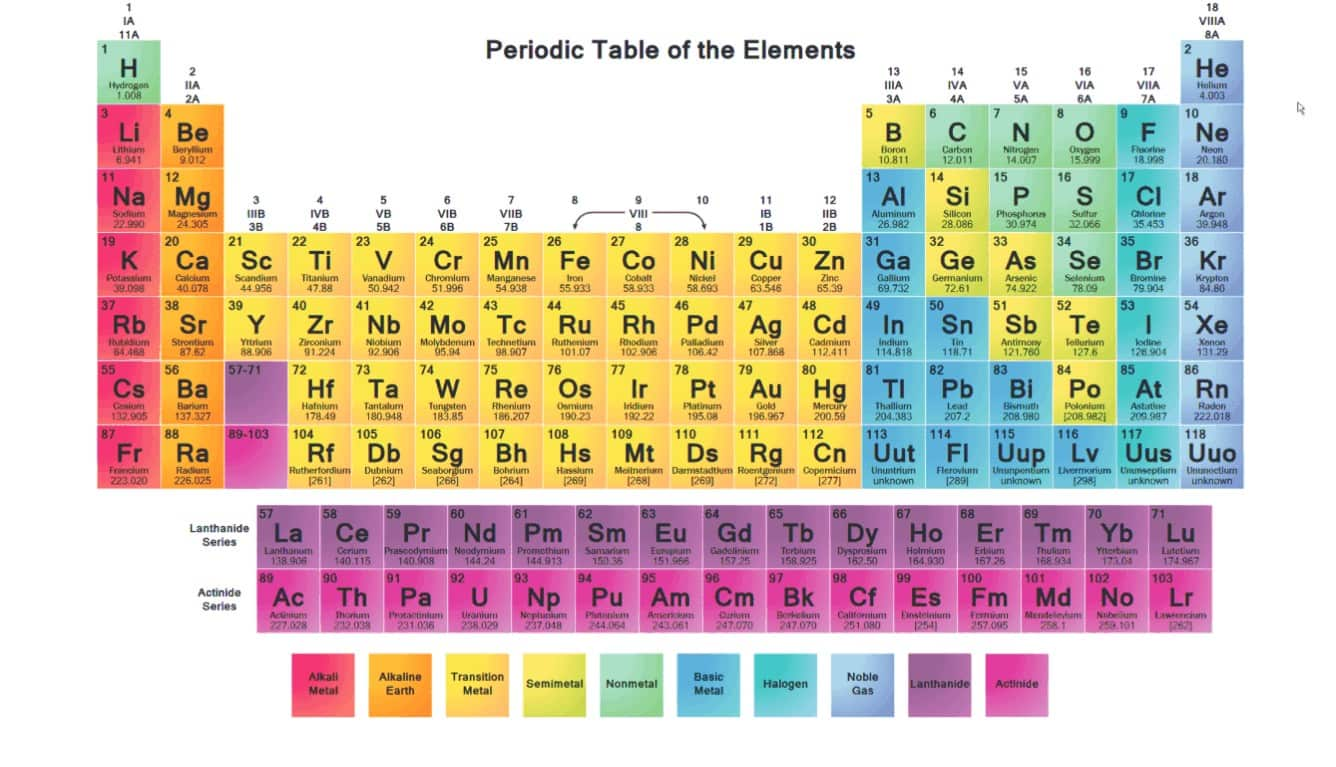
Alkali Metals Chemical Elements Properties Alkali Metals Periodic The chemistry of alkali metal germanides, involving the germanide ion ge 4− and other cluster ions such as ge 2− 4, ge 4− 9, ge 2− 9, and [(ge 9) 2] 6−, is largely analogous to that of the corresponding silicides. Further, as can be seen from the data in table 8.3.1 8.3. 1, both the melting and boiling points decrease down the alkali metal group. this decrease in melting and boiling points reflects a decrease in metallic bonding strength as the atomic size (and consequently average electron nucleus distance) increases down the group. table 8.3.1 8.3. The chemistry of the alkali metals reflects their tendency to form 1 cations. the alkali metals tend to form 1 cations. cation formation is favored by the relatively low ionization energies of the free metal (which makes it easier to form the cation) and the high solvation energy of their cations (which indicates that the cation is thermodynamically stabilized in solution). Alkali metal properties, reactivity, uses: the alkali metals have the high thermal and electrical conductivity, lustre, ductility, and malleability that are characteristic of metals. each alkali metal atom has a single electron in its outermost shell. this valence electron is much more weakly bound than those in inner shells. as a result, the alkali metals tend to form singly charged.
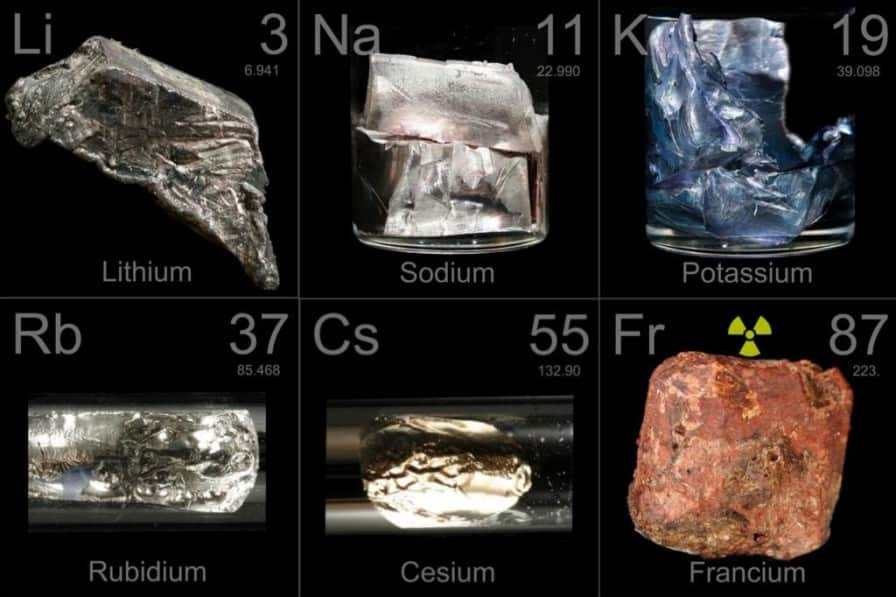

Alkali Metals Chemical Elements Properties Alkali Metals Periodic The chemistry of the alkali metals reflects their tendency to form 1 cations. the alkali metals tend to form 1 cations. cation formation is favored by the relatively low ionization energies of the free metal (which makes it easier to form the cation) and the high solvation energy of their cations (which indicates that the cation is thermodynamically stabilized in solution). Alkali metal properties, reactivity, uses: the alkali metals have the high thermal and electrical conductivity, lustre, ductility, and malleability that are characteristic of metals. each alkali metal atom has a single electron in its outermost shell. this valence electron is much more weakly bound than those in inner shells. as a result, the alkali metals tend to form singly charged.

Comments are closed.